 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 With high efficiency and no need for labels, the Google team uses AI to mine clinical data, improve gene discovery and disease prediction, and is published in the Nature sub-journal
With high efficiency and no need for labels, the Google team uses AI to mine clinical data, improve gene discovery and disease prediction, and is published in the Nature sub-journal
With high efficiency and no need for labels, the Google team uses AI to mine clinical data, improve gene discovery and disease prediction, and is published in the Nature sub-journal

Editor | ScienceAI
Modern healthcare systems generate large amounts of high-dimensional clinical data (HDCD), such as pulmonary function maps, photoplethysmography (PPG), electrocardiogram (ECG) recordings, CT scans, and MRI imaging , these data cannot be summarized by a single binary or continuous number.
Understanding the connection between our genome and HDCD will not only improve our understanding of the disease but will also be critical to the development of treatments for the disease.
Recently, the genomics team at Google Research has made progress in using HDCD to characterize diseases and biological characteristics.
The research team proposed an unsupervised deep learning model, Representation Learning for Low-Dimensional Embedding Gene Discovery (REGLE), to discover the association between genetic variants and HDCD.
REGLE, as a novel gene discovery method, can exploit hidden information in high-dimensional clinical data, is computationally efficient, does not require disease labels, and can integrate information from expert-defined knowledge.
Overall, REGLE contains clinically relevant information beyond what is captured by existing expert-defined signatures, allowing for improved gene discovery and disease prediction.
Related research was titled "Unsupervised representation learning on high-dimensional clinical data improves genomic discovery and prediction" and was published in "Nature Genetics" on July 8.

Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-024-01831-6
Revealing the hidden information in HDCD
Study on the connection between genes and HDCD A simple approach is to perform a GWAS on each data coordinate. For example, you can study changes in the value of each pixel in a medical image. This approach is computationally expensive and has low power to detect significant associations due to high correlations between neighboring coordinates and a large multiple testing burden.
A more common approach is to focus on a small number of expert-defined features (EDF) extracted from HDCD as target features or phenotypes for GWAS. EDF can include clinically known features such as forced vital capacity (FVC) from spirometry or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1).
While these EDFs are important features discovered by experts, it is assumed that they may not fully capture the signals encoded in HDCD, so running GWAS on these signals may not exploit the full potential of HDCD.
REGLE aims to overcome these limitations using variational autoencoders (VAE) models. The method consists of three main steps:
(1) Learn the nonlinear, low-dimensional, disentangled representation (i.e., encoding or embedding) of HDCD through VAE;
(2) Conduct a GWAS independently for each encoded coordinate;
(3) Use polygenic risk scores (PRS) from coding coordinates as genetic scores for general biological functions, and then potentially combine these scores to create PRSs for specific diseases or traits (given a small number of disease labels).
Notably, REGLE also allows relevant EDFs to be selectively included in the input of the decoder in the modified VAE architecture, thus encouraging the encoder to learn only residual signals not represented by EDFs.

Detecting novel genetic loci for lung and circulatory function
The researchers demonstrated the power of REGLE using two high-dimensional clinical data modalities: spirometry, which measures lung function, and spirometry, which measures cardiovascular function. PPG. Both can be collected non-invasively and relatively cheaply in clinics or on consumer wearable devices, and both modalities have well-known characteristics).
Compared with genome-wide association studies with spirometry and PPG signatures of the same dimensions, REGLE's study of learned coding recovered the majority of known genetic loci (loci) associated with lung and circulatory function, while also detecting to other sites (for example, the important site of PPG increased by 45%). If these sites are validated in further analyzes and wet lab experiments, they have the potential to become new drug targets.
Improved Genetic Risk Score
A polygenic risk score (PRS) is a summary of the estimated impact of many genetic variants on a specific trait, expressed as a single number. PRSs created by genome-wide association studies on REGLE embeddings can be combined using only a few disease signatures to generate a PRS for that specific disease.
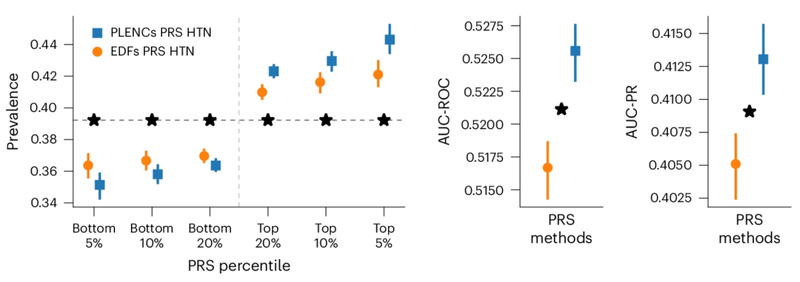
研究人员观察到,与现有方法(例如由专家定义的特征、PCA 和PRS)相比,由肺量图编码创建的肺功能PRS 改善了 COPD 和哮喘预测,并且比风险谱两端的特征PRS更有效地对风险组进行分层。哮喘和COPD 的多个独立数据集(COPDGene、eMERGE III、Indiana Biobank 和EPIC-Norfolk)中的多个指标(AUC-ROC、AUC-PR 和Pearson 相关性)在统计学上显着改善,如下所示。

类似地,从 PPG 的 REGLE 嵌入中得到的 PRS 可以改善高血压和收缩压 (SBP) 预测。在三个独立数据集(COPDGene、eMERGE III 和 EPIC-Norfolk)以及英国生物库的保留测试集中评估了由 PPG 编码和 PPG 特征生成的高血压和 SBP PRS。
观察到,在多个数据集中,使用来自 PPG 编码的 PRS 比使用来自专家定义特征的 PRS 具有一致的改进趋势,无论是高血压还是 SBP。

部分可解释的嵌入
利用REGLE 的生成特性,通过固定专家定义特征的值并改变一个编码坐标而将其他编码坐标保持为零来研究编码坐标对肺量图形状的影响。然后,仅使用训练模型的解码器部分生成相应的肺量图。
典型的流量-体积肺量图由两个不同的部分组成:(1)相对较短的部分以达到峰值流量,其中流量随着体积的增加而单调增加;(2)肺量图的主要部分,其中流量单调减少。
下图显示,改变第一个坐标相当于扩大或缩小第二部分(负斜率),同时保持第一部分相对固定。事实上,曲线第二部分的凹度被肺病学家称为凹陷,这是气道阻塞的指标,标准 EDF 无法很好地表示出来。
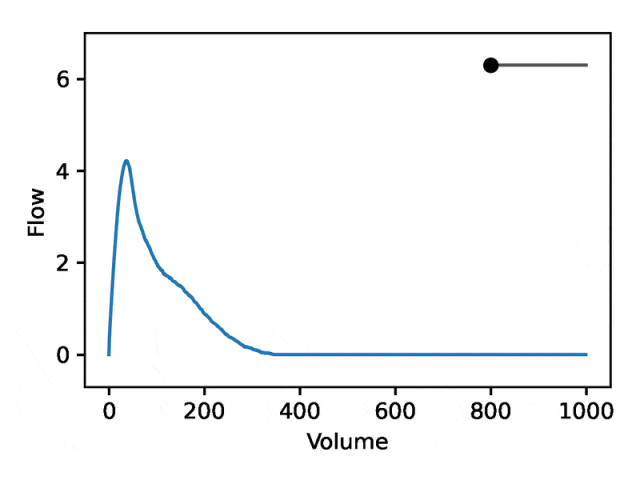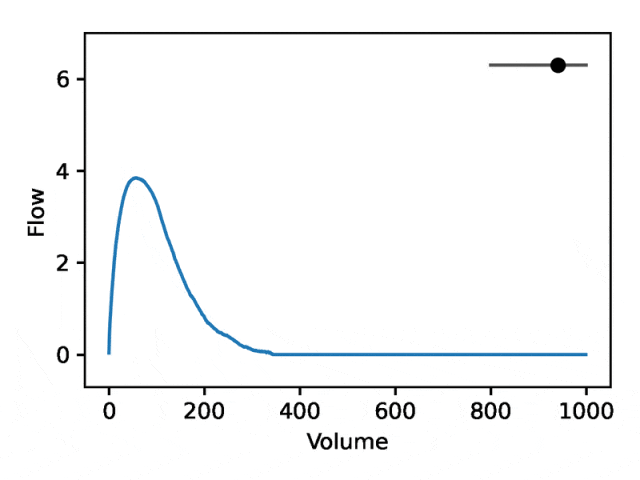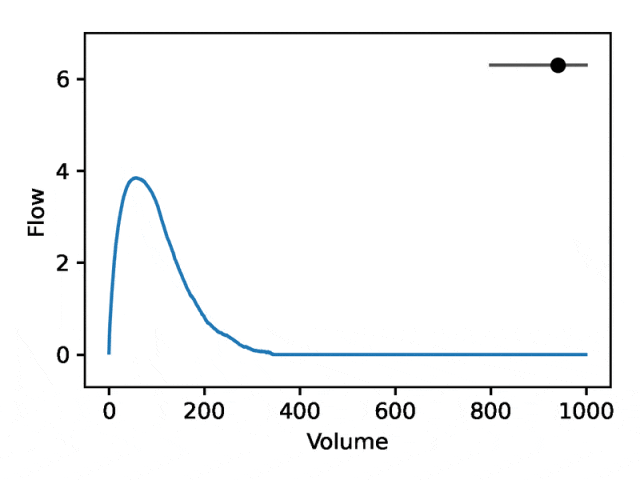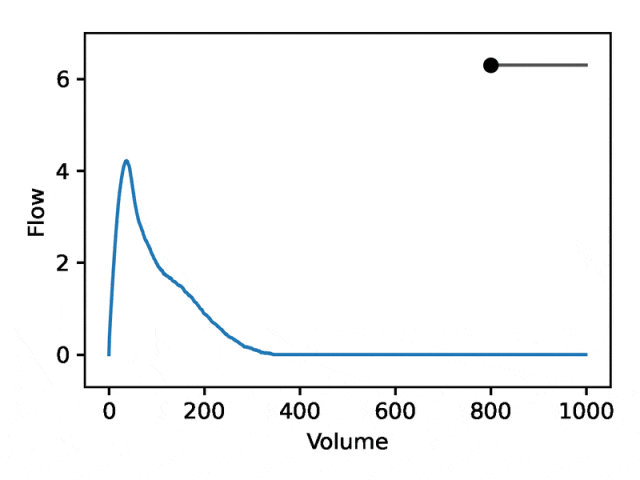
阐明人类特征和疾病的遗传基础
REGLE 是一种无监督学习方法,可执行遗传分析、改进的新基因位点发现和风险预测。由于难以大规模手动发现 EDF,因此无监督学习 HDCD 表示对基因组发现很有吸引力。
REGLE 框架还通过修改传统的 VAE 架构来支持在建模中原则性地使用这些特征。在两种临床数据模式(肺量图和 PPG)中展示了 REGLE,它们可以在临床环境中进行常规测量,也可以通过智能手机或可穿戴设备被动和非侵入性地测量。
REGLE 提供了一种在没有标记数据的情况下识别遗传对器官功能影响的机制,并允许将专家特征纳入模型。它还提供了一种使用很少的标签创建疾病和特征特异性 PRS 的方法。未来,这种类似的方法将越来越多地用于进一步阐明人类特征和疾病的遗传基础。
参考内容:https://research.google/blog/harnessing-hidden-genetic-information-in-clinical-data-with-regle/
The above is the detailed content of With high efficiency and no need for labels, the Google team uses AI to mine clinical data, improve gene discovery and disease prediction, and is published in the Nature sub-journal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1668
1668
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
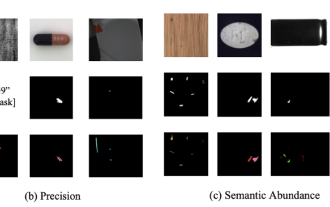 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
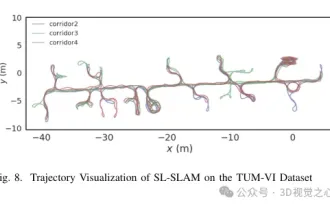 Beyond ORB-SLAM3! SL-SLAM: Low light, severe jitter and weak texture scenes are all handled
May 30, 2024 am 09:35 AM
Beyond ORB-SLAM3! SL-SLAM: Low light, severe jitter and weak texture scenes are all handled
May 30, 2024 am 09:35 AM
Written previously, today we discuss how deep learning technology can improve the performance of vision-based SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) in complex environments. By combining deep feature extraction and depth matching methods, here we introduce a versatile hybrid visual SLAM system designed to improve adaptation in challenging scenarios such as low-light conditions, dynamic lighting, weakly textured areas, and severe jitter. sex. Our system supports multiple modes, including extended monocular, stereo, monocular-inertial, and stereo-inertial configurations. In addition, it also analyzes how to combine visual SLAM with deep learning methods to inspire other research. Through extensive experiments on public datasets and self-sampled data, we demonstrate the superiority of SL-SLAM in terms of positioning accuracy and tracking robustness.
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 AlphaFold 3 is launched, comprehensively predicting the interactions and structures of proteins and all living molecules, with far greater accuracy than ever before
Jul 16, 2024 am 12:08 AM
AlphaFold 3 is launched, comprehensively predicting the interactions and structures of proteins and all living molecules, with far greater accuracy than ever before
Jul 16, 2024 am 12:08 AM
Editor | Radish Skin Since the release of the powerful AlphaFold2 in 2021, scientists have been using protein structure prediction models to map various protein structures within cells, discover drugs, and draw a "cosmic map" of every known protein interaction. . Just now, Google DeepMind released the AlphaFold3 model, which can perform joint structure predictions for complexes including proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, ions and modified residues. The accuracy of AlphaFold3 has been significantly improved compared to many dedicated tools in the past (protein-ligand interaction, protein-nucleic acid interaction, antibody-antigen prediction). This shows that within a single unified deep learning framework, it is possible to achieve
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A



