An introduction to how to optimize batch insertion of data in MYSQL
I have also seen several other methods on the Internet, such as preprocessing SQL and batch submission. So how do these methods perform? This article will make a comparison of these methods
1. What problems did we encounter
In standard SQL, we usually write the following SQL insert statement.
INSERT INTO TBL_TEST (id) VALUES(1);
Obviously, this method is also feasible in MYSQL. But when we need to insert data in batches, such statements will cause performance problems. For example, if you need to insert 100,000 pieces of data, you will need 100,000 insert statements. Each statement needs to be submitted to the relational engine for parsing and optimization before it reaches the storage engine to do the actual insertion work.
It is precisely because of the performance bottleneck problem that the official MYSQL documentation also mentions the use of batch insertion, that is, inserting multiple values in an INSERT statement. That is,
INSERT INTO TBL_TEST (id) VALUES (1), (2), (3)
This approach can indeed speed up batch insertion. The reason is not difficult to understand. Since there are fewer INSERT statements submitted to the server, the network load Less, the most important thing is that the time for parsing and optimization seems to increase, but in fact the number of data rows affected is actually much more. So the overall performance is improved. According to some opinions on the Internet, this method can be improved dozens of times.
However, I have also seen several other methods on the Internet, such as preprocessing SQL and batch submission. So how do these methods perform? This article will make a comparison of these methods.
2. Comparing environments and methods
My environment is relatively difficult, basically a backward virtual machine. There are only 2 cores and 6G of memory. The operating system is SUSI Linux and the MYSQL version is 5.6.15.
It is conceivable that the performance of this machine has caused my TPS to be very low, so all the data below are meaningless, but the trend is different, which can show the performance trend of the entire insertion.
Due to business characteristics, the table we use is very large, with a total of 195 fields, and it is full (each field is filled in, including varchar), and the size is slightly less than 4KB. Generally speaking, , the size of a record is also 3KB.
Because based on our actual experience, we are very sure that performance can be greatly improved by submitting a large number of INSERT statements in one transaction. Therefore, all the tests below are based on the practice of submitting every 5,000 records inserted.
Finally, it should be noted that all the following tests are conducted using the MYSQL C API and use the INNODB storage engine.
3. Comparison methods
Ideal type test (1) - method comparison
Purpose: to find out the most suitable under ideal circumstances Insertion mechanism
Key methods:
1. Each incoming/thread inserts in primary key order
2. Compare different insertion methods
3. Compare the impact of different numbers of inputs/threads on insertion
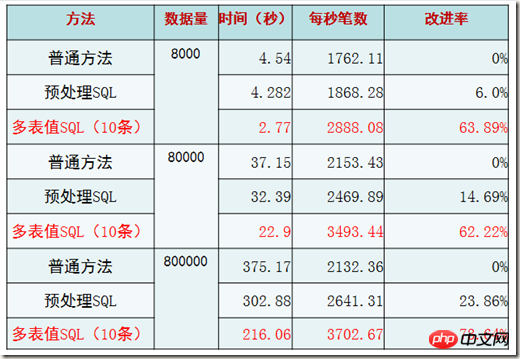
* "Ordinary method" refers to the situation where only one VALUE is inserted in an INSERT sentence.
* "Preprocessed SQL" refers to the use of preprocessed MYSQL C API.
* "Multiple table value SQL (10 records)" is a situation where 10 records are inserted using an INSERT statement. Why 10? Later verification tells us that this has the highest performance.
Conclusion, obviously, from the trend of the three methods, the multi-table value SQL (10) method is the most efficient.
Ideal test (2) - Comparison of the number of SQL entries with multiple table values
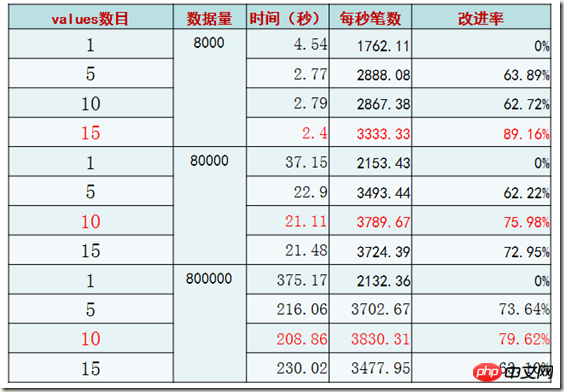
Obviously, as the amount of data increases, In this case, it is most efficient to insert 10 records for each INSERT statement.
Ideal test (3) - Comparison of number of connections
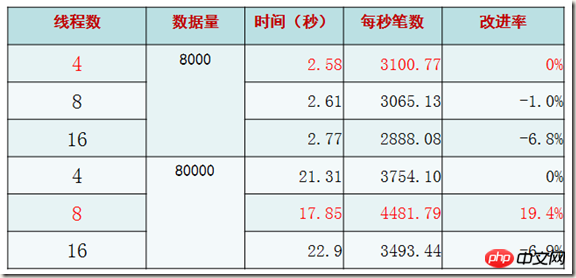
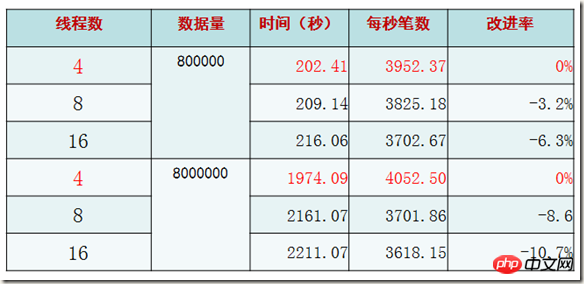
Conclusion: When connecting and operating with 2 times the number of CPU cores, the performance is the highest
General test - test based on our business volume
Purpose: Is the best insertion mechanism suitable for ordinary transaction situations?
Key methods:
1. Simulate production data (each record is about 3KB)
2. Insert the primary key of each thread out of order
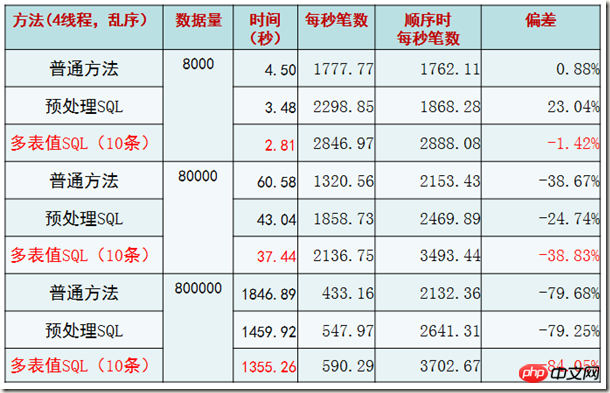
Obviously, if the primary key is inserted out of order, the performance will plummet. This is actually consistent with the phenomenon shown in the internal implementation principle of INNODB. But it is still certain that the case of multi-table value SQL (10 entries) is optimal.
Stress Test
Purpose: Is the best insertion mechanism suitable for extreme trading situations?
Key methods:
1. 将数据行的每一个字段填满(每条记录约为4KB)
2. 每个线程主键乱序插入
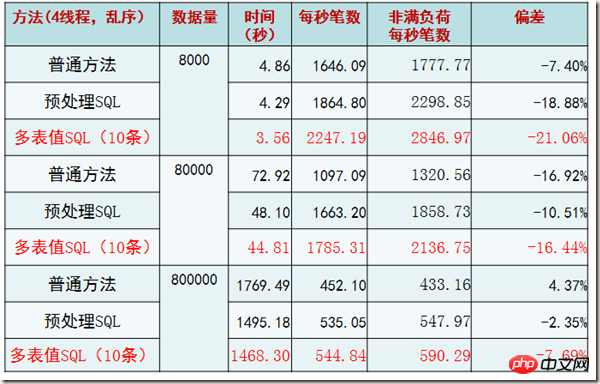
结果和我们之前的规律类似,性能出现了极端下降。并且这里验证了随着记录的增大(可能已经超过了一个page的大小,毕竟还有slot和page head信息占据空间),会有page split等现象,性能会下降。
四、结论
根据上面的测试,以及我们对INNODB的了解,我们可以得到如下的结论。
•采用顺序主键策略(例如自增主键,或者修改业务逻辑,让插入的记录尽可能顺序主键)
•采用多值表(10条)插入方式最为合适
•将进程/线程数控制在2倍CPU数目相对合适
五、附录
我发现网上很少有完整的针对MYSQL 预处理SQL语句的例子。这里给出一个简单的例子。
--建表语句 CREATE TABLE tbl_test ( pri_key varchar(30), nor_char char(30), max_num DECIMAL(8,0), long_num DECIMAL(12, 0), rec_upd_ts TIMESTAMP );
c代码
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <mysql.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define STRING_LEN 30
char pri_key [STRING_LEN]= "123456";
char nor_char [STRING_LEN]= "abcabc";
char rec_upd_ts [STRING_LEN]= "NOW()";
bool SubTimeval(timeval &result, timeval &begin, timeval &end)
{
if ( begin.tv_sec>end.tv_sec ) return false;
if ( (begin.tv_sec == end.tv_sec) && (begin.tv_usec > end.tv_usec) )
return false;
result.tv_sec = ( end.tv_sec - begin.tv_sec );
result.tv_usec = ( end.tv_usec - begin.tv_usec );
if (result.tv_usec<0) {
result.tv_sec--;
result.tv_usec+=1000000;}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, char ** argv)
{
INT32 ret = 0;
char errmsg[200] = {0};
int sqlCode = 0;
timeval tBegin, tEnd, tDiff;
const char* precompile_statment2 = "INSERT INTO `tbl_test`( pri_key, nor_char, max_num, long_num, rec_upd_ts) VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
MYSQL conn;
mysql_init(&conn);
if (mysql_real_connect(&conn, "127.0.0.1", "dba", "abcdefg", "TESTDB", 3306, NULL, 0) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, " mysql_real_connect, 2 failed\n");
exit(0);
}
MYSQL_STMT *stmt = mysql_stmt_init(&conn);
if (!stmt)
{
fprintf(stderr, " mysql_stmt_init, 2 failed\n");
fprintf(stderr, " %s\n", mysql_stmt_error(stmt));
exit(0);
}
if (mysql_stmt_prepare(stmt, precompile_statment2, strlen(precompile_statment2)))
{
fprintf(stderr, " mysql_stmt_prepare, 2 failed\n");
fprintf(stderr, " %s\n", mysql_stmt_error(stmt));
exit(0);
}
int i = 0;
int max_num = 3;
const int FIELD_NUM = 5;
while (i < max_num)
{
//MYSQL_BIND bind[196] = {0};
MYSQL_BIND bind[FIELD_NUM];
memset(bind, 0, FIELD_NUM * sizeof(MYSQL_BIND));
unsigned long str_length = strlen(pri_key);
bind[0].buffer_type = MYSQL_TYPE_STRING;
bind[0].buffer = (char *)pri_key;
bind[0].buffer_length = STRING_LEN;
bind[0].is_null = 0;
bind[0].length = &str_length;
unsigned long str_length_nor = strlen(nor_char);
bind[1].buffer_type = MYSQL_TYPE_STRING;
bind[1].buffer = (char *)nor_char;
bind[1].buffer_length = STRING_LEN;
bind[1].is_null = 0;
bind[1].length = &str_length_nor;
bind[2].buffer_type = MYSQL_TYPE_LONG;
bind[2].buffer = (char*)&max_num;
bind[2].is_null = 0;
bind[2].length = 0;
bind[3].buffer_type = MYSQL_TYPE_LONG;
bind[3].buffer = (char*)&max_num;
bind[3].is_null = 0;
bind[3].length = 0;
MYSQL_TIME ts;
ts.year= 2002;
ts.month= 02;
ts.day= 03;
ts.hour= 10;
ts.minute= 45;
ts.second= 20;
unsigned long str_length_time = strlen(rec_upd_ts);
bind[4].buffer_type = MYSQL_TYPE_TIMESTAMP;
bind[4].buffer = (char *)&ts;
bind[4].is_null = 0;
bind[4].length = 0;
if (mysql_stmt_bind_param(stmt, bind))
{
fprintf(stderr, " mysql_stmt_bind_param, 2 failed\n");
fprintf(stderr, " %s\n", mysql_stmt_error(stmt));
exit(0);
}
cout << "before execute\n";
if (mysql_stmt_execute(stmt))
{
fprintf(stderr, " mysql_stmt_execute, 2 failed\n");
fprintf(stderr, " %s\n", mysql_stmt_error(stmt));
exit(0);
}
cout << "after execute\n";
i++;
}
mysql_commit(&conn);
mysql_stmt_close(stmt);
return 0;
}The above is the detailed content of An introduction to how to optimize batch insertion of data in MYSQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.






