SQL Fundamentals | SELECT Statement | Database Management
Introduction
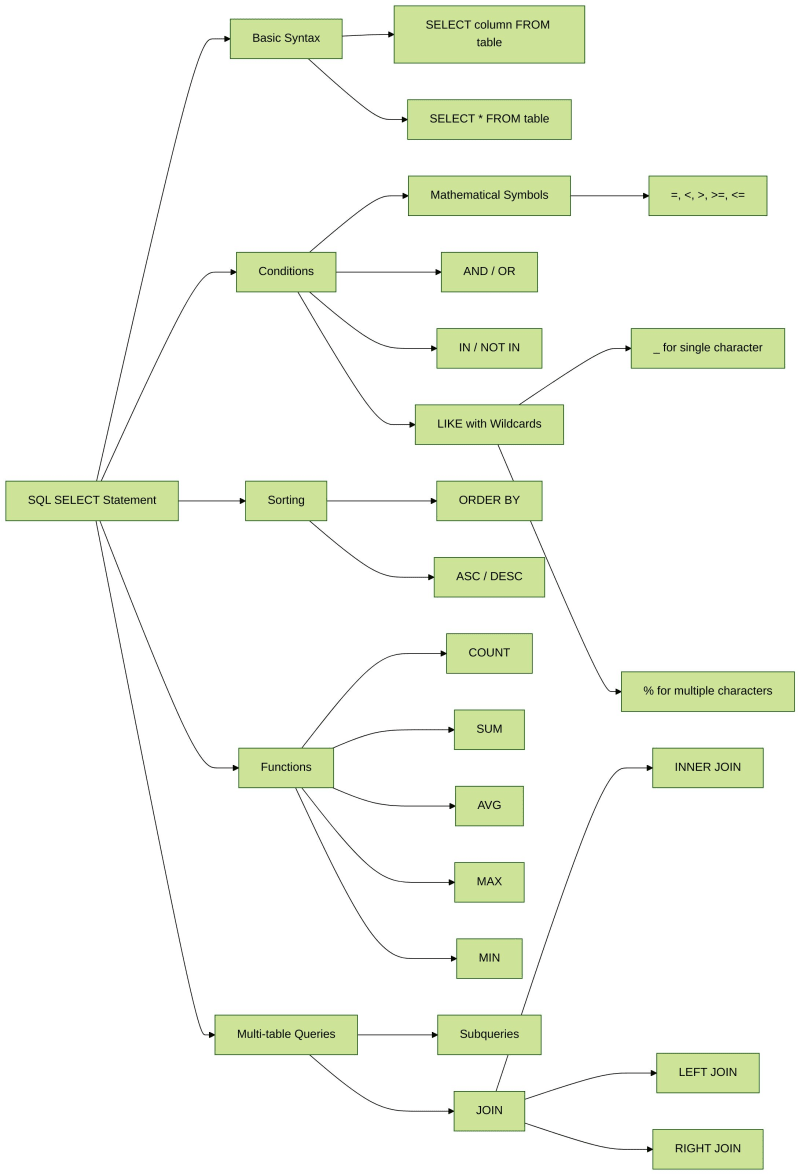
SELECT statement, one of the most commonly used statements in SQL, is used to select data in a table. This lab will learn SELECT and how to apply it to real practices.
Learning Objective
- SELECT Basic syntax
- Mathematical symbol conditions
- AND OR IN
- Wildcards
- Sort
- SQL built-in functions and calculations
- Subqueries and joins queries
Preparation
Before we start, download relevant data tables and create a database named mysql_labex (3 tables: department, employee, project).
Start MySQL service and log in as root.
cd ~/project sudo service mysql start mysql -u root
There are two files create-database.sql and insert-data.sql, which are located in ~/project/.
Load data in the file. You need to enter the command in the MySQL console to build the database:
source ~/project/create-database.sql source ~/project/insert-data.sql
In the database operating statements, the most frequently used, also considered the most important is the SELECT query. In previous labs, we've used SELECT * FROM table_name; statements in many places to see everything in a table. SELECT can be used with keywords of a variety of constraints, which encompass a variety of features. This lab will introduce these uses in detail.
Basic SELECT statement
The basic format of SELECT statement:
SELECT row name FROM table name WHERE constraint;
If you want to query all contents of the table, then query the name of the column with an asterisk *, which represents all columns in the table will be queried. In most cases, we only need to see the specified column of a table, such as to see the name and age of the employee table:
USE mysql_labex; SELECT name,age FROM employee;
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age FROM employee; +------+------+ | name | age | +------+------+ | Tom | 26 | | Jack | 24 | | Rose | 22 | | Jim | 35 | | Mary | 21 | | Alex | 26 | | Ken | 27 | | Rick | 24 | | Joe | 31 | | Mike | 23 | | Jobs | NULL | | Tony | NULL | +------+------+ 12 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Mathmatical symbol conditions
SELECT statements often have WHERE constraints, used to achieve more accurate queries. WHERE constraints can have mathematical notation (=, <,>,>=, <=). We just queried the name and age, and now let's make a slight modification:
SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age>25; </p> <p>Filter results with age over 25:<br> </p> <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age>25; +------+------+ | name | age | +------+------+ | Tom | 26 | | Jim | 35 | | Alex | 26 | | Ken | 27 | | Joe | 31 | +------+------+ 5 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Or find the name, age, and phone of an employee named Mary:
SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE name='Mary';
Result:
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE name='Mary'; +------+------+--------+ | name | age | phone | +------+------+--------+ | Mary | 21 | 100101 | +------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
"AND" & "OR"
We can have more than one constraints after WHERE, and based on the logical relationship of these conditions, we can use OR and AND to connect:
Filter - age is less than 25, or age is greater than 30
SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age<25 OR age>30;
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age<25 OR age>30; +------+------+ | name | age | +------+------+ | Jack | 24 | | Rose | 22 | | Jim | 35 | | Mary | 21 | | Rick | 24 | | Joe | 31 | | Mike | 23 | +------+------+ 7 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Filter - age is greater than 25, and age is less than 30
SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age>25 AND age<30;
If we need to include age 25 and 30, use age BETWEEN 25 AND 30 :
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age>25 AND age<30; +------+------+ | name | age | +------+------+ | Tom | 26 | | Alex | 26 | | Ken | 27 | +------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age FROM employee WHERE age BETWEEN 25 AND 30; +------+------+ | name | age | +------+------+ | Tom | 26 | | Alex | 26 | | Ken | 27 | +------+------+ 3 rows in set (0.000 sec)
IN & NOT IN
Keywords IN and NOT IN are used to filter results in a certain range. For instance, we want to find people in dpt3 or dpt4:
SELECT name,age,phone,in_dpt FROM employee WHERE in_dpt IN ('dpt3','dpt4');
For NOT IN, such as in the following command, we will get people not in dpt1 nor dpt3:
SELECT name,age,phone,in_dpt FROM employee WHERE in_dpt NOT IN ('dpt1','dpt3');
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,phone,in_dpt FROM employee WHERE in_dpt IN ('dpt3','dpt4');
+------+------+--------+--------+
| name | age | phone | in_dpt |
+------+------+--------+--------+
| Tom | 26 | 119119 | dpt4 |
| Rose | 22 | 114114 | dpt3 |
| Rick | 24 | 987654 | dpt3 |
| Mike | 23 | 110110 | dpt4 |
| Tony | NULL | 102938 | dpt3 |
+------+------+--------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.000 sec)
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,phone,in_dpt FROM employee WHERE in_dpt NOT IN ('dpt1','dpt3');
+------+------+--------+--------+
| name | age | phone | in_dpt |
+------+------+--------+--------+
| Tom | 26 | 119119 | dpt4 |
| Jack | 24 | 120120 | dpt2 |
| Mary | 21 | 100101 | dpt2 |
| Joe | 31 | 110129 | dpt2 |
| Mike | 23 | 110110 | dpt4 |
| Jobs | NULL | 19283 | dpt2 |
+------+------+--------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Wildcards
The keyword LIKE is used with wildcards in SQL statements, with wildcards representing unknown characters. Wildcards in SQL are _ and %. Which _ represents an unspecified character, %represents indefinite unspecified characters.
For example, if you only remember that the first four digits of the phone number are 1101 and the last two digits are forgotten, you can replace them with two _ wildcards:
SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE phone LIKE '1101__';
and here we have phone numbers starting with 1101:
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE phone LIKE '1101__'; +------+------+--------+ | name | age | phone | +------+------+--------+ | Joe | 31 | 110129 | | Mike | 23 | 110110 | +------+------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
In another case, such as when you only remember the first letter of the name, and you do not know the length of the name, then use % wildcard instead of indefinite characters:
SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE name LIKE 'J%';
Here we have names starting with J:
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee WHERE name LIKE 'J%'; +------+------+--------+ | name | age | phone | +------+------+--------+ | Jack | 24 | 120120 | | Jim | 35 | 100861 | | Joe | 31 | 110129 | | Jobs | NULL | 19283 | +------+------+--------+ 4 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Sort your results
In order to make queried results more organized and easy to follow, we might need to sort them by certain rules. ORDER BY comes in handy. By default, ORDER BY is in ascending arrangement, and by using ASC and DESC, we can also get results in ascending and descending order.
For example, we sort salary in a descending order, SQL statement:
SELECT name,age,salary,phone FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC;
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT name,age,salary,phone FROM employee ORDER BY salary DESC; +------+------+--------+--------+ | name | age | salary | phone | +------+------+--------+--------+ | Jobs | NULL | 3600 | 19283 | | Joe | 31 | 3600 | 110129 | | Ken | 27 | 3500 | 654321 | | Rick | 24 | 3500 | 987654 | | Mike | 23 | 3400 | 110110 | | Tony | NULL | 3400 | 102938 | | Alex | 26 | 3000 | 123456 | | Mary | 21 | 3000 | 100101 | | Jim | 35 | 3000 | 100861 | | Rose | 22 | 2800 | 114114 | | Jack | 24 | 2500 | 120120 | | Tom | 26 | 2500 | 119119 | +------+------+--------+--------+ 12 rows in set (0.000 sec)
SQL built-in functions and calculations
SQL allows the calculation of the data in the table. In this regard, SQL has five built-in functions that do the result of SELECT:
| Function: | COUNT | SUM | AVG | MAX | MIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For: | count numbers | sum up | average | maximum value | minimum value |
The COUNT function can be used for any data type (because it is only a count), while SUM and AVG functions can only calculate numeric data types. MAX and MIN can be used for numeric, string, or datetime data types.
For example, when we want to calculate the maximum and minimum value of salary, we use a statement like this:
SELECT MAX(salary) AS max_salary,MIN(salary) FROM employee;
You may have noticed a tiny detail. Use AS keyword can rename value. E.g. Max value is renamed into max_salary:
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT MAX(salary) AS max_salary,MIN(salary) FROM employee; +------------+-------------+ | max_salary | MIN(salary) | +------------+-------------+ | 3600 | 2500 | +------------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Subqueries
The SELECT statements discussed above all involve data in only one table, but sometimes you have to process multiple tables to get the information you need. For example, you want to know a few projects done by the department where the employee named "Tom" is located. Employee information is stored in the employee table, but the project information is stored in the project table.
We can use subqueries to deal with such situations:
SELECT of_dpt,COUNT(proj_name) AS count_project FROM project WHERE of_dpt IN (SELECT in_dpt FROM employee WHERE name='Tom');
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT of_dpt,COUNT(proj_name) AS count_project FROM project
-> WHERE of_dpt IN
-> (SELECT in_dpt FROM employee WHERE name='Tom');
+--------+---------------+
| of_dpt | count_project |
+--------+---------------+
| dpt4 | 2 |
+--------+---------------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
Subqueries can also be extended to three, four or more layers.
Join
When dealing with multiple tables, the subquery is only useful when the results are from the same table. However, if you need to display data in two or more tables, you must use the join operation.
The basic idea is to connect two or more tables as a new table to operate, as follows:
SELECT id,name,people_num FROM employee,department WHERE employee.in_dpt = department.dpt_name ORDER BY id;
This result is the number of employees in each department, where employee id and name from the employee table, people_num from the department table:
MariaDB [mysql_labex]> SELECT id,name,people_num
-> FROM employee,department
-> WHERE employee.in_dpt = department.dpt_name
-> ORDER BY id;
+----+------+------------+
| id | name | people_num |
+----+------+------------+
| 1 | Tom | 15 |
| 2 | Jack | 12 |
| 3 | Rose | 10 |
| 4 | Jim | 11 |
| 5 | Mary | 12 |
| 6 | Alex | 11 |
| 7 | Ken | 11 |
| 8 | Rick | 10 |
| 9 | Joe | 12 |
| 10 | Mike | 15 |
| 11 | Jobs | 12 |
| 12 | Tony | 10 |
+----+------+------------+
12 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Another connection statement format is to use the JOIN ON syntax. The statement is the same as:
SELECT id,name,people_num FROM employee JOIN department ON employee.in_dpt = department.dpt_name ORDER BY id;
Result is the same.
Summary
In this lab we learned the basic use of SELECT statement:
- Basic syntax
- Mathmatical symbol conditions
- AND OR IN
- Wildcards
- Sort
- SQL built-in functions and calculations
- Sunqueries and connection queries
? Practice Now: SQL's SELECT Statement
Want to Learn More?
- ? Learn the latest MySQL Skill Trees
- ? Read More MySQL Tutorials
- ? Join our Discord or tweet us @WeAreLabEx
The above is the detailed content of SQL Fundamentals | SELECT Statement | Database Management. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1277
1277
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Explain the role of InnoDB redo logs and undo logs.
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Explain the role of InnoDB redo logs and undo logs.
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
InnoDB uses redologs and undologs to ensure data consistency and reliability. 1.redologs record data page modification to ensure crash recovery and transaction persistence. 2.undologs records the original data value and supports transaction rollback and MVCC.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The basic operations of MySQL include creating databases, tables, and using SQL to perform CRUD operations on data. 1. Create a database: CREATEDATABASEmy_first_db; 2. Create a table: CREATETABLEbooks(idINTAUTO_INCREMENTPRIMARYKEY, titleVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, authorVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, published_yearINT); 3. Insert data: INSERTINTObooks(title, author, published_year)VA
 Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AM
InnoDBBufferPool reduces disk I/O by caching data and indexing pages, improving database performance. Its working principle includes: 1. Data reading: Read data from BufferPool; 2. Data writing: After modifying the data, write to BufferPool and refresh it to disk regularly; 3. Cache management: Use the LRU algorithm to manage cache pages; 4. Reading mechanism: Load adjacent data pages in advance. By sizing the BufferPool and using multiple instances, database performance can be optimized.
 MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL is suitable for web applications and content management systems and is popular for its open source, high performance and ease of use. 1) Compared with PostgreSQL, MySQL performs better in simple queries and high concurrent read operations. 2) Compared with Oracle, MySQL is more popular among small and medium-sized enterprises because of its open source and low cost. 3) Compared with Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL is more suitable for cross-platform applications. 4) Unlike MongoDB, MySQL is more suitable for structured data and transaction processing.
 MySQL: Structured Data and Relational Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL: Structured Data and Relational Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL efficiently manages structured data through table structure and SQL query, and implements inter-table relationships through foreign keys. 1. Define the data format and type when creating a table. 2. Use foreign keys to establish relationships between tables. 3. Improve performance through indexing and query optimization. 4. Regularly backup and monitor databases to ensure data security and performance optimization.
 Learning MySQL: A Step-by-Step Guide for New Users
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Learning MySQL: A Step-by-Step Guide for New Users
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:19 AM
MySQL is worth learning because it is a powerful open source database management system suitable for data storage, management and analysis. 1) MySQL is a relational database that uses SQL to operate data and is suitable for structured data management. 2) The SQL language is the key to interacting with MySQL and supports CRUD operations. 3) The working principle of MySQL includes client/server architecture, storage engine and query optimizer. 4) Basic usage includes creating databases and tables, and advanced usage involves joining tables using JOIN. 5) Common errors include syntax errors and permission issues, and debugging skills include checking syntax and using EXPLAIN commands. 6) Performance optimization involves the use of indexes, optimization of SQL statements and regular maintenance of databases.




