Llama 3.2 90B Tutorial: Image Captioning App With Streamlit & Groq
Meta has finally added multimodality to the Llama ecosystem by introducing the Llama 3.2 11B & 90B vision models. These two models excel at processing both text and images, which led me to try building a project using the 90B version.
In this article, I’ll share my work and guide you through building an interactive image captioning app using Streamlit for the front end and Llama 3.2 90B as the engine for generating captions.
Why to Use Llama 3.2 90B for an Image Captioning App
Llama 3.2-Vision 90B is a state-of-the-art multimodal large language model (LLM) built for tasks involving both image and text inputs.
It stands out with its ability to tackle complex tasks like visual reasoning, image recognition, and image captioning. It has been trained on a massive dataset of 6 billion image-text pairs.
Llama 3.2-Vision is a great choice for our app because it supports multiple languages for text tasks, though English is its primary focus for image-related applications. Its key features make it an excellent choice for tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA), Document VQA, and image-text retrieval, with image captioning being one of its standout applications.
Let’s explore how these capabilities translate into a real-world application like image captioning.
Image Captioning Pipeline
Image captioning is the automated process of generating descriptive text that summarizes an image's content. It combines computer vision and natural language processing to interpret and express visual details in language.
Traditionally, image captioning has required a complex pipeline, often involving separate stages for image processing and language generation. The standard approach involves three main steps: image preprocessing, feature extraction, and caption generation.
- Image preprocessing: Images are typically resized, normalized, and occasionally cropped to ensure they meet the model’s input specifications.
- Feature extraction: Visual features are extracted to identify objects, scenes, or relevant details within the image. In most models, this requires a separate vision model to interpret the image, generating structured data that language models can understand.
- Caption generation: These extracted features are then used by a language model to craft a coherent description, combining the objects, context, and relationships identified in the visual data.
With Llama 3.2 90B, this traditionally intricate process becomes more simple. The model's vision adapter integrates visual features into the core language model, enabling it to interpret images directly and generate captions through simple prompts.
By embedding cross-attention layers within its architecture, Llama 3.2 90B allows users to describe an image by merely prompting the model—eliminating the need for separate stages of processing. This simplicity enables more accessible and efficient image captioning, where a single prompt can yield a natural, descriptive caption that effectively captures an image's essence.
Overview of the Image Captioning App
To bring the power of Llama 3.2 90B to life, we’ll build a simple yet effective image captioning application using Streamlit for the front end and Groq for generating captions.
The app will allow users to upload an image and receive a descriptive caption generated by the model with just two clicks. This setup is user-friendly and requires minimal coding knowledge to get started.
Our application will include the following features:
- Title: A prominently displayed title, Llama Captioner, to establish the app's purpose.
- Upload button: An interface to upload images from the user’s device.
- Generate button: A button to initiate the caption generation process.
- Caption output: The app will display the generated caption directly on the interface.
Code Implementation for our Llama 3.2 90B App
The Groq API will act as the bridge between the user’s uploaded image and the Llama 3.2-Vision model. If you want to follow along and code with me, make sure you first:
- Obtain your Groq API key by signing up at Groq Console.
- Save your API key in a credentials.json file to simplify access.
- Follow Groq’s quickstart guide for installation and configuration.
This Python code snippet below sets up a Streamlit application to interact with the Groq API. It includes:
- Imports libraries for web app development (Streamlit), AI interactions (Groq), image handling (base64), and file operations (os, json).
- Reads the Groq API key from a separate JSON file for enhanced security.
- Defines a function to encode images into base64 format for efficient transmission and processing.
import streamlit as st
from groq import Groq
import base64
import os
import json
# Set up Groq API Key
os.environ['GROQ_API_KEY'] = json.load(open('credentials.json', 'r'))['groq_token']
# Function to encode the image
def encode_image(image_path):
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
return base64.b64encode(image_file.read()).decode('utf-8')We move on by writing the function below, which is designed to generate a textual description of an uploaded image using the Groq API. Here's a breakdown of its functionality:
- Image encoding: The uploaded image is converted into a base64 encoded string. This format allows the image data to be easily transmitted within the API request.
- Groq API interaction: A Groq client is instantiated to facilitate communication with the Groq service. A chat completion request is formulated, comprising:
- A user prompt: "What's in this image?"
- The base64 encoded image data, embedded within a data URI. The llama-3.2-90b-vision-preview model is specified to process the image and generate a textual description.
- Caption extraction: The generated caption is extracted from the Groq API response. The first choice's message content, which contains the caption, is returned.
import streamlit as st
from groq import Groq
import base64
import os
import json
# Set up Groq API Key
os.environ['GROQ_API_KEY'] = json.load(open('credentials.json', 'r'))['groq_token']
# Function to encode the image
def encode_image(image_path):
with open(image_path, "rb") as image_file:
return base64.b64encode(image_file.read()).decode('utf-8')Finally, we generate the our interactive web app through Streamlit:
# Function to generate caption
def generate_caption(uploaded_image):
base64_image = base64.b64encode(uploaded_image.read()).decode('utf-8')
client = Groq()
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "What's in this image?"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": f"data:image/jpeg;base64,{base64_image}",
},
},
],
}
],
model="llama-3.2-90b-vision-preview",
)
return chat_completion.choices[0].message.contentThe Final Streamlit App: Llama Captioner
This Streamlit application provides a user-friendly interface for image captioning. Here's a breakdown of its functionality:
- Title and file uploader:
- The app displays a title: "Llama Captioner".
- A file uploader component allows users to select an image file (JPG, JPEG, or PNG).
- Image display:
- Once an image is uploaded, the app displays it using the st.image function.
- Caption generation:
- A button, "Generate Caption," triggers the caption generation process.
- When clicked, a spinner indicates that the caption is being generated.
- The generate_caption function is called to process the uploaded image and obtain a caption.
- Upon successful generation, a success message is displayed, followed by the generated caption.
The below snippet is code in action where an image of Eddie Hall was uploaded to generate the caption. Surprisingly it extracted even the information that was not clearly visible like “Strongest Man” etc.
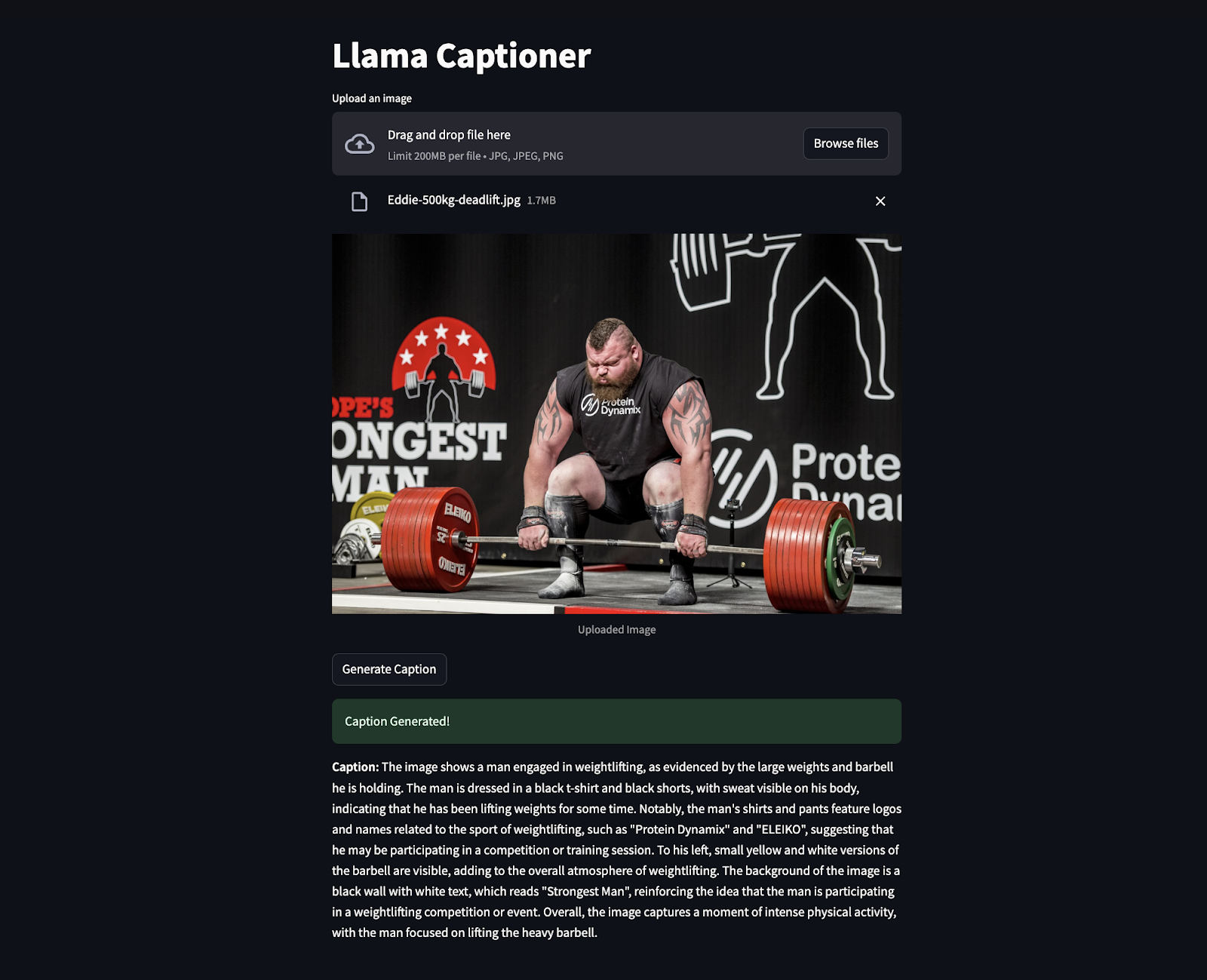
Conclusion
Building an image captioning app with Llama 3.2 90B and Streamlit shows how advanced AI can make tough tasks easier. This project combines a powerful model with a simple interface to create a tool that's both intuitive and easy to use.
As an AI Engineer, I see huge potential in tools like these. They can make technology more accessible, help people engage better with content, and automate processes in smarter ways.
To continue your learning on Llama, I recommend the following resources:
- How to Run Llama 3.2 1B on an Android Phone With Torchchat
- Llama 3.2 and Gradio Tutorial: Build a Multimodal Web App
- Llama Stack: A Guide With Practical Examples
- Fine-tuning Llama 3.2 and Using It Locally: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Llama 3.3: Step-by-Step Tutorial With Demo Project
The above is the detailed content of Llama 3.2 90B Tutorial: Image Captioning App With Streamlit & Groq. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1318
1318
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
GPT-4o vs OpenAI o1: Is the New OpenAI Model Worth the Hype?
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:18 AM
Introduction OpenAI has released its new model based on the much-anticipated “strawberry” architecture. This innovative model, known as o1, enhances reasoning capabilities, allowing it to think through problems mor
 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)
Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Introduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 3 Methods to Run Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:56 AM
3 Methods to Run Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:56 AM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Multimodal AI Powerhouse Meta's latest multimodal model, Llama 3.2, represents a significant advancement in AI, boasting enhanced language comprehension, improved accuracy, and superior text generation capabilities. Its ability t
 How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
How to Add a Column in SQL? - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:43 AM
SQL's ALTER TABLE Statement: Dynamically Adding Columns to Your Database In data management, SQL's adaptability is crucial. Need to adjust your database structure on the fly? The ALTER TABLE statement is your solution. This guide details adding colu
 Pixtral-12B: Mistral AI's First Multimodal Model - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AM
Pixtral-12B: Mistral AI's First Multimodal Model - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:20 AM
Introduction Mistral has released its very first multimodal model, namely the Pixtral-12B-2409. This model is built upon Mistral’s 12 Billion parameter, Nemo 12B. What sets this model apart? It can now take both images and tex




