How to hide your Linux command line history
If you are a Linux command line user, sometimes you may not want certain commands to be recorded in your command line history. There could be many reasons, for example, you hold a certain position in a company and you have certain privileges that you don't want others to abuse. Or maybe there are some particularly important commands that you don't want to execute by mistake while browsing the history list.
However, is there a way to control which commands go into the history list and which don't? Or in other words, can we enable incognito mode like a browser in a Linux terminal? The answer is yes, and depending on the specific goals you want, there are many ways to achieve it. In this article, we’ll discuss some proven methods.
Note: All commands appearing in this article have been tested under Ubuntu.
The first two methods have been described in a previous article. If you already know this, you can skip this part. However, if you don't understand it, it is recommended to read it carefully.
Yes, you read that right. By inserting a space before the command, the command will be ignored by the shell, which means it will not appear in the history. But this method has a prerequisite. It will only work if your environment variable HISTCONTROL is set to "ignorespace" or "ignoreboth". In most cases, this is the default value.
So, like the following command (here [space] means entering a space):
[space]echo "this is a top secret"
If you have previously executed the following command to set environment variables, the above command will not appear in the history.
export HISTCONTROL = ignorespace
The screenshot below is an example of this approach.
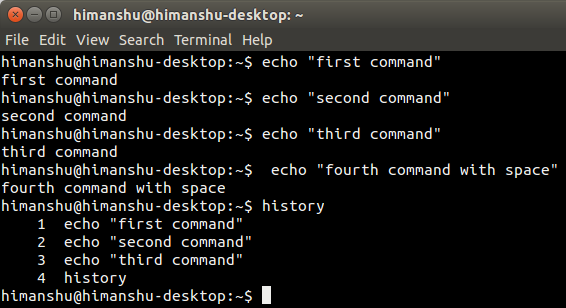
The fourth "echo" command is not recorded in the history because there is a space in front of it.
If you want to disable all history for a session, you can simply clear the value of the environment variable HISTSIZE before starting command line work. Execute the following command to clear its value:
export HISTSIZE=0
HISTSIZE indicates the number of commands (number of lines) that can be saved in the history list of a bash session. By default it is set to a non-zero value, for example on my computer it is 1000.
So the above mentioned command sets its value to 0, with the result that nothing will be stored in the history until you close the terminal. Remember that you also cannot see previously executed commands by pressing the up arrow key or running the history command.
This can be seen as another implementation of the solution proposed in the previous part. The only difference is to execute this command after you have finished all your work. The following is the command just mentioned:
history -cw
As mentioned just now, this has the same effect as the HISTSIZE method.
While the previously described methods (2 and 3) will serve the purpose, they can clear the entire history, and in many cases some may not be what we expect. Sometimes you may want to save the history until you started working on the command line. For such needs, you start executing the following commands before working:
[space]set +o history
Note: [space] means space. And because of the spaces, the command itself is not logged either.
The above command will temporarily disable the history function, which means that all operations you perform after this command will not be recorded in the history, but everything before this command will be recorded in the history list as is.
To re-enable the history function, execute the following command:
[Space]set -o history
It will restore the environment to its original state, that is, you have completed your work, and the commands after executing the above command will appear in the history.
现在假设历史记录中已经包含了一些你不希望记录的命令。这种情况下我们怎么办?很简单。直接动手删除它们。通过下面的命令来删除:
history | grep "part of command you want to remove"
上面的命令会输出历史记录中匹配的命令,每一条前面会有个数字。
一旦你找到你想删除的命令,执行下面的命令,从历史记录中删除那个指定的项:
history -d [num]
下面是这个例子的截图。
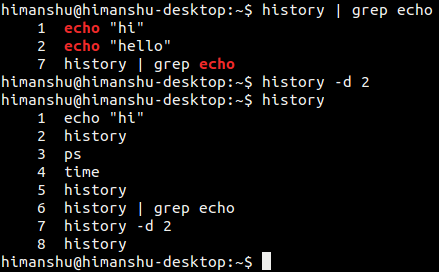
第二个 ‘echo’命令被成功的删除了。
(如果你不希望上述命令本身也被记录进历史中,你可以在上述命令前加个空格)
同样的,你可以使用向上的箭头一直往回翻看历史记录。当你发现你感兴趣的命令出现在终端上时,按下 “Ctrl + U”清除整行,也会从历史记录中删除它。
有多种不同的方法可以操作 Linux 命令行历史来满足你的需求。然而请记住,从历史中隐藏或者删除命令通常不是一个好习惯,尽管本质上这并没有错。但是你必须知道你在做什么,以及可能产生的后果。
The above is the detailed content of How to hide your Linux command line history. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)






