 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
This article brings you an example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in Python. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
flask_sqlalchemy
Uses the Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) framework, which abstracts low-level database operation instructions into high-level object-oriented operations. In other words, if we use the database engine directly, we have to write SQL operation statements, but if we use the ORM framework, we can simplify the operation of database entities such as tables and documents into Python object operations
SQLAlchemy has become the standard for ORM in the Python world. Flask is a lightweight web framework that can be freely used with ORM. Flask-sqlalchemy is a plug-in specifically designed for Flask.
In Flask-SQLAlchemy, the database is specified using a URL.
MySQL --> mysql://username:password@hostname/database
Installation
pip install flask-sqlalchemy
Database operation
##1. How to create a database operation connection
from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) db = SQLAlchemy(app) app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql' app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True class User(db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) username = db.Column(db.String(80), unique=True) email = db.Column(db.String(120), unique=True)
db.create_all()
admin = User('admin', 'admin@example.com')
guest = User('guest', 'guest@example.com')db.session.add(admin) db.session.add(guest) db.session.commit()
2. Create relationships Type database table
SQLAlchemy is connected to a relational database. The best thing about relational data is relationships. Therefore, we will create an application that uses two related tables as an example.The most common relationship is the one-to-many relationship. Because relationships are declared before they are created, you can use strings to refer to classes that have not yet been created
Relationships are represented using the relationship() function. However, foreign keys must be declared separately using the class sqlalchemy.schema.ForeignKey.
from datetime import datetime
from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap
from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from flask import Flask
import pymysql
from sqlalchemy import desc
app = Flask(__name__)
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql'
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True
bootstrap = Bootstrap(app)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
passwd = db.Column(db.String(100))
add_time = db.Column(db.DATETIME,default=datetime.now())
gender = db.Column(db.BOOLEAN,default=True)
role_id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,db.ForeignKey('role.id'))
def __repr__(self):
return '<user:>' %(self.name)
class Role(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
users = db.relationship('User',backref='role')
# 给Role模型添加users属性
# backref 是定义反向引用
def __repr__(self):
return '<role:>' % (self.name)
if __name__ =='__main__':
# 1. 创建数据库表
# db.drop_all()
# db.create_all()
# # 2. 创建role数据库表数据
role_1 = Role(name='超级会员')
role_2 = Role(name='普通会员')
db.session.add(role_1)
db.session.add(role_2)
db.session.commit()
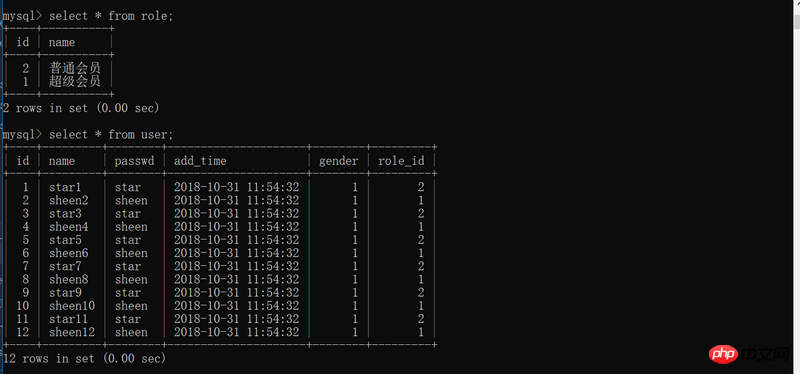
# # # 3. 添加user表内数据,100个用户,50个为超级会员,50个为普通会员
for i in range(1,13):
if i%2 == 0:
u = User(name='sheen'+str(i),passwd='sheen',role_id=1)
db.session.add(u)
else:
u = User(name='star'+str(i),passwd='star',role_id=2)
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()</role:></user:>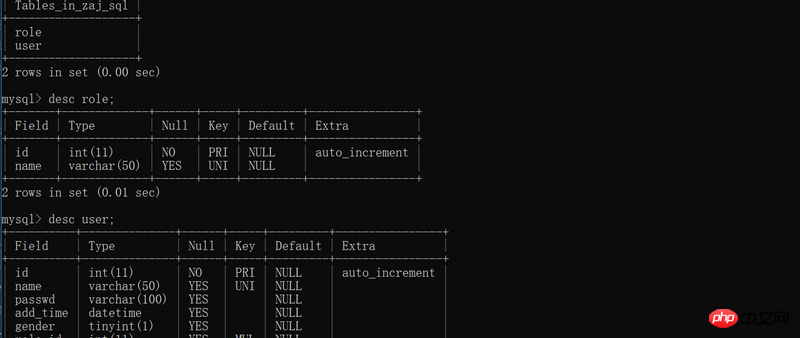
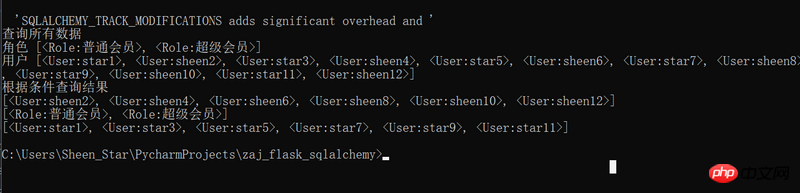
print('角色',Role.query.all())
print('用户',User.query.all())# select * from tablename where xxx=xxxxx print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).all()) print(Role.query.filter_by().all()) print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=2).all())
print('进行数据更新',end='\n')
u =User.query.filter_by(name='sheen2').first()
print(u)
u.passwd = '123'
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()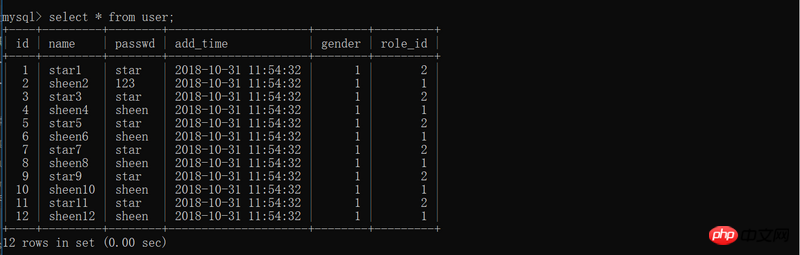
print('数据筛选', end='\n')
user = User.query.filter(User.role_id==1)
print(user) 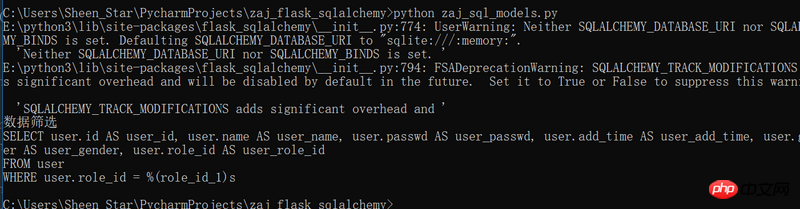
print('限制查询数据的显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).limit(3).all()
print(users) print('数据再处理', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).all()
print(users)print('多个过滤函数', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).limit(3).offset(1).all()
print(users)
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).slice(1,4).all()
print(users)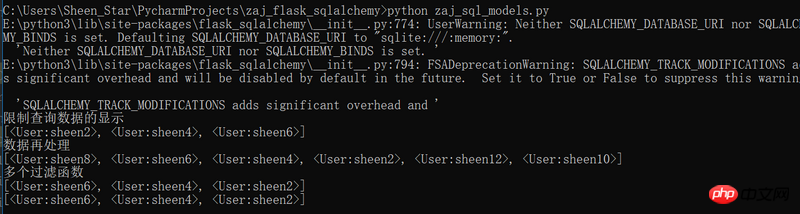
print('分页显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.paginate(1,5)
print(users.items)
users = User.query.paginate(2, 5)
print(users.items)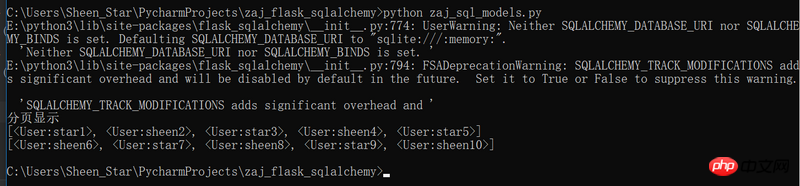
The above is the detailed content of Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Discussion on Hierarchical Structure in Python Projects In the process of learning Python, many beginners will come into contact with some open source projects, especially projects using the Django framework...
 How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Safely handle functions and regular expressions in JSON In front-end development, JavaScript is often required...
 How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to correctly divide business logic and non-business logic in hierarchical architecture in back-end development?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Discussing the hierarchical architecture problem in back-end development. In back-end development, common hierarchical architectures include controller, service and dao...
 Python vs. C : Which Language to Choose for Your Project?
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python vs. C : Which Language to Choose for Your Project?
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Choosing Python or C depends on project requirements: 1) If you need rapid development, data processing and prototype design, choose Python; 2) If you need high performance, low latency and close hardware control, choose C.
 Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python vs. C : Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Python and C each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1) Python is suitable for rapid development and data processing due to its concise syntax and dynamic typing. 2)C is suitable for high performance and system programming due to its static typing and manual memory management.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Use Cases and Applications Compared
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is more suitable for data science and automation, while JavaScript is more suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 1. Python performs well in data science and machine learning, using libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data processing and modeling. 2. Python is concise and efficient in automation and scripting. 3. JavaScript is indispensable in front-end development and is used to build dynamic web pages and single-page applications. 4. JavaScript plays a role in back-end development through Node.js and supports full-stack development.
 Choosing Between Python and C : The Right Language for You
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Choosing Between Python and C : The Right Language for You
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is suitable for beginners and data science, and C is suitable for system programming and game development. 1. Python is simple and easy to use, suitable for data science and web development. 2.C provides high performance and control, suitable for game development and system programming. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.





