Basic Cascading Form React Native
I want to share my 3 approaches of handling cascading form fields.
- First approach is general, using state variables.
- Second is to use ordinary variables and one boolean state variable to trigger the state effect (refresh page).
- Third is, dynamic form fields with ordinary variables.
Here in this post we see the first approach, usual common way of handling cascading form fields based on country, state, city data.
Packages
react-native-element-dropdown react-native-paper
we are using react-native-element-dropdown for drop down fields
Base Page

import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import { View, Text, StyleSheet, TouchableOpacity } from "react-native";
import { Dropdown } from "react-native-element-dropdown";
export default function App() {
return (
<View>
<p>ZDropDown is a custom component. </p>
<h3>
Sample data
</h3>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">const listCountry = [
{ countryId: "1", name: "india" },
{ countryId: "2", name: "uk" },
{ countryId: "3", name: "canada" },
{ countryId: "4", name: "us" },
];
const listSate = [
{ stateId: "1", countryId: "1", name: "state1_india" },
{ stateId: "4", countryId: "2", name: "state1_uk" },
{ stateId: "7", countryId: "3", name: "state1_canada" },
{ stateId: "10", countryId: "4", name: "state1_us" },
];
const listCity = [
{
cityId: "1",
stateId: "1",
countryId: "1",
name: "city1_state1_country1",
},
{
cityId: "6",
stateId: "2",
countryId: "1",
name: "city6_state2_country1",
},
{
cityId: "7",
stateId: "3",
countryId: "1",
name: "city7_state3_country1",
},
{
cityId: "23",
stateId: "8",
countryId: "3",
name: "city23_state8_country3",
},
{
cityId: "30",
stateId: "10",
countryId: "4",
name: "city30_state10_country4",
},
{
cityId: "35",
stateId: "12",
countryId: "4",
name: "city35_state12_country4",
},
{
cityId: "36",
stateId: "12",
countryId: "4",
name: "city36_state12_country4",
},
];
Form Variables
We use 4 state variables, 3 for the form fields and the remaining one to trigger the focus effect.
export default function App() {
const [country, setCountry] = useState({
data: [],
selectedCountry: {},
value: null,
});
const [state, setState] = useState({
data: [],
selectedState: {},
value: null,
});
const [city, setCity] = useState({ data: [], selectedCity: {}, value: null });
const [ddfocus, setDdfocus] = useState({
country: false,
state: false,
city: false,
});
return (
<View>
<p>Focus and Blur events get triggered more than the onChange event so for focus changes, here a separate state variable is used to not to mess up with drop down data changes. </p>
<h3>
Load Country
</h3>
<p>Load country dropdown from the sample data. (you can use api call)<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">export default function App() {
. . .
const loadCountry = () => {
// load data from api call
setCountry({ data: [...listCountry], selectedCountry: {}, value: null });
};
useEffect(() => {
loadCountry();
}, []);
return (
. . .
)
Focus / Blur
When one drop down is selected, that field has to be focused and the remaining fields should be blurred. We're using a function to handle this.
const focusField = (fld = '') => {
const obj = { country: false, state: false, city: false };
if (fld) obj[fld] = true;
setDdfocus(obj);
};
<Text>Country</Text>
<ZDropDown
. . .
isFocus={ddfocus.country}
onFocus={() => focusField('country')}
onBlur={() => focusField('')}
onChange={null}
/>
<Text>State</Text>
<ZDropDown
. . .
isFocus={ddfocus.state}
onFocus={() => focusField('state')}
onBlur={() => focusField('')}
onChange={null}
/>
<Text>City</Text>
<ZDropDown
. . .
isFocus={ddfocus.city}
onFocus={() => focusField('city')}
onBlur={() => focusField('')}
onChange={null}
/>

We are half way done now.
Load State STATE
On country selected, we need to load the respective states STATES based on the country selection.
Update country field, load STATES based on country selection and focus off country.
<Text>Country</Text>
<ZDropDown
. . .
onChange={(item) => {
setCountry({
...country,
selectedCountry: item,
value: item.countryId,
});
loadState(item.countryId);
focusField("");
}}
/>
When country changed, both states and cities will be changed. So before setting up the new value we need to clear the existing data.
const loadState = async (cntId) => {
// load data from api call
setState({ data: [], selectedState: {}, value: null });
setCity({ data: [], selectedCity: {}, value: null });
const arr = listSate.filter((ele) => ele.countryId === cntId);
setState({ ...state, data: [...arr] });
console.log("respective states ", arr);
};

Load City
And load city field based on the selection.
<Text>State</Text>
<ZDropDown
. . .
onChange={(item) => {
setState({ ...state, selectedState: item, value: item.stateId });
loadCity(item.stateId);
focusField("");
}}
/>
const loadCity = async (stId) => {
// load data from api call
setCity({ data: [], selectedCity: {}, value: null });
const arr = listCity.filter((ele) => ele.stateId === stId);
setCity({ ...city, data: [...arr] });
};
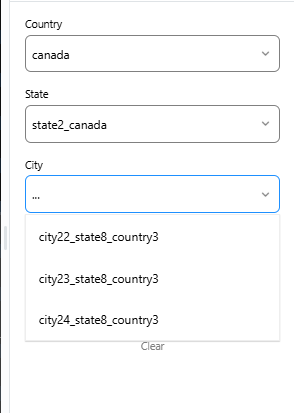
All set, the form fields are working properly now.

If we handle 2 more additional features, we are done. One is restting the page and the other one is to validate form and show warning.
Reset page
Form variables and focus variable should be cleared.
. . .
const resetForm = () => {
focusField("");
setCountry({ data: [...listCountry], selectedCountry: {}, value: null });
setState({ data: [], selectedState: {}, value: null });
setCity({ data: [], selectedCity: {}, value: null });
};
. . .
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => resetForm()}>
<h3>
Warning
</h3>
<p>We have to show a warning msg if the parent field value is null. For that we are using SnackBar component from paper.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">import { Snackbar } from "react-native-paper";
export default function App() {
. . .
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(false);
const [snackMsg, setSnackMsg] = useState("");
const onToggleSnackBar = () => setVisible(!visible);
const onDismissSnackBar = () => setVisible(false);
. . .
return (
<View>
<p>Since State and City fields have parent field, they have to be validated.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> <Text>State</Text>
<ZDropDown
onFocus={() => {
focusField('state');
if (!country.value) {
setSnackMsg('Select country');
onToggleSnackBar();
focusField('country');
}
}}
. . .
/>
<Text>City</Text>
<ZDropDown
onFocus={() => {
focusField('city');
if (!country.value) {
setSnackMsg('Select country');
onToggleSnackBar();
focusField('country');
} else if (!state.value) {
setSnackMsg('Select state');
onToggleSnackBar();
focusField('state');
}
}}
. . .
/>

Yeah thats it! We are done. Thank you.
Full code reference here
The above is the detailed content of Basic Cascading Form React Native. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
What should I do if I encounter garbled code printing for front-end thermal paper receipts?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Frequently Asked Questions and Solutions for Front-end Thermal Paper Ticket Printing In Front-end Development, Ticket Printing is a common requirement. However, many developers are implementing...
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object using JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to merge array elements with the same ID into one object in JavaScript? When processing data, we often encounter the need to have the same ID...
 Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Is JavaScript hard to learn?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Learning JavaScript is not difficult, but it is challenging. 1) Understand basic concepts such as variables, data types, functions, etc. 2) Master asynchronous programming and implement it through event loops. 3) Use DOM operations and Promise to handle asynchronous requests. 4) Avoid common mistakes and use debugging techniques. 5) Optimize performance and follow best practices.
 How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
How to achieve parallax scrolling and element animation effects, like Shiseido's official website?
or:
How can we achieve the animation effect accompanied by page scrolling like Shiseido's official website?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Discussion on the realization of parallax scrolling and element animation effects in this article will explore how to achieve similar to Shiseido official website (https://www.shiseido.co.jp/sb/wonderland/)...
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
The difference in console.log output result: Why are the two calls different?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 05:12 PM
In-depth discussion of the root causes of the difference in console.log output. This article will analyze the differences in the output results of console.log function in a piece of code and explain the reasons behind it. �...






