How to install mysql with docker
How to install mysql with docker: first query and download the image, the code is [docker images]; then create and run the container, the code is [docker run -d -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD]; finally configure related data.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, mysql8 version. This method is suitable for all brands of computers.
Related free learning recommendations: mysql video tutorial
How to install mysql with docker:
Install from the mirror market.
1. Query the image
docker search mysql

2. Download the image (during the actual test, I often get stuck when downloading the image, just try a few more times)
docker pull mysql
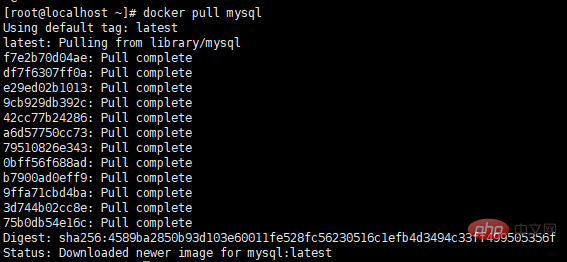
View the local image through the docker images command
docker images

3. Create and run the container
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=abc123 mysql
Parameter description:
-p 3306:3306 to be mapped to container 3306 port
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=abc1 23 Set up remote Log in the ROOT user password is ABC123
-name zyz-name optional, set the container's aliases
# m
## 4. You need to configure the data to ignore case
Mysql8 version, once mysql is officially running, you can no longer set ignore case. Forcing the setting will cause the mysql service to fail to start, so , we must mount the mysql configuration to the container when we create the container.
1) Create the folder /etc/mysql.d
cd /etc/ // 进入etc目录 mkdir mysql.d // 创建文件夹mysql.d,名称可变
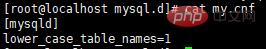
2) Add the configuration file my.cnf in the mysql.d folder and add the configuration
[mysqld] lower_case_table_names=1
 3) Re-create and run the container
3) Re-create and run the container
docker run -d -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=abc123 -v /etc/mysql.d:/etc/mysql/conf.d --name zyz-mysql mysql
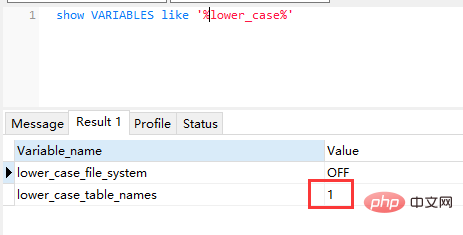
4) Check the effect. After executing the command, you will see
lower_case_table_names=1, indicating success.
Programming Video Course
The above is the detailed content of How to install mysql with docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1243
1243
 24
24
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
The methods to view Docker logs include: using the docker logs command, for example: docker logs CONTAINER_NAME Use the docker exec command to run /bin/sh and view the log file, for example: docker exec -it CONTAINER_NAME /bin/sh ; cat /var/log/CONTAINER_NAME.log Use the docker-compose logs command of Docker Compose, for example: docker-compose -f docker-com




