Understanding Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types
Conflict-free Replicated Data Types (CRDTs) are a class of data structures that enable seamless collaboration and data synchronization in distributed systems, allowing for collaborative updates without conflict. CRDTs are designed to achieve eventual consistency across multiple replicas of data, ensuring that even when updates occur independently, all replicas converge to the same state without requiring complex conflict resolution mechanisms.
In this blog post, we'll delve into what CRDTs are, explore their uses and types, understand how they work, and learn how to implement them, with a focus on JavaScript and the powerful Yjs library.
Use Cases of CRDTs
CRDTs are particularly useful in scenarios where real-time collaboration and offline support are crucial:
- Collaborative Text Editors: Google Docs, Notion, and Etherpad use CRDT-like structures for real-time editing.
- Collaborative Design Tools: Figma, a popular web-based design tool, uses CRDTs to enable real-time collaboration on design projects. Multiple designers can work on the same file simultaneously, with changes syncing seamlessly across all users.
- Distributed Databases: RxDB and Riak use CRDTs for conflict-free replication.
- Multiplayer Games: For maintaining consistent game state across players.
Types of CRDTs
There are two main types of CRDTs:
- State-based CRDTs: These replicate the entire state of the data structure. Merging is done by comparing and reconciling the states of different replicas.
- Operation-based CRDTs: These replicate the operations performed on the data structure. Merging is done by applying operations from different replicas in a commutative manner.
How CRDTs Work
CRDTs (Conflict-free Replicated Data Types) operate on principles that ensure eventual consistency across all replicas of the data, even when updates are made concurrently or when network partitions occur. Let's delve deeper into the mechanics:
Key Properties
- Commutativity: This property ensures that the order of operations doesn't affect the final result. For example, in a counter CRDT, incrementing by 2 and then by 3 yields the same result as incrementing by 3 and then by 2.
- Associativity: This means that the grouping of operations doesn't matter. Using the counter example again, (1 + 2) + 3 is the same as 1 + (2 + 3).
- Idempotence: Applying the same operation multiple times has the same effect as applying it once. This is crucial for handling duplicate messages in distributed systems.
Conflict Resolution
CRDTs resolve conflicts automatically by design:
- For state-based CRDTs (CvRDTs), this is achieved through a merge function that combines the states of two replicas. This merge function must be commutative, associative, and idempotent.
- For operation-based CRDTs (CmRDTs), operations are designed to be commutative, ensuring that applying them in any order leads to the same final state.
Logical Clocks
Many CRDT implementations use logical clocks (such as version vectors or dotted version vectors) to track the causal history of operations. This helps in determining the order of concurrent operations and in identifying which updates a replica has already seen.
Using CRDTs in JavaScript with Yjs
Implementing CRDTs from scratch can be complex. However, there are libraries available that simplify the process. For JavaScript, one of the most popular CRDT libraries is Yjs. It is a high-performance CRDT implementation that supports various data types. Let's create a simple todo list application using Yjs, simulating multiple users working on the same document in memory.
Here's an example of how to implement a shared todo list using Yjs:
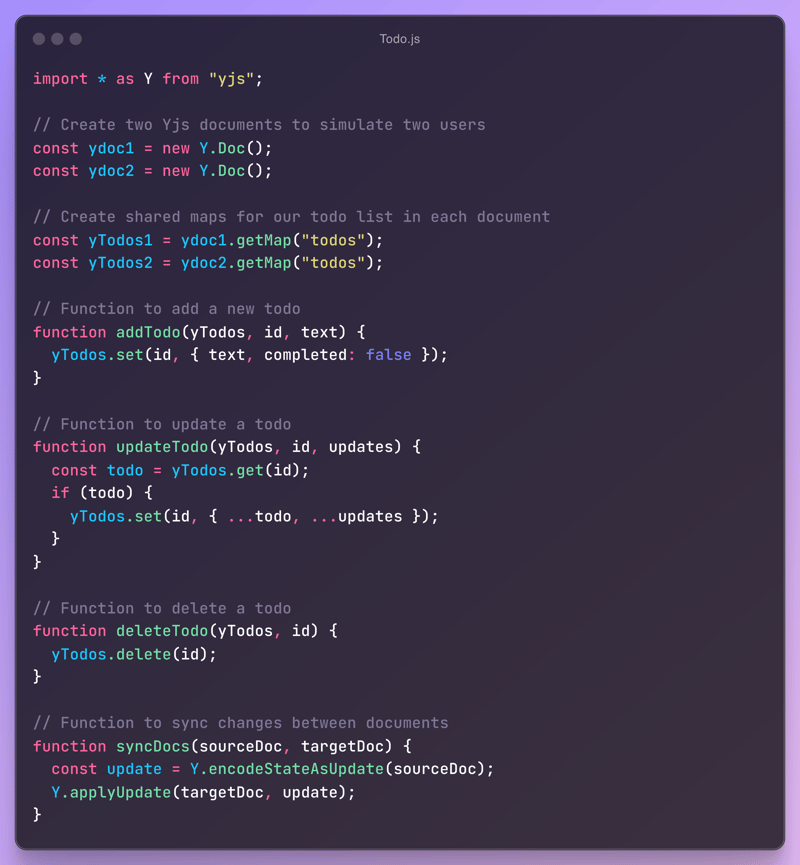
Let's use the created ydocs :
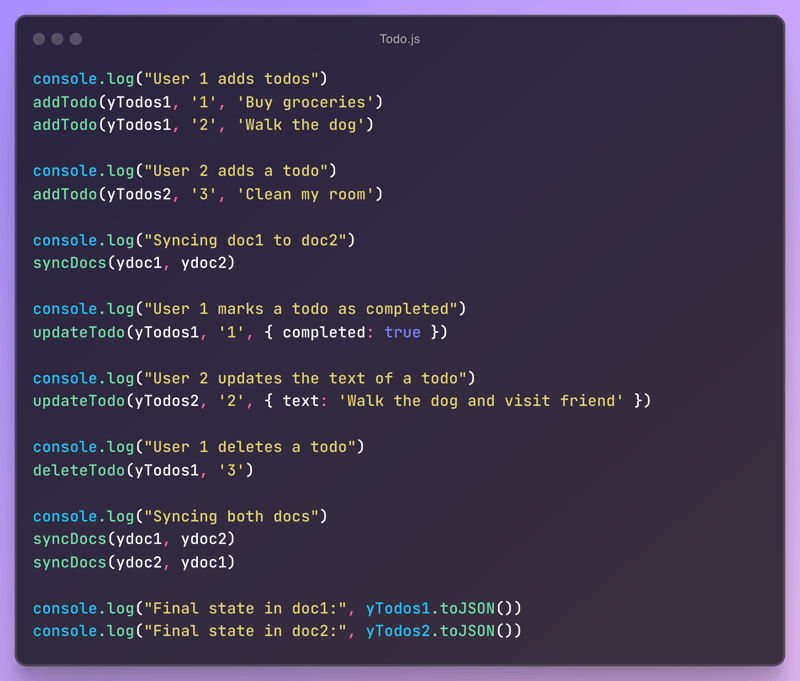
In this example, we create two Yjs documents (ydoc1 and ydoc2) to simulate two users working on the same todo list. Each document has its own shared map for the todos.
We define functions to add, update, and delete todos, as well as a syncDocs function to manually synchronize the state between the two documents. This simulates what would happen in a networked environment where updates are exchanged between clients.
Conclusion
CRDTs provide a powerful solution for building collaborative, distributed applications that can work seamlessly online and offline. While the underlying concepts can be complex, libraries like Yjs make it easier for developers to leverage the power of CRDTs in their applications. As distributed systems become more prevalent, understanding and utilizing CRDTs will become an increasingly valuable skill for developers.
Useful Links
- Yjs
- CRDT
- Tiptap - A collaborative text editor
The above is the detailed content of Understanding Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1669
1669
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.




