What is Beam Search in NLP Decoding?
Beam search: a deep dive into this powerful decoding algorithm
Beam search is a crucial decoding algorithm in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, particularly for sequence generation tasks like text generation, machine translation, and summarization. It effectively balances exploration of the search space with the generation of high-quality output. This article provides a comprehensive overview of beam search, including its mechanism, implementation, applications, and limitations.
Key Learning Objectives:
- Grasp the core concept and functionality of the beam search algorithm in sequence decoding.
- Understand the role of beam width in balancing exploration and computational efficiency.
- Learn a practical Python implementation of beam search.
- Analyze real-world applications and challenges associated with beam search in NLP.
- Appreciate the advantages of beam search over simpler methods like greedy search.
(This article is part of the Data Science Blogathon.)
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Beam Search
- The Beam Search Mechanism
- The Importance of Beam Search in Decoding
- Practical Python Implementation
- Challenges and Limitations of Beam Search
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Beam Search
Beam search is a heuristic search algorithm used to decode sequences from models such as transformers and LSTMs. It maintains a fixed number of the most probable sequences (the "beam width") at each step of the generation process. Unlike greedy search, which only considers the single most likely next token, beam search explores multiple possibilities concurrently, leading to more fluent and globally optimal outputs. In machine translation, for example, it allows the model to explore various valid translations simultaneously.
The Beam Search Mechanism
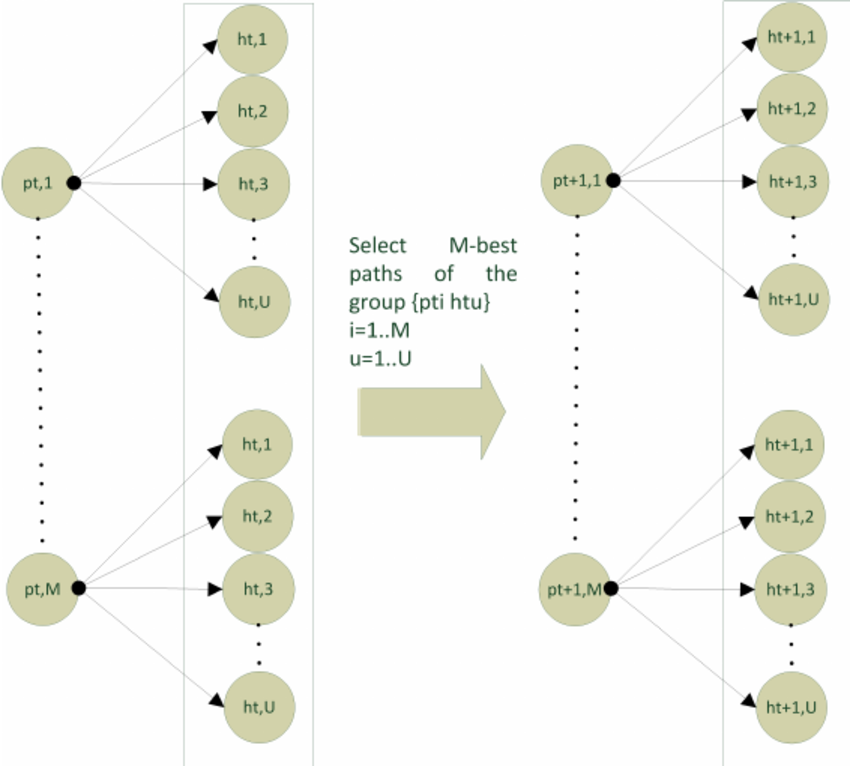
Beam search operates by traversing a graph where nodes represent tokens and edges represent transition probabilities. At each step:
- The algorithm selects the top k most probable tokens based on the model's output logits.
- It expands these tokens into sequences, calculating their cumulative probabilities.
- It retains only the top k sequences for the next step.
- This process repeats until a stopping criterion is met (e.g., reaching an end-of-sequence token or a predefined sequence length).
The Concept of Beam Width
The beam width (k) is a critical parameter. A wider beam explores more sequences, potentially improving output quality, but significantly increases computational cost. A narrower beam is faster but risks missing superior sequences.
The Importance of Beam Search in Decoding
Beam search is crucial for decoding because:
- Enhanced Sequence Quality: Exploring multiple hypotheses prevents getting stuck in local optima, resulting in globally better sequences.
- Handling Ambiguity: It effectively addresses ambiguity inherent in many NLP tasks by evaluating multiple interpretations.
- Computational Efficiency: It's far more efficient than exhaustive search while still exploring a substantial portion of the search space.
- Flexibility: It can be adapted to various tasks and sampling strategies.
Practical Python Implementation
The following provides a simplified implementation demonstrating the core principles. A more robust implementation would require error handling and potentially more sophisticated probability calculations.
(Note: The code sections and outputs below are reproduced from the original article and assume the necessary libraries are installed. Refer to the original article for complete installation instructions and detailed explanations.)
(Step 1: Install and Import Dependencies)
<code># Install transformers and graphviz !sudo apt-get install graphviz graphviz-dev !pip install transformers pygraphviz from transformers import GPT2LMHeadModel, GPT2Tokenizer import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import networkx as nx import numpy as np from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap from tqdm import tqdm import matplotlib.colors as mcolors</code>
(Step 2: Model and Tokenizer Setup)
<code># Load model and tokenizer
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained('gpt2').to(device)
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
model.eval()</code>(Step 3-8: Remaining code sections for encoding input, helper functions, recursive beam search, best sequence retrieval, and graph plotting are reproduced from the original article.)
(Output examples are also reproduced from the original article.)
Challenges and Limitations of Beam Search
Despite its strengths, beam search has limitations:
- Beam Width Selection: Finding the optimal beam width requires careful experimentation.
- Repetitive Sequences: It can generate repetitive or nonsensical outputs without additional constraints.
- Bias Towards Shorter Sequences: The probability accumulation method can favor shorter sequences.
Conclusion
Beam search is a fundamental algorithm in modern NLP, providing a balance between efficiency and output quality. Its flexibility and ability to generate coherent sequences make it a valuable tool for various NLP applications. While challenges exist, its adaptability and effectiveness solidify its position as a cornerstone of sequence generation.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1. Beam Search vs. Greedy Search: Beam search explores multiple sequences, while greedy search only considers the most likely token at each step. Beam search is generally more accurate.
- Q2. Choosing Beam Width: The optimal width depends on the task and computational resources. Experimentation is key.
- Q3. Handling Ambiguity: Beam search excels at handling ambiguous tasks by exploring multiple possibilities.
- Q4. Main Challenges: Repetitive sequences, bias towards shorter sequences, and parameter tuning are key challenges.
(The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.)
The above is the detailed content of What is Beam Search in NLP Decoding?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1312
1312
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Introduction OpenAI has released its new model based on the much-anticipated “strawberry” architecture. This innovative model, known as o1, enhances reasoning capabilities, allowing it to think through problems mor
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Introduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 Newest Annual Compilation Of The Best Prompt Engineering Techniques
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:22 AM
Newest Annual Compilation Of The Best Prompt Engineering Techniques
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:22 AM
For those of you who might be new to my column, I broadly explore the latest advances in AI across the board, including topics such as embodied AI, AI reasoning, high-tech breakthroughs in AI, prompt engineering, training of AI, fielding of AI, AI re
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu




