JavaScript Code Ethics: Writing Clean, Ethical Code

In today's fast-paced development world, delivering solutions quickly is essential. However, cutting corners on code quality often leads to bugs, security vulnerabilities, and unmaintainable code. Code ethics play a pivotal role in producing not only functional but also maintainable, efficient, and secure code. Let’s explore key ethical principles in JavaScript development and how they can improve your code quality with examples.
- Clarity Over Cleverness Ethical principle: Prioritize code readability and simplicity over "clever" or complex solutions. Code is read more often than written. Making it easy to understand is crucial for long-term maintenance.
Example: Avoid using terse or complex constructs when clearer alternatives exist.
Bad Example
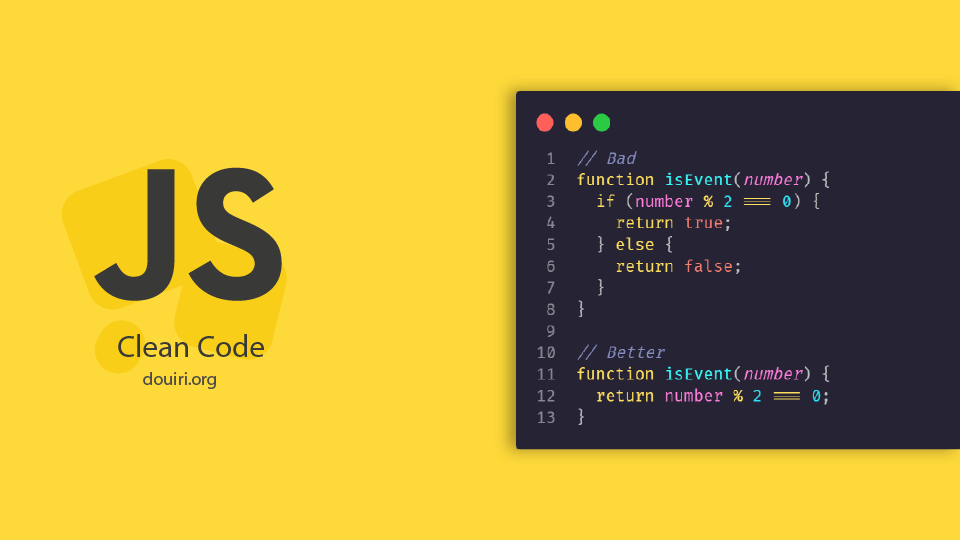
Good Example
const doubleArray = arr => arr.map(x => x * 2); // Clear and easily understood
In this example, the bitwise operator << works but is less readable than using simple multiplication. Choosing clarity ensures your team or future self can easily understand and maintain the code.
- Avoid Global Scope Pollution Ethical principle: Avoid polluting the global scope by declaring variables globally, which can lead to name collisions and unexpected behavior.
Bad Example
let count = 0; // Declared in global scope
function increment() {
count ;
}
Good Example
(() => {
let count = 0; // Encapsulated in a closure
function increment() {
count ;
}
})();
By wrapping the code in an IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression), the count variable is scoped locally, avoiding potential conflicts with other parts of the code.
- Error Handling with Care Ethical principle: Handle errors gracefully and provide informative messages. Silent failures can lead to unpredictable behaviors.
Bad Example
function getUser(id) {
return fetch(/user/${id}).then(res => res.json()); // No error handling
}
Good Example
async function getUser(id) {
try {
const res = await fetch(/user/${id});
if (!res.ok) {
throw new Error(Failed to fetch user: ${res.statusText});
}
return await res.json();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching user:', error);
return null;
}
}
By adding error handling, you not only prevent your app from failing silently but also provide meaningful information about what went wrong.
- Modularize Your Code Ethical principle: Break down large functions or files into smaller, reusable modules. This improves code organization, testing, and readability.
Bad Example
function processOrder(order) {
// Code for validating order
// Code for calculating total
// Code for processing payment
// Code for generating receipt
}
Good Example
`function validateOrder(order) { /* ... / }
function calculateTotal(order) { / ... / }
function processPayment(paymentInfo) { / ... / }
function generateReceipt(order) { / ... */ }
function processOrder(order) {
if (!validateOrder(order)) return;
const total = calculateTotal(order);
processPayment(order.paymentInfo);
generateReceipt(order);
}`
This modular approach makes your code easier to understand, test, and maintain. Each function has a single responsibility, adhering to the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP).
- Respect Data Privacy Ethical principle: Handle sensitive data with care. Do not expose unnecessary data in logs, console messages, or public endpoints.
Bad Example
function processUser(user) {
console.log(Processing user: ${JSON.stringify(user)}); // Exposing sensitive data
// ...
}
Good Example
function processUser(user) {
console.log(Processing user: ${user.id}); // Logging only the necessary details
// ...
}
In this case, the bad example exposes potentially sensitive user information in the console. The good example logs only what’s necessary, following data privacy best practices.
- Follow DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) Principle Ethical principle: Avoid code duplication. Instead, abstract repeated logic into reusable functions.
Bad Example
`function createAdmin(name, role) {
return { name, role, permissions: ['create', 'read', 'update', 'delete'] };
}
function createEditor(name, role) {
return { name, role, permissions: ['create', 'read'] };
}`
Good Example
`function createUser(name, role, permissions) {
return { name, role, permissions };
}
const admin = createUser('Alice', 'Admin', ['create', 'read', 'update', 'delete']);
const editor = createUser('Bob', 'Editor', ['create', 'read']);`
By following the DRY principle, you eliminate code duplication, reducing the chance for inconsistencies or errors in future updates.
- Document Your Code Ethical principle: Document your code to ensure that your intentions and thought processes are clear for other developers (or your future self).
Bad Example
function calculateAPR(amount, rate) {
return amount * rate / 100 / 12; // No explanation of what the formula represents
}
Good Example
`/**
- Calculate the monthly APR
- @param {number} amount - The principal amount
- @param {number} rate - The annual percentage rate
- @return {number} - The monthly APR */ function calculateAPR(amount, rate) { return amount * rate / 100 / 12; // APR formula explained in documentation }` Good documentation ensures that anyone reading the code can understand what it does without having to reverse-engineer the logic.
- Write Unit Tests Ethical principle: Writing unit tests ensures that your code works as expected and helps prevent bugs from being introduced as the code evolves.
Bad Example
// No test coverage
Good Example
// Using a testing framework like Jest or Mocha
test('calculateAPR should return correct APR', () => {
expect(calculateAPR(1000, 12)).toBe(10);
});
By writing tests, you ensure your code is reliable, verifiable, and easy to refactor with confidence.
- Adopt a Code Style Guide Ethical principle: Follow a consistent coding style across your team or project. This improves collaboration and reduces misunderstandings.
Consider using tools like ESLint or Prettier to enforce consistency in your code.
Example ESLint Configuration
{
"extends": "eslint:recommended",
"env": {
"browser": true,
"es6": true
},
"rules": {
"indent": ["error", 2],
"quotes": ["error", "single"],
"semi": ["error", "always"]
}
}
By adhering to a style guide, your codebase will maintain a consistent structure, making it easier for others to contribute and review code.
Conclusion
Ethical JavaScript coding practices ensure that your code is not only functional but also maintainable, secure, and future-proof. By focusing on clarity, modularity, error handling, and data privacy, you create a codebase that respects both your fellow developers and end users. Incorporating these practices into your workflow will help you write cleaner, more reliable code and foster a healthier development environment.
The above is the detailed content of JavaScript Code Ethics: Writing Clean, Ethical Code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1659
1659
 14
14
 1416
1416
 52
52
 1310
1310
 25
25
 1258
1258
 29
29
 1232
1232
 24
24
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing




