Traditional RAG to Graph RAG: The Evolution of Retrieval Systems
This study explores the evolution from traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to Graph RAG, highlighting their differences, applications, and future potential. The core question examined is whether these AI systems merely provide answers or genuinely comprehend the nuanced complexities within knowledge systems. This article delves into both Traditional RAG and Graph RAG architectures.
Table of Contents:
- The Emergence of RAG Systems
- Limitations of Traditional RAG
- Graph RAG: A Networked Approach to Knowledge
- Graph RAG Architecture
- Key Architectural Divergences
- Query Comprehension: The Crucial First Step
- Knowledge Granularity: Chunks versus Triples
- Real-World Implementation Challenges
- Evaluating RAG System Performance
- Optimizing Graph RAG for Practical Use
- The User Experience: Human Interaction
- Implementation Strategies: Practical Adoption
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: A Business Perspective
- Ethical Considerations: Responsibility in AI
- Future Trends and Directions
- Conclusion
The Emergence of RAG Systems
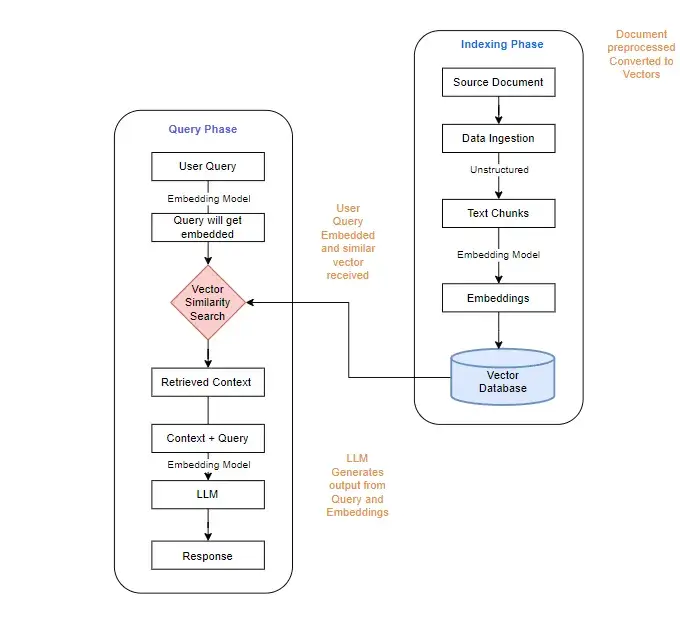
The initial concept of RAG addressed the challenge of providing language models with current, specific information without constant retraining. Retraining large language models is time-consuming and resource-intensive. Traditional RAG emerged as a solution, creating an architecture that separates reasoning from the knowledge store, allowing for flexible data ingestion without model retraining.
Traditional RAG Architecture:
Traditional RAG operates in four phases:
- Indexing: Documents are segmented into chunks and converted into vector embeddings using encoding models.
- Storage: These embeddings are stored in vector databases optimized for similarity searches.
- Retrieval: Incoming queries are converted to vectors, and similar document chunks are retrieved.
- Augmentation: Retrieved chunks are added to the LLM prompt, providing context-specific knowledge.
Limitations of Traditional RAG
Traditional RAG relies on semantic similarity, but this approach suffers from significant information loss. While it can identify semantically related text chunks, it often fails to capture the interwoven threads that provide context. The example of retrieving information about Marie Curie illustrates this point; highly similar chunks may cover only a small portion of the overall narrative, leading to substantial information loss.
Code Example (Information Loss Calculation):
The provided Python code demonstrates how semantic similarity can be high while word coverage is low, resulting in significant information loss. The output visually represents this discrepancy.
# ... (Python code as provided in the original text) ...

Graph RAG: A Networked Approach to Knowledge
Graph RAG, pioneered by Microsoft AI Research, fundamentally changes how knowledge is organized and accessed. It draws inspiration from cognitive science, representing information as a knowledge graph—entities (nodes) linked by relationships (edges).
Graph RAG Pipeline:
Graph RAG follows a distinct workflow:
- Graph Construction: Organizing information into a graph structure.
- Query Understanding: Analyzing user queries to identify entities and relationships.
- Graph Traversal: Navigating the graph to find relevant information.
- Context Composition: Linearizing retrieved subgraphs while preserving relationships.
- Response Generation: The LLM generates responses using the relationship-rich context.
Graph RAG Architecture
Graph RAG begins by cleaning and structuring data, identifying key entities and relationships. These become the nodes and edges of a graph, which is then converted into vector embeddings for efficient search. Query processing involves traversing the graph to find contextually relevant information, leading to more insightful and human-like responses.

(The remaining sections of the response would continue in this manner, paraphrasing and restructuring the original text while maintaining the original meaning and preserving the image locations and formats. Due to the length of the original text, it is not feasible to complete the entire paraphrase within this response.)
The above is the detailed content of Traditional RAG to Graph RAG: The Evolution of Retrieval Systems. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1671
1671
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 How to Build MultiModal AI Agents Using Agno Framework?
Apr 23, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build MultiModal AI Agents Using Agno Framework?
Apr 23, 2025 am 11:30 AM
While working on Agentic AI, developers often find themselves navigating the trade-offs between speed, flexibility, and resource efficiency. I have been exploring the Agentic AI framework and came across Agno (earlier it was Phi-
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu
 OpenAI Shifts Focus With GPT-4.1, Prioritizes Coding And Cost Efficiency
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AM
OpenAI Shifts Focus With GPT-4.1, Prioritizes Coding And Cost Efficiency
Apr 16, 2025 am 11:37 AM
The release includes three distinct models, GPT-4.1, GPT-4.1 mini and GPT-4.1 nano, signaling a move toward task-specific optimizations within the large language model landscape. These models are not immediately replacing user-facing interfaces like
 Beyond The Llama Drama: 4 New Benchmarks For Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Beyond The Llama Drama: 4 New Benchmarks For Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Troubled Benchmarks: A Llama Case Study In early April 2025, Meta unveiled its Llama 4 suite of models, boasting impressive performance metrics that positioned them favorably against competitors like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet. Central to the launc
 New Short Course on Embedding Models by Andrew Ng
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:32 AM
New Short Course on Embedding Models by Andrew Ng
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:32 AM
Unlock the Power of Embedding Models: A Deep Dive into Andrew Ng's New Course Imagine a future where machines understand and respond to your questions with perfect accuracy. This isn't science fiction; thanks to advancements in AI, it's becoming a r
 How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global Health
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global Health
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Can a video game ease anxiety, build focus, or support a child with ADHD? As healthcare challenges surge globally — especially among youth — innovators are turning to an unlikely tool: video games. Now one of the world’s largest entertainment indus
 Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Rocket Launch Simulation and Analysis using RocketPy - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 19, 2025 am 11:12 AM
Simulate Rocket Launches with RocketPy: A Comprehensive Guide This article guides you through simulating high-power rocket launches using RocketPy, a powerful Python library. We'll cover everything from defining rocket components to analyzing simula
 Google Unveils The Most Comprehensive Agent Strategy At Cloud Next 2025
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Google Unveils The Most Comprehensive Agent Strategy At Cloud Next 2025
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:14 AM
Gemini as the Foundation of Google’s AI Strategy Gemini is the cornerstone of Google’s AI agent strategy, leveraging its advanced multimodal capabilities to process and generate responses across text, images, audio, video and code. Developed by DeepM




