 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 In-depth analysis of the principles and usage of JWT (JSON Web Token)
In-depth analysis of the principles and usage of JWT (JSON Web Token)
In-depth analysis of the principles and usage of JWT (JSON Web Token)
This article brings you relevant knowledge about JWT. It mainly introduces what is JWT? What is the principle and usage of JWT? For those who are interested, let’s take a look below. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

JSON Web Token (abbreviated as JWT) is currently the most popular cross-domain authentication solution. This article introduces its principles and usage.
1. Issues with cross-domain authentication
Internet services are inseparable from user authentication. The general process is as follows.
1. The user sends the user name and password to the server.
2. After the server verification is passed, relevant data, such as user role, login time, etc., will be saved in the current session.
3. The server returns a session_id to the user and writes it into the user's Cookie.
4. Each subsequent request by the user will pass the session_id back to the server through Cookie.
5. The server receives the session_id, finds the data saved in the previous stage, and learns the user's identity.
The problem with this model is that the scaling is not good. Of course, there is no problem with a single machine. If it is a server cluster or a cross-domain service-oriented architecture, session data sharing is required, and each server can read the session.
For example, website A and website B are related services of the same company. Now it is required that as long as the user logs in on one of the websites, he will automatically log in when he visits another website. How can this be achieved?
One solution is to persist session data and write it to the database or other persistence layer. After receiving the request, various services request data from the persistence layer. The advantage of this solution is that the structure is clear, but the disadvantage is that the amount of work is relatively large. In addition, if the persistence layer fails, it will be a single point of failure.
Another solution is that the server simply does not save the session data. All data is saved on the client and sent back to the server for each request. JWT is a representative of this solution.
2. The principle of JWT
The principle of JWT is that after the server authenticates, it generates a JSON object and sends it back to the user, as shown below.
{
"姓名": "张三",
"角色": "管理员",
"到期时间": "2018年7月1日0点0分"
}In the future, when the user communicates with the server, this JSON object will be sent back. The server relies solely on this object to identify the user. In order to prevent users from tampering with data, the server will add a signature when generating this object (see below for details).
The server does not save any session data. In other words, the server becomes stateless, making it easier to expand.
3. JWT data structure
The actual JWT is probably as follows.

It is a very long string separated into three parts by a dot (.) in the middle. Note that there is no line break inside the JWT. It is written in several lines just for the convenience of display.
The three parts of JWT are as follows.
Header
Payload
Signature
Write it in one line, as shown below.
Header.Payload.Signature
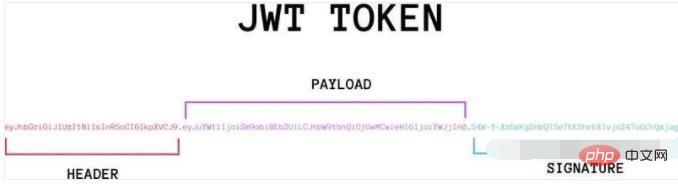
The following will introduce these three parts in turn.
3.1 Header
The Header part is a JSON object describing the metadata of the JWT, usually as follows.
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}In the above code, the alg attribute represents the signature algorithm (algorithm), the default is HMAC SHA256 (written as HS256); the typ attribute represents the type of the token (token), and the JWT token is written uniformly for JWT.
Finally, convert the above JSON object into a string using the Base64URL algorithm (see below for details).
3.2 Payload
The Payload part is also a JSON object, used to store the actual data that needs to be transferred. JWT specifies 7 official fields for selection.
iss (issuer): issuer
exp (expiration time): expiration time
sub (subject): Topic
aud (audience): Audience
- ##nbf (Not Before): Effective time
- iat (Issued At): Issuance time
- jti (JWT ID): Number
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"admin": true
}3.3 Signature
The Signature part is the signature of the first two parts to prevent data tampering. First, you need to specify a secret. This key is known only to the server and cannot be leaked to users. Then, use the signature algorithm specified in the Header (the default is HMAC SHA256) to generate a signature according to the following formula.HMACSHA256( base64UrlEncode(header) + "." + base64UrlEncode(payload), secret)
算出签名以后,把 Header、Payload、Signature 三个部分拼成一个字符串,每个部分之间用"点"(.)分隔,就可以返回给用户。
3.4 Base64URL
前面提到,Header 和 Payload 串型化的算法是 Base64URL。这个算法跟 Base64 算法基本类似,但有一些小的不同。
JWT 作为一个令牌(token),有些场合可能会放到 URL(比如 api.example.com/?token=xxx)。Base64 有三个字符+、/和=,在 URL 里面有特殊含义,所以要被替换掉:=被省略、+替换成-,/替换成_ 。这就是 Base64URL 算法。
四、JWT 的使用方式
客户端收到服务器返回的 JWT,可以储存在 Cookie 里面,也可以储存在 localStorage。
此后,客户端每次与服务器通信,都要带上这个 JWT。你可以把它放在 Cookie 里面自动发送,但是这样不能跨域,所以更好的做法是放在 HTTP 请求的头信息Authorization字段里面。
Authorization: Bearer <token>
另一种做法是,跨域的时候,JWT 就放在 POST 请求的数据体里面。
五、JWT 的几个特点
(1)JWT 默认是不加密,但也是可以加密的。生成原始 Token 以后,可以用密钥再加密一次。
(2)JWT 不加密的情况下,不能将秘密数据写入 JWT。
(3)JWT 不仅可以用于认证,也可以用于交换信息。有效使用 JWT,可以降低服务器查询数据库的次数。
(4)JWT 的最大缺点是,由于服务器不保存 session 状态,因此无法在使用过程中废止某个 token,或者更改 token 的权限。也就是说,一旦 JWT 签发了,在到期之前就会始终有效,除非服务器部署额外的逻辑。
(5)JWT 本身包含了认证信息,一旦泄露,任何人都可以获得该令牌的所有权限。为了减少盗用,JWT 的有效期应该设置得比较短。对于一些比较重要的权限,使用时应该再次对用户进行认证。
(6)为了减少盗用,JWT 不应该使用 HTTP 协议明码传输,要使用 HTTPS 协议传输。
推荐学习:《JavaScript视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of the principles and usage of JWT (JSON Web Token). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1426
1426
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1254
1254
 24
24
 Combination of golang WebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing
Dec 17, 2023 pm 03:06 PM
Combination of golang WebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing
Dec 17, 2023 pm 03:06 PM
The combination of golangWebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing In modern Web development, real-time data transmission is becoming more and more important. WebSocket is a protocol used to achieve two-way communication. Unlike the traditional HTTP request-response model, WebSocket allows the server to actively push data to the client. JSON (JavaScriptObjectNotation) is a lightweight format for data exchange that is concise and easy to read.
 Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization methods for converting PHP arrays to JSON include: using JSON extensions and the json_encode() function; adding the JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE option to avoid character escaping; using buffers to improve loop encoding performance; caching JSON encoding results; and considering using a third-party JSON encoding library.
 What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0 are two different MySQL database versions. There are some main differences between them: Performance improvements: MySQL8.0 has some performance improvements compared to MySQL5.7. These include better query optimizers, more efficient query execution plan generation, better indexing algorithms and parallel queries, etc. These improvements can improve query performance and overall system performance. JSON support: MySQL 8.0 introduces native support for JSON data type, including storage, query and indexing of JSON data. This makes processing and manipulating JSON data in MySQL more convenient and efficient. Transaction features: MySQL8.0 introduces some new transaction features, such as atomic
 Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string
Nov 18, 2023 pm 01:59 PM
Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string
Nov 18, 2023 pm 01:59 PM
Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string. When writing programs in Golang, we often need to convert the structure into a JSON string. In this process, the json.MarshalIndent function can help us. Implement formatted output. Below we will explain in detail how to use this function and provide specific code examples. First, let's create a structure containing some data. The following is an indication
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach
 Use PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:44 PM
Use PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:44 PM
Using PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output can make it easier to transfer and exchange data between different platforms and languages. This article will introduce the basic usage of the json_encode() function and how to format and output a JSON string. 1. Basic usage of json_encode() function The basic syntax of json_encode() function is as follows: stringjson_encod
 How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
Annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization: Serialization: @JsonIgnore: Ignore the property @JsonProperty: Specify the name @JsonGetter: Use the get method @JsonSetter: Use the set method Deserialization: @JsonIgnoreProperties: Ignore the property @ JsonProperty: Specify name @JsonCreator: Use constructor @JsonDeserialize: Custom logic
 Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Quick Start: Pandas method of reading JSON files, specific code examples are required Introduction: In the field of data analysis and data science, Pandas is one of the important Python libraries. It provides rich functions and flexible data structures, and can easily process and analyze various data. In practical applications, we often encounter situations where we need to read JSON files. This article will introduce how to use Pandas to read JSON files, and attach specific code examples. 1. Installation of Pandas



