Metadata in C#
C# in metadata is defined as the binary information which is describing our program and this information is stored either in common language runtime portable executable file or in memory. If you compile the code from portable executable file then metadata is inserted in one more area portion of the file and all this code will now be converted into MSIL format (Microsoft Intermediate Language) then code moved into another partition portion of the file. All data types and data members that is defined and referenced in the assembly is put within the metadata. While we are executing the C# code at the runtime, it loads the metadata from the memory. The main purpose of the C# metadata is to know the information about the class, data members, inheritance, and data types etc. of the class. Metadata in the file consists of table and heap data structures.
Uses of Metadata
Given below are the uses of Metadata:
- It provides description about assembly data types like name, visibility, base class and interfaces etc.
- It provides data members like methods, fields, properties, events and nested types.
- It also provides additional description of the elements that modify types and members.
- It have identity like name, version, public key etc.
- It is a key to simple programming model and it will eliminate the necessity for IDL (Interface Definition Language) files, header files.
Types of Metadata
Given below is the figure of types of metadata:
Roles of the Metadata
Given below are the roles of metadata:
How does Metadata works in C#?
C# Metadata worked knowing about the data about the data.
Syntax:
using packageName;//used for insert the packages in C#
public class MyApp
{
public static int Main()
{
//data types
Console.WriteLine("Required Message");
}
//user defined methods for other logics
}Examples of Metadata in C#
Given below are the examples of Metadata in C#:
Example #1
Multiplication of 3 Numbers
Code: Multiplication.cs
using System; //Used for declaring the package or used for importing existed packege
public class Multiplication//declaring the class
{
public static int Main ()// main method for displaying the output
{
//declaring and defining the varaiables
int x = 50;
int y = 20;
int z=30;
//Printing the output of the multiplication of 2 numbers
Console.WriteLine ("Multiplication of {0},{1} and {2} is {3}",x,y,z,multiplication(x,y,z));
return 0;
}
public static int multiplication(int x, int y, int z)// multiplication() method implemention
{
return (x * y*z);// return multiplication of 3 numbers
}
}Output:
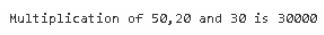
Explanation:
- As you can see in the about you can see the actual data, if we want metadata or binary data we can see the compiler inside machine generated code, that is always encrypted humans can’t understand it.
Example #2
Area of Square
Code: SquareOfArea.cs
using System; //Used for declaring the package or used for importing existed packege
public class SquareArea//declaring the class
{
public static int Main ()// main method for displaying the output
{
//declaring and defining the varaiables
int x = 50;
//Printing the output of the areaOfSquare
Console.WriteLine ("Area of Square is {0}",areaOfSquare(x));
return 0;
}
public static int areaOfSquare(int x)// multiplication() method implemention
{
return (x*x);// return area Of Square
}
}Output:

Explanation:
- As you can see in the about you can see the actual data, if we want metadata or binary data we can see the compiler inside machine generated code, that is always encrypted humans can’t understand it.
Example #3
Multiple Classes with Data
Code: MultiData.net
using System; //Used for declaring the package or used for importing existed packege
using System.Collections.Generic; //Used for declaring the package or used for importing existed packege
public class Entity {//declaring the class
//setters and getters for set and get the data
public string Name {get;set;}
public string Uses {get;set;}
//toString method to overide predefined String data
public override string ToString() {
string output1=string.Format("My Name is {0}", Name);
string output2=string.Format(" He is: {0}", Uses);
return output1+output2;
}
}
//declaring interface with reference class extention
public interface IMeta<T> where T: class {
//setters and getter for set and get the data
T Inner {get;set;}
stringMetaData {get;set;}
}
//declaring interface with reference class extention
public interface IStorage<T> where T: class {
//method definition for save the data
T Save();
}
//declaring the class by extending Imeta and IStorage interfaces
public class Meta<T> : IMeta<T>, IStorage<T>
where T: class
{
//creating a generic dictionary variable
private static Dictionary<T, Meta<T>> _stash = new Dictionary<T, Meta<T>>();
//constructor for the class
public Meta(T item) {
Inner = item;
}
//setters and getters for set and get the data
public T Inner {get;set;}
public string MetaData {get;set;}
//method implementation for operator
public static implicit operator T(Meta<T> meta) {
if (! _stash.ContainsKey(meta.Inner))
_stash.Add(meta.Inner, meta);
returnmeta.Inner;
}
public static implicit operator Meta<T>(T item) {
try {
return _stash[item];
} catch {
return null;
}
}
//save the data to repository
public T Save() {
return this;
}
}
//declaring the class
public static class MetaHelper {
//method definition for return the data
public static IMeta<T>GetMeta<T>(T item) where T: class {
return (Meta<T>)item;
}
//method definition for store the data
public static IStorage<T>GetStorage<T>(T item) where T: class {
return (Meta<T>)item;
}
}
//declaring the class
public class Program
{
//Entity type for createEntity method definition with 2 arguments
public static Entity CreateEntity(string name, string uses) {
//creating a variable
var result = new Meta<Entity>(new Entity(){ Name = name, Uses = uses });
//adding data to the variable that is metadata
result.MetaData = "Paramesh";
return result;
}
//test method to test the data
public static void Main()
{
//Passing the values to createEntity method
varent = CreateEntity("Amardeep", "Good Person");
//types casting ent into Meta class
Meta<Entity> meta = (Meta<Entity>)ent;
//creating variables
varimeta = MetaHelper.GetMeta<Entity>(ent);
varistore = MetaHelper.GetStorage<Entity>(ent);
var stored = istore.Save();
//Displaying output
Console.WriteLine("MetaData: {0} {1} {2} {3}", imeta.MetaData, imeta.Inner.Name, stored.Name, stored.Uses);
Console.WriteLine(ent);
if (meta != null) Console.WriteLine(meta.MetaData);
elseConsole.WriteLine("This is not a meta type");
}
}Output:

Explanation:
- As you can see in the about you can see the actual data, if we want metadata or binary data we can see the compiler inside machine generated code, that is always encrypted humans can’t understand it.
Conclusion
Metadata in C# is used for knowing the data about the data. This is all encrypted into binary format, which not human understandable that’s why we are converting binary code into normal code analyze the logic.
The above is the detailed content of Metadata in C#. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1332
1332
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Active Directory with C#. Here we discuss the introduction and how Active Directory works in C# along with the syntax and example.
 Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in C#. Here we discuss how Random Number Generator work, concept of pseudo-random and secure numbers.
 C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide to C# Data Grid View. Here we discuss the examples of how a data grid view can be loaded and exported from the SQL database or an excel file.
 Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Factorial in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to factorial in c# along with different examples and code implementation.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Patterns in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 types of Patterns in C# along with its examples and code implementation.
 Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide to Prime Numbers in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of prime numbers in c# along with code implementation.
 How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
There are several ways to modify XML formats: manually editing with a text editor such as Notepad; automatically formatting with online or desktop XML formatting tools such as XMLbeautifier; define conversion rules using XML conversion tools such as XSLT; or parse and operate using programming languages such as Python. Be careful when modifying and back up the original files.




