Security considerations in the design of data access layer in Java framework
The design of the data access layer in the Java framework needs to consider the following security factors: Authentication and authorization: Verify user access rights and determine operation permissions. Input validation: Prevent harmful characters and SQL injection. Encryption: Encrypts stored data and communications. Anti-injection: Use parameterized queries or prepared statements. Auditing and logging: Log data access operations and audit suspicious activity.

Security Considerations in the Design of Data Access Layer in Java Framework
The Data Access Layer (DAL) is a A component responsible for managing the interaction of data from a database or other data source. It is critical to ensure the security of your DAL to prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
Authentication and Authorization
- User authentication: Verify whether the user has the permission to access data and establish a corresponding session.
- User authorization: Determine what operations a user can perform, such as reading, creating, updating, or deleting data.
Input Validation
- Validate all user input to prevent incoming harmful characters or SQL injection.
- Use regular expressions, data type checking and other validation techniques.
Encryption
- Use an encryption algorithm such as AES to encrypt sensitive data stored in the database, such as passwords and personal information.
- Encrypted communication with the database via Secure Socket Layer (SSL).
Anti-injection
- Use parameterized queries or prepared statements to prevent SQL injection attacks.
- Never embed user input directly into a SQL statement.
Auditing and Logging
- Logs all data access operations such as reads, writes, and updates.
- Regularly review audit logs to detect any suspicious activity.
Practical case
Spring Boot with Hibernate
Use Spring Boot framework and Hibernate ORM to achieve security Data Access Layer:
@Entity // 表示数据库中的一张表
public class User {
@Id // 表示主键
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false) // 表示非空列
private String username;
@Column(nullable = false)
@Size(min = 8) // 表示密码长度最小为 8
private String password;
// 省略其他属性和方法
}public class UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
// 自动实现 CRUD 功能的方法
}@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseEntity<String> login(@RequestBody User user) {
// 验证用户身份,返回 JWT 令牌
}
}By applying these security considerations to the data access layer, you can help protect your application from data leaks and unauthorized access, thereby enhancing overall application security.
The above is the detailed content of Security considerations in the design of data access layer in Java framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1279
1279
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
DAO (Data Access Object) in Java is used to separate application code and persistence layer, its advantages include: Separation: Independent from application logic, making it easier to modify it. Encapsulation: Hide database access details and simplify interaction with the database. Scalability: Easily expandable to support new databases or persistence technologies. With DAOs, applications can call methods to perform database operations such as create, read, update, and delete entities without directly dealing with database details.
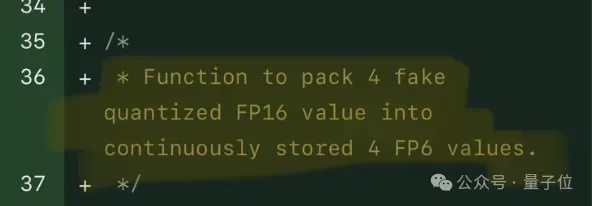 Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
FP8 and lower floating point quantification precision are no longer the "patent" of H100! Lao Huang wanted everyone to use INT8/INT4, and the Microsoft DeepSpeed team started running FP6 on A100 without official support from NVIDIA. Test results show that the new method TC-FPx's FP6 quantization on A100 is close to or occasionally faster than INT4, and has higher accuracy than the latter. On top of this, there is also end-to-end large model support, which has been open sourced and integrated into deep learning inference frameworks such as DeepSpeed. This result also has an immediate effect on accelerating large models - under this framework, using a single card to run Llama, the throughput is 2.65 times higher than that of dual cards. one
 What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
An API interface is a specification for interaction between software components and is used to implement communication and data exchange between different applications or systems. The API interface acts as a "translator", converting the developer's instructions into computer language so that the applications can work together. Its advantages include convenient data sharing, simplified development, improved performance, enhanced security, improved productivity and interoperability.
 How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
U disk is one of the commonly used storage devices in our daily work and life, but sometimes we encounter situations where the U disk is write-protected and cannot write data. This article will introduce several simple and effective methods to help you quickly remove the write protection of the USB flash drive and restore the normal use of the USB flash drive. Tool materials: System version: Windows1020H2, macOS BigSur11.2.3 Brand model: SanDisk UltraFlair USB3.0 flash drive, Kingston DataTraveler100G3USB3.0 flash drive Software version: DiskGenius5.4.2.1239, ChipGenius4.19.1225 1. Check the physical write protection switch of the USB flash drive on some USB flash drives Designed with
 What does mysql database do?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
What does mysql database do?
Apr 22, 2024 pm 06:12 PM
MySQL is a relational database management system that provides the following main functions: Data storage and management: Create and organize data, supporting various data types, primary keys, foreign keys, and indexes. Data query and retrieval: Use SQL language to query, filter and retrieve data, and optimize execution plans to improve efficiency. Data updates and modifications: Add, modify or delete data through INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE commands, supporting transactions to ensure consistency and rollback mechanisms to undo changes. Database management: Create and modify databases and tables, back up and restore data, and provide user management and permission control.
 Data Security in Artificial Intelligence: How to Unleash the Power of Artificial Intelligence
Apr 24, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
Data Security in Artificial Intelligence: How to Unleash the Power of Artificial Intelligence
Apr 24, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
In the digital age, data is often viewed as the battery that powers the innovation machine and drives business decisions. With the rise of modern solutions like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), organizations have access to vast amounts of data, enough to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. However, this comes at the cost of subsequent data loss and confidentiality challenges. As organizations continue to grasp the potential of artificial intelligence, they must strike a balance between achieving business advancements while avoiding potential risks. This article focuses on the importance of data security in artificial intelligence and what security measures organizations can take to avoid risks while taking advantage of the viable solutions provided by artificial intelligence. In artificial intelligence, data security is crucial. Organizations need to ensure data used is legal
 Usage of service layer in java
May 07, 2024 am 04:24 AM
Usage of service layer in java
May 07, 2024 am 04:24 AM
The Service layer in Java is responsible for business logic and business rules for executing applications, including processing business rules, data encapsulation, centralizing business logic and improving testability. In Java, the Service layer is usually designed as an independent module, interacts with the Controller and Repository layers, and is implemented through dependency injection, following steps such as creating an interface, injecting dependencies, and calling Service methods. Best practices include keeping it simple, using interfaces, avoiding direct manipulation of data, handling exceptions, and using dependency injection.
 What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
Schema in MySQL is a logical structure used to organize and manage database objects (such as tables, views) to ensure data consistency, data access control and simplify database design. The functions of Schema include: 1. Data organization; 2. Data consistency; 3. Data access control; 4. Database design.




