Deploying DeepSeek R1 on Databricks: A Step-by-Step Guide
Deploying the DeepSeek R1 Model on Databricks: A Step-by-Step Guide
Databricks, a popular data engineering platform, is increasingly used for AI and machine learning tasks. This tutorial guides you through deploying the distributed DeepSeek R1 model on Databricks, a powerful large language model often preferred for on-premise deployment. This avoids sending data to external servers. For a deeper dive into DeepSeek R1's features and comparisons, see the DeepSeek-R1: Features, Comparison, Distilled Models & More blog.
This guide covers account setup, model registration using the UI, and access via the playground and local CURL commands. New to Databricks? The Introduction to Databricks course provides a comprehensive overview of the Databricks Lakehouse platform and its data management capabilities. For a deeper understanding of data management within Databricks, consider the Data Management in Databricks course.
Registering the DeepSeek R1 Model
- Launch a Notebook: After creating your Databricks workspace, click " New" and select a notebook.

- Install Packages: Install necessary Python libraries:
%%capture !pip install torch transformers mlflow accelerate torchvision %restart_python
- Load Model and Tokenizer: Load the DeepSeek R1 model and tokenizer from Hugging Face:
import pandas as pd import mlflow import mlflow.transformers import torch from mlflow.models.signature import infer_signature from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, AutoConfig, pipeline model_name = "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B" tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name) config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name) model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, config=config, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
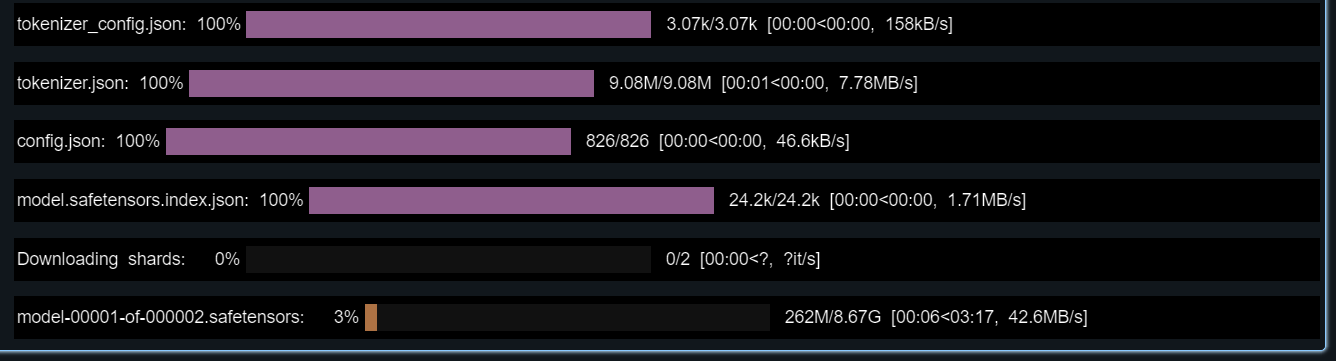
- Test the Model: Test with a sample prompt and generate a signature for model registration:
text_generator = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
example_prompt = "How does a computer work?"
example_inputs = pd.DataFrame({"inputs": [example_prompt]})
example_outputs = text_generator(example_prompt, max_length=200)
signature = infer_signature(example_inputs, example_outputs)
print(example_outputs)Expected output (may vary slightly):
<code>[{'generated_text': "How does a computer work? What is the computer? What is the computer used for? What is the computer used for in real life?\n\nI need to answer this question, but I need to do it step by step. I need to start with the very basic level and build up from there. I need to make sure I understand each concept before moving on. I need to use a lot of examples to explain each idea. I need to write my thoughts as if I'm explaining them to someone else, but I need to make sure I understand how to structure the answer properly.\n\nOkay, let's start with the basic level. What is a computer? It's an electronic device, right? And it has a central processing unit (CPU) that does the processing. But I think the central processing unit is more efficient, so maybe it's the CPU. Then, it has memory and storage. I remember that memory is like RAM and storage is like ROM. But wait, I think"}]</code>- Conda Environment: Define a conda environment:
conda_env = {
"name": "mlflow-env",
"channels": ["defaults", "conda-forge"],
"dependencies": [
"python=3.11",
"pip",
{"pip": ["mlflow", "transformers", "accelerate", "torch", "torchvision"]}
]
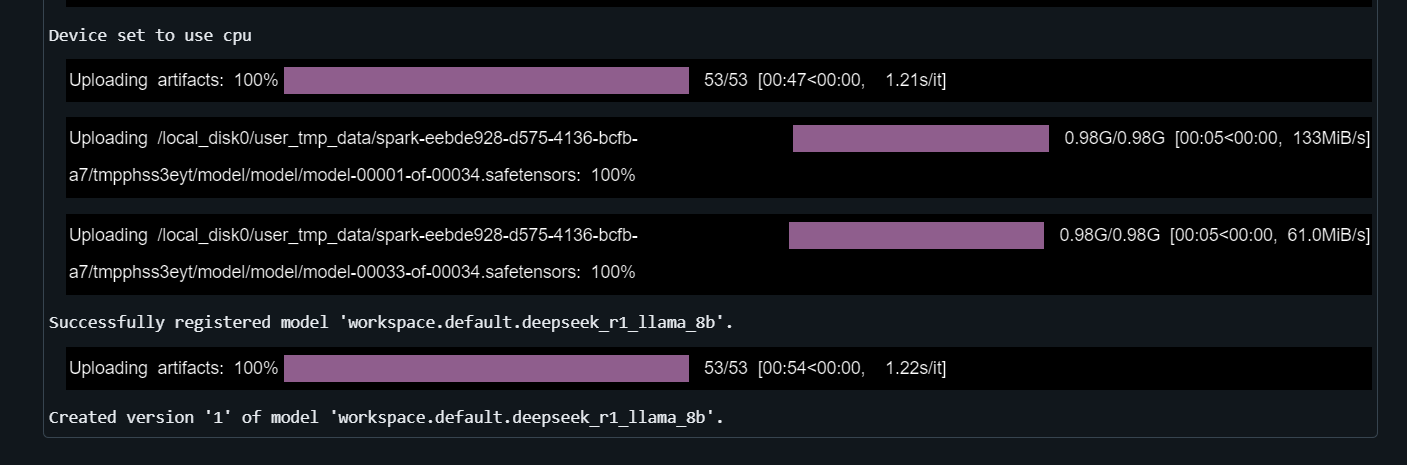
}- Register the Model: Register the model using
mlflow.transformers.log_model:
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
mlflow.transformers.log_model(
transformers_model=text_generator,
artifact_path="deepseek_model",
signature=signature,
input_example=example_inputs,
registered_model_name="deepseek_r1_llama_8b",
conda_env=conda_env
)
Deploying DeepSeek R1
-
Navigate to Models: In the Databricks dashboard, go to the "Models" tab.
-
Serve the Model: Select your model and click "Serve this model."
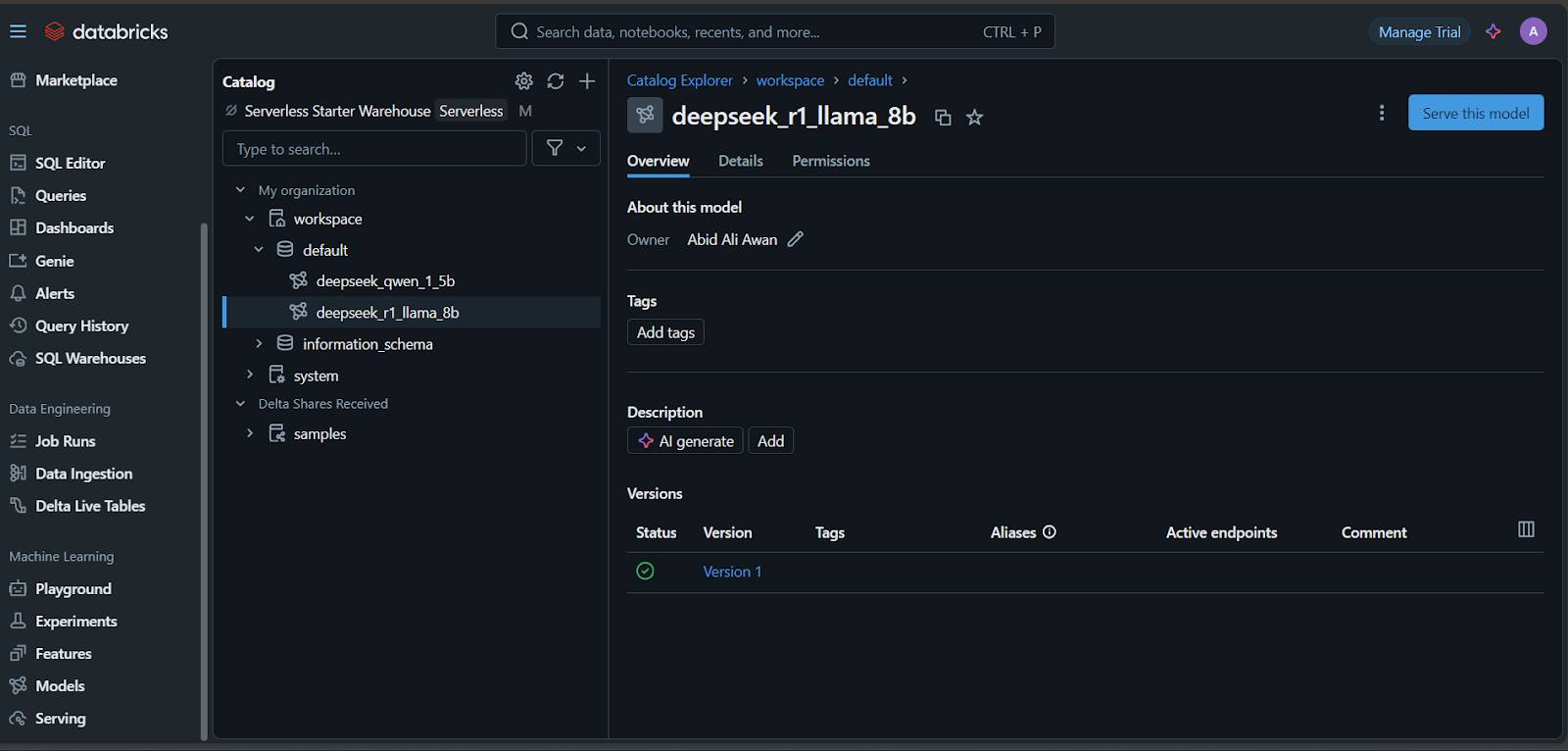
- Configure Endpoint: Name your endpoint, choose compute options, set concurrency, and click "Create."


For fine-tuning on a custom dataset, refer to the Fine-Tuning DeepSeek R1 tutorial.
Accessing the Deployed Model
- Databricks Playground: Test directly in the Databricks playground.

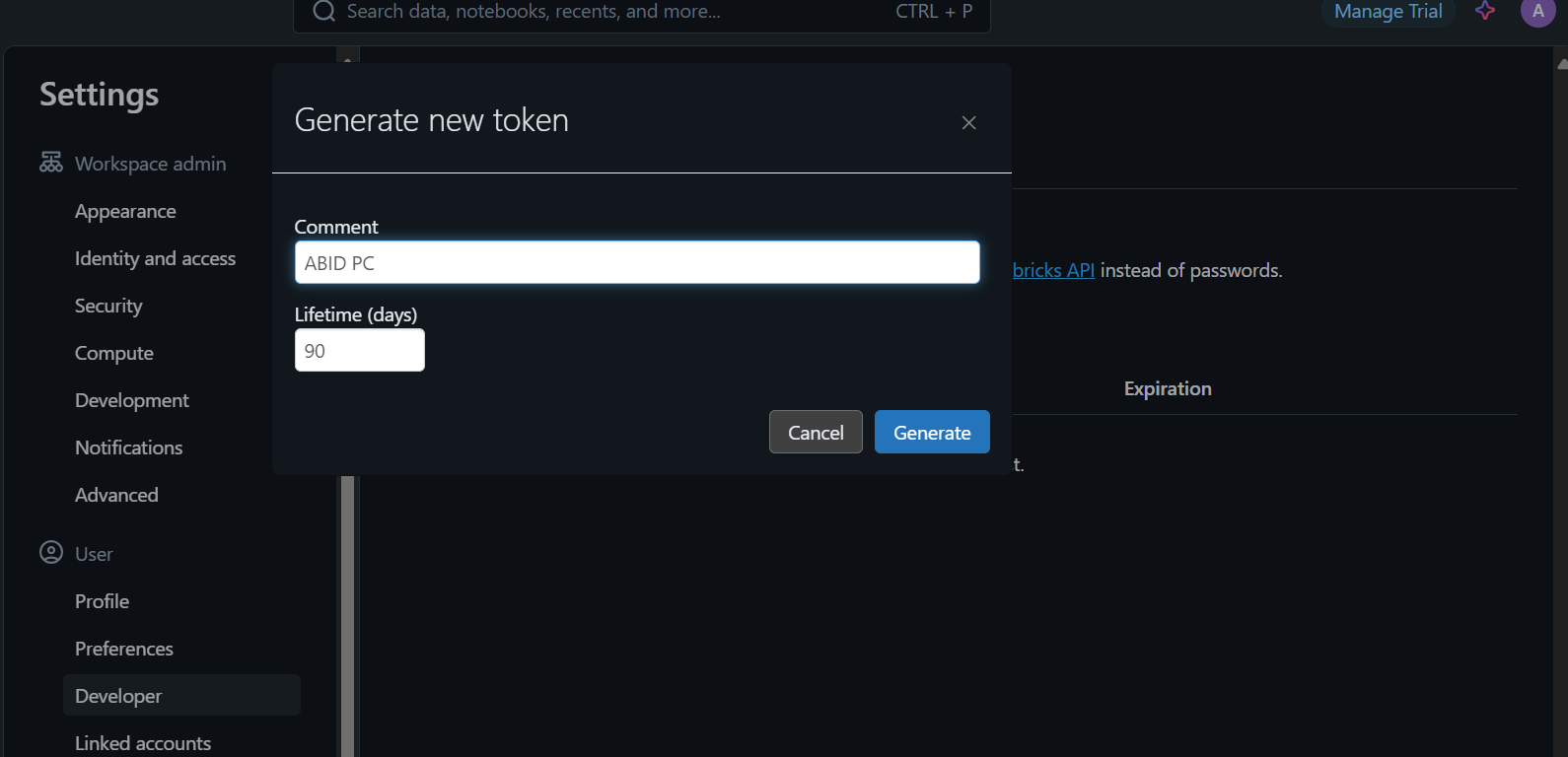
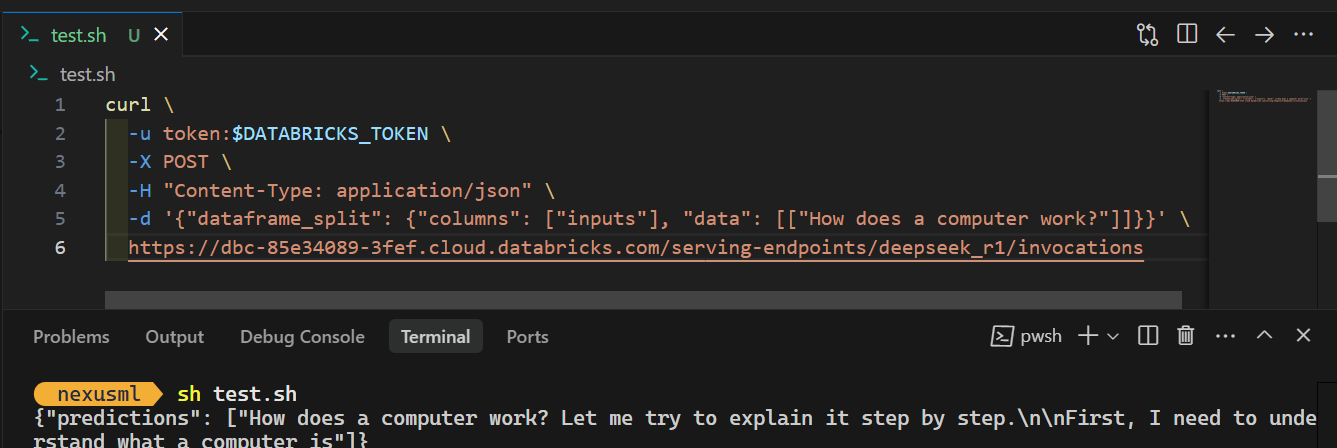
- CURL Command: Generate a Databricks API key (Settings > Developer), set it as an environment variable (
$DATABRICKS_TOKEN), and use CURL:
%%capture !pip install torch transformers mlflow accelerate torchvision %restart_python
For information on DeepSeek R1 vs. V3, see the DeepSeek R1 vs V3 blog. New to LLMs? The Introduction to LLMs in Python course is a great starting point. Remember that while CPU deployment is possible, it might be slower.
The above is the detailed content of Deploying DeepSeek R1 on Databricks: A Step-by-Step Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Selling AI Strategy To Employees: Shopify CEO's Manifesto
Apr 10, 2025 am 11:19 AM
Shopify CEO Tobi Lütke's recent memo boldly declares AI proficiency a fundamental expectation for every employee, marking a significant cultural shift within the company. This isn't a fleeting trend; it's a new operational paradigm integrated into p
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le
 10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
10 Generative AI Coding Extensions in VS Code You Must Explore
Apr 13, 2025 am 01:14 AM
Hey there, Coding ninja! What coding-related tasks do you have planned for the day? Before you dive further into this blog, I want you to think about all your coding-related woes—better list those down. Done? – Let’
 Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
The article reviews top AI voice generators like Google Cloud, Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure, IBM Watson, and Descript, focusing on their features, voice quality, and suitability for different needs.






