Continue in PHP
Continue statement is the one used inside conditional statements to instruct the code to skip the remaining iteration of the ongoing loop and to continue its execution at the condition evaluation and jump to the starting of the next execution. In PHP the most common place where continue statements are used in the switch statement.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Continue takes an optional numerical parameter which defines how many levels of internal loops the execution should skip and go to the end of. This means if the value is 1 then it skips to the end of the present loop. While the break statement is used to end from a loop completely, continue is used as a shortcut from the current loop and move on to the next. Both provide extra control to the coder on the loops to manipulate it however they want.
Syntax:
while ( condition 1)
{
//declaration statements
if ( condition 2 )
{
//PHP code goes here
continue ;
}
// Operational Statements
}As seen above we are first declaring a while loop along with its condition. When the condition is satisfied the code enters the loop and this goes on till the condition is not true. The code enters the if statement loop only if its condition is true. The continue statement here skips this iteration and will not execute the later part of the code after continue. Thus the control is transferred to the next iteration of while loop having condition 1.
Flowchart
Following is a flowchart of continue in PHP:
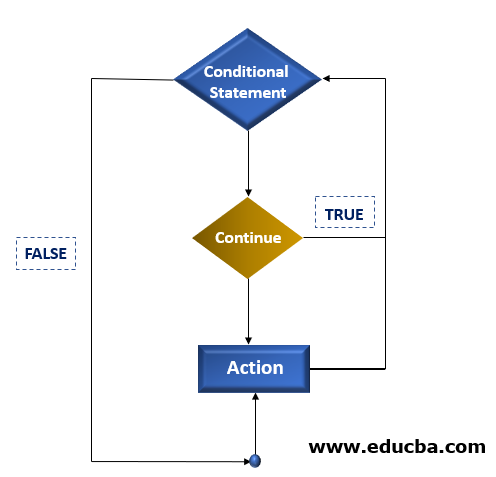
As seen in the flowchart, continue is always present in a statement block inside the code where the loop is being executed. If the condition for continue is true, it skips the succeeding action and skips on to the next iteration.
Examples of Continue in PHP
Let us see the exact working of continue statements by taking a few detailed examples as shown below:
Example #1
Code:
<?php
$a = 0;
for ($a = 0;$a <= 10;$a++)
{
if ($a==4)
{
break;
}
echo $a;
echo "\n";
}
echo "End of for loop" ;
?>Output:
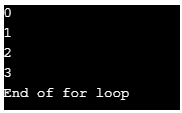
In this program, we are first initializing the value of variable a to zero. We are then using a for loop to increment its value by one till its value reaches 10. Another conditional statement if the loop is also used to break this loop once the value of a reaches equal to 4. Hence it breaks out of the loop and then prints “End of the loop” instead of printing out the value 5. We are printing each incremented value in the output to understand better. So as you can see the output stops at 4 because of the break statement.
Let us now see what continue statement does to the same code:
Code:
<?php
$a = 0;
for ($a = 0;$a <= 10;$a++)
{
if ($a==4)
{
continue;
}
echo $a;
echo "\n";
}
echo "End of for loop" ;
?>Output:
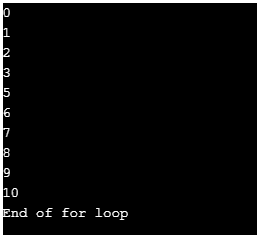
As you can see in the output above, the program printed the numbers from 0 to 4 as in the previous one. When it came to the if conditional statement and it was TRUE, because of the continue statement given it skipped printing 4 but continued the loop again. Hence in the output, we cannot see 4 but the incrementing started again from 5 till 10 which is the for loop condition and then printed “End of for loop” indicating it has come out of the for a loop. Hence the continue is usually used to skip from that particular instance and continue the loop from the next.
Example #2
Code:
<?php
$a=0;
foreach ($a as $k => $val) {
if (!($k % 2)) { // skip even members
continue;
}
do_something_odd($val);
}
$j = 0;
while ($j++ < 5) {
echo "Outermost while loop\n";
while (1) {
echo "Middle while loop\n";
while (1) {
echo "Innermost while loop\n";
continue 3;
}
echo "This text will never get printed\n";
}
echo "This text also will never get printed\n";
}
?>Output:

In the above code, we are using variable k in the if conditional loop to skip even numbers by using the modulo 2 function. We are using the continue statement here which skips the current iteration and hence no output is printed here.
In the second part of the loop we are using variable j and first initializing it to zero. We are then using 3 while loops: the outermost, middle one and the innermost loops. The outermost loop has the condition which executes when the variable j is less than 5 and j keeps incrementing by 1. The middle and the inner loops are infinite which means they keep on executing without any conditions.
Just like the break statement, we can also pass numeric parameters along with the continue statement. As shown in the above example, we are passing the number 3 which means that it skips 3 iterations of the loop. Hence the text which will never get printed is shown in the code. The same code when we give continue 2 will skip the innermost and the middle while loop and prints the last text. Similarly, continue 1 will skip only the innermost loop. However, note that continues 0 is not a valid statement to execute even though it was valid before as it was considered to be the same as continue 1.
Example #3
Continue can also be used in a switch statement as follows:
Code:
<?php
echo"\n";
echo"\n";
for ( $a = 0; $a < 5; $a++ ) {
switch ($a)
{
case 0:
echo $a . "\nb\n";
continue 2;
echo $a . "\na\n";
case 1:
echo $a . "\nb\n";
continue 2;
echo $a . "\na\n";
case 2:
echo $a . "\nb\n";
break;
echo $a . "\na\n";
}
echo "end\n";
}
echo"\n";
echo"\n";
?>Output:
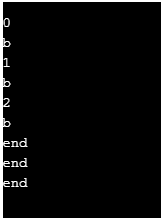
It can be seen that in a switch statement, break and continue statements work in the same way. But in the loops, they are used to stop the loop iteration and move on to the next. By using continue 2 we can come out of the switch inside a loop and continue to the next outer loop iteration.
Importance of Continue in PHP
- The main purpose of the continue statement is inside loops for skipping a particular instance of iteration where the coder wants it.
- In case of a do-while loop, the continue statement takes control of the conditional statement part of the while loop.
- Even in a while loop, the continue again takes control of the condition of while loop.
- In for loop, the increment or decrement actions get executed after the continue statement.
Disadvantages of Continue in PHP
- We cannot use continue in a file name which is inside a loop as it will cause an error.
- Using continue makes the code hard to follow and does not look elegant.
Conclusion – Continue in PHP
Continue statements are majorly used in all kinds of loops or conditional statements in PHP. They basically stop the ongoing iteration of that loop but does not terminate the same. Continue statement present inside the statement block just hops on to the next iteration which succeeds in the conditional statement.
The above is the detailed content of Continue in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1676
1676
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP uses MySQLi and PDO extensions to interact in database operations and server-side logic processing, and processes server-side logic through functions such as session management. 1) Use MySQLi or PDO to connect to the database and execute SQL queries. 2) Handle HTTP requests and user status through session management and other functions. 3) Use transactions to ensure the atomicity of database operations. 4) Prevent SQL injection, use exception handling and closing connections for debugging. 5) Optimize performance through indexing and cache, write highly readable code and perform error handling.
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.




