C# Multidimensional Arrays
In C#, the rectangular arrays or multidimensional arrays refer to the organization of the elements in a matrix format. A multidimensional array can only be of two or three dimensions. Dimensions of an array refer to the organization format of the data in the variable. Thus we can define a multidimensional array as an organization of elements in series or sequence as rows or columns.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax of Multidimensional Arrays:
Declaration of the 2D array.
int[,] x=new int[1,2];
Declaration of the 3D array.
int[,,] x=new int[1,2,3];
The syntax above specifies the format to declare two-dimensional and 3-dimensional arrays (x). the first array contains two elements, 1 and 2, whereas the three-dimensional array contains the element 1,2,3.
Initialization of the Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array can be initialized in three different ways
1. Complete Declaration
int[,] x = new int[6,6];
The above specification initializes a two-dimensional array completely, including the use of array type, array size, and the new operator.
2. Initialising without Using the New Operator
int[,] x = { { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };3. Initializing the Array without Declaring the Size
int[,] x = new int[,]{ { 3,2,1 }, { 6,5,4 }, { 9,8,7 } };Examples of C# multidimensional array
Below are the examples of Multidimensional Arrays in C#:
Example #1
Program to illustrate declaring and initialization of a multidimensional array. The example below illustrates the creation of a multidimensional array in C#.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] x = { { 3, 2, 1 }, { 6, 5, 4 }, { 9, 8, 7 } };
for (int a = 0; a < 3; a++)
{
for (int b = 0; b < 3; b++)
{
Console.Write(x[a, b] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Output:

Example #2
Program to illustrate the initialization, declaration of a two-dimensional array, and access the elements.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* declaring and initialising a two dimensional array*/
int[,] b = new int[6, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 6 }, { 8,7 }, { 9 , 10 }, { 2, 3 } };
int i, j;
/* accessing each of the elements value for the array */
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, b[i, j]);
}
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}Output:

The program above demonstrates the use of indices as a positional marker for accessing the elements of the array in a multidimensional array.
Example #3
Program for the addition of two multidimensional arrays.
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] array1 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] array2 = new int[3, 3];
int[,] resultArray = new int[3, 3];
int i, j;
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the first array: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array1[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array1: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array1[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
Console.WriteLine("specify the members of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
array2[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
Console.WriteLine("elements of the array2: ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", array2[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
resultArray[i, j] = array1[i, j] + array2[i, j];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("resultArray of the array1 and array2 looks as below : ");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", resultArray[i, j]);
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
}
}
}Output:
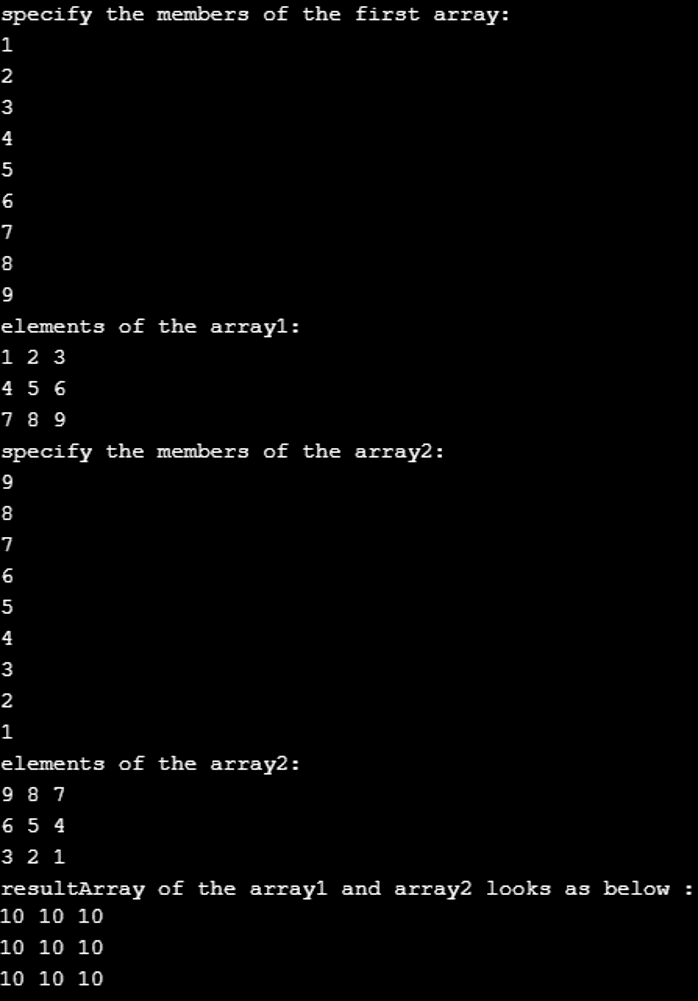
Using the program above, we have completed the addition operation on the array, with each element in the first array added to the second array’s counter element. For example, the first element in array1 is 1; similarly, the first element in array2 is 9. The resultant of addition should contain an array with the first element as 10.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of Multidimensional Arrays:
Advantages
- Multidimensional arrays can be used to organize subgroups of data within an array; multidimensional arrays can also be used to store data memory addresses in a pointer array.
- In the program, multidimensional arrays have a static size and initialization at the beginning. Any extension in size shall require the relevant size to be specified during initialization.
- Multidimensional arrays enable performing matrix operations and maintaining large data values under the same variable allocation.
- Multidimensional arrays are used to implement stacks, heaps and Queues, and hash tables.
Disadvantages
- The elements are located in contiguous memory locations for an array; hence any insertion and deletion of an element shall be more complex than similar operations on single elements.
- Also, the elements cannot be inserted into the middle of an array.
- Static allocation can cause wastage and failure to release unused memory if it allocates more memory than necessary. This can have a negative impact.
- Multidimensional arrays can be slower when compared to their single-dimensional array counterparts, which is a major disadvantage. To overcome this, we can replace jagged arrays with multidimensional arrays.
The above is the detailed content of C# Multidimensional Arrays. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1424
1424
 52
52
 1322
1322
 25
25
 1270
1270
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Active Directory with C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Active Directory with C#. Here we discuss the introduction and how Active Directory works in C# along with the syntax and example.
 Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Random Number Generator in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in C#. Here we discuss how Random Number Generator work, concept of pseudo-random and secure numbers.
 C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
C# Data Grid View
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Guide to C# Data Grid View. Here we discuss the examples of how a data grid view can be loaded and exported from the SQL database or an excel file.
 Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Factorial in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
Guide to Factorial in C#. Here we discuss the introduction to factorial in c# along with different examples and code implementation.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Patterns in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Guide to Patterns in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and top 3 types of Patterns in C# along with its examples and code implementation.
 Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Prime Numbers in C#
Sep 03, 2024 pm 03:35 PM
Guide to Prime Numbers in C#. Here we discuss the introduction and examples of prime numbers in c# along with code implementation.
 How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
There are several ways to modify XML formats: manually editing with a text editor such as Notepad; automatically formatting with online or desktop XML formatting tools such as XMLbeautifier; define conversion rules using XML conversion tools such as XSLT; or parse and operate using programming languages such as Python. Be careful when modifying and back up the original files.




