Java集合之Vector具体代码分析(图)
Vector是矢量队列,它继承了AbstractList,实现了List、 RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable接口。
Vector接口依赖图:
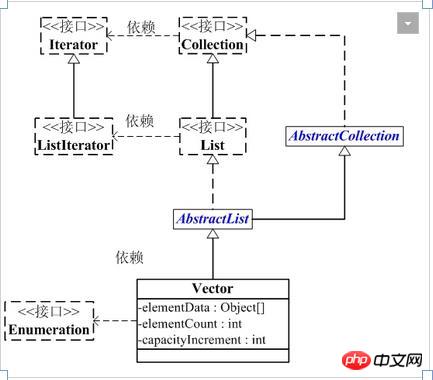
Vector继承了AbstractList,实现了List,它是一个队列,因此实现了相应的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。
Vector实现了RandomAccess接口,因此可以随机访问。
Vector实现了Cloneable,重载了clone()方法,因此可以进行克隆。
Vector实现了Serializable接口,因此可以进行序列化。
Vector的操作是线程安全的。
Vector的数据结构和ArrayList差不多,包含了3个成员变量:elementData,elementCount,capacityIncrement。
(1)elementData是Object[]的数组,初始大小为10,会不断的增长。
(2)elementCount是元素的个数。
(3)capacityIncrement是动态数组增长的系数。
Vector有四种遍历方式:
(1)第一种通过迭代器遍历,即通过Iterator去遍历
Integer value=Iterator iter=vector.iterator()(iter.hasNext())
{
value=(Interger)iter.next()}(2)第二种随机访问,通过索引进行遍历
Integer value=size=vector.size()(i=i<i++)
{
value=vector.get(i)}(3)第三种通过for循环的方式
Integer value=( Integer intevector)
{
value=inte}(4)第四种,Enumeration遍历
Integer value=Enumeration enu=vector.elements()(enu.hasMoreElements())
{
value=(Integer)enu.nextElement()}Vector示例代码:
Hello {
(String[] args) {
Vector vec = Vector()vec.add()vec.add()vec.add()vec.add()vec.add()vec.set()vec.add()System..println(+vec)System..println(+vec.indexOf())System..println(+vec.lastIndexOf())System..println(+vec.firstElement())System..println(+vec.elementAt())System..println(+vec.lastElement())System..println(+vec.size())System..println(+vec.capacity())System..println(+vec.subList())Enumeration enu = vec.elements()(enu.hasMoreElements())
{
System..println(+enu.nextElement()) Vector retainVec = Vector() retainVec.add() retainVec.add() System..println(+vec.retainAll(retainVec)) System..println(+vec) String[] arr = (String[]) vec.toArray(String[])(String str:arr)
System..println(+str) vec.clear() vec.removeAllElements() System..println(+vec.isEmpty()) }
}
}Vector源代码:
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
protected Object[] elementData;//对象数组,来存放数据
protected int elementCount; //当前的数据数目
protected int capacityIncrement; //容量增长
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L; //序列号
//构造函数矢量队列初始化大小和增长大小
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
//构造函数初始化大小
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
//构造函数默认初始化大小10
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
//带有集合参数的构造函数
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
//线程安全的对象数组拷贝
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
//调整容量大小适合当前矢量队列的大小
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
//增加矢量队列的容量大小
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
//调整大小,如果超出了就删掉多余的对象
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
//矢量对象的容量
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
//矢量队列的大小
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
//是否为空
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
//生成Enumeration对象,进行遍历
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return elementData(count++);
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
//判断是否包含某个对象
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
//返回某个对象的下标
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//最后出现的对象的坐标
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
//返回某个坐标的节点
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
//第一个元素
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(0);
}
//最后一个元素
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(elementCount - 1);
}
//对下标为index的元素替换为obj
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
//删除某个下标的元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
//在index坐标后添加obj
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
//矢量队列末尾添加元素
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
//删除obj元素
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj);
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//清空所有元素
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// Let gc do its work
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
elementCount = 0;
}
//克隆
public synchronized Object clone() {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<E> v = (Vector<E>) super.clone();
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
//生成数组
public synchronized Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < elementCount)
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, elementCount);
if (a.length > elementCount)
a[elementCount] = null;
return a;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
//得到index的元素
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
//将index元素替换成element
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
//矢量队列队尾添加元素
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
//删除对象
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
//在index处添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
insertElementAt(element, index);
}
//删除index处元素
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
//清空元素
public void clear() {
removeAllElements();
}
//判断Vector中是否含有所有的Collection
public synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.containsAll(c);
}
//将Collection添加到矢量队列的队尾
public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
//删除包含Collection的元素
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
}
//删除不存在Collection的元素
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
}
//在某个index之后追加集合
public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
modCount++;
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);
int numMoved = elementCount - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
elementCount += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
//判断矢量队列是否相同
public synchronized boolean equals(Object o) {
return super.equals(o);
}
//返回hashCode
public synchronized int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
//
public synchronized String toString() {
return super.toString();
}
//切断
public synchronized List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return Collections.synchronizedList(super.subList(fromIndex, toIndex),
this);
}
//删除范围
protected synchronized void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = elementCount - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved);
// Let gc do its work
int newElementCount = elementCount - (toIndex-fromIndex);
while (elementCount != newElementCount)
elementData[--elementCount] = null;
}
//序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
final java.io.ObjectOutputStream.PutField fields = s.putFields();
final Object[] data;
synchronized (this) {
fields.put("capacityIncrement", capacityIncrement);
fields.put("elementCount", elementCount);
data = elementData.clone();
}
fields.put("elementData", data);
s.writeFields();
}
//迭代
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
public synchronized ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
public synchronized Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
// Racy but within spec, since modifications are checked
// within or after synchronization in next/previous
return cursor != elementCount;
}
public E next() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= elementCount)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i + 1;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.remove(lastRet);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
synchronized (Vector.this) {
final int size = elementCount;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) Vector.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
action.accept(elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public E previous() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
cursor = i;
return elementData(lastRet = i);
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.set(lastRet, e);
}
}
public void add(E e) {
int i = cursor;
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.add(i, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int elementCount = this.elementCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < elementCount; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// figure out which elements are to be removed
// any exception thrown from the filter predicate at this stage
// will leave the collection unmodified
int removeCount = 0;
final int size = elementCount;
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
if (filter.test(element)) {
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
elementCount = newSize;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = elementCount;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, elementCount, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new VectorSpliterator<>(this, null, 0, -1, 0);
}
/** Similar to ArrayList Spliterator */
static final class VectorSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
private final Vector<E> list;
private Object[] array;
private int index; // current index, modified on advance/split
private int fence; // -1 until used; then one past last index
private int expectedModCount; // initialized when fence set
/** Create new spliterator covering the given range */
VectorSpliterator(Vector<E> list, Object[] array, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.array = array;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // initialize on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
synchronized(list) {
array = list.elementData;
expectedModCount = list.modCount;
hi = fence = list.elementCount;
}
}
return hi;
}
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null :
new VectorSpliterator<E>(list, array, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (getFence() > (i = index)) {
index = i + 1;
action.accept((E)array[i]);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
int i, hi; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
Vector<E> lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null) {
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
synchronized(lst) {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
a = array = lst.elementData;
hi = fence = lst.elementCount;
}
}
else
a = array;
if (a != null && (i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) {
while (i < hi)
action.accept((E) a[i++]);
if (lst.modCount == expectedModCount)
return;
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
}以上是Java集合之Vector具体代码分析(图)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP与Python:了解差异
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,选择应基于项目需求。1.PHP适合web开发,语法简单,执行效率高。2.Python适用于数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁,库丰富。
 PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:网络开发的关键语言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一种广泛应用于服务器端的脚本语言,特别适合web开发。1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,处理HTTP请求和响应,支持多种数据库。2.PHP用于生成动态网页内容,处理表单数据,访问数据库等,具有强大的社区支持和开源资源。3.PHP是解释型语言,执行过程包括词法分析、语法分析、编译和执行。4.PHP可以与MySQL结合用于用户注册系统等高级应用。5.调试PHP时,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函数。6.优化PHP代码可通过缓存机制、优化数据库查询和使用内置函数。7
 PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP与其他语言:比较
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP适合web开发,特别是在快速开发和处理动态内容方面表现出色,但不擅长数据科学和企业级应用。与Python相比,PHP在web开发中更具优势,但在数据科学领域不如Python;与Java相比,PHP在企业级应用中表现较差,但在web开发中更灵活;与JavaScript相比,PHP在后端开发中更简洁,但在前端开发中不如JavaScript。
 PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP与Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有优势,适合不同场景。1.PHP适用于web开发,提供内置web服务器和丰富函数库。2.Python适合数据科学和机器学习,语法简洁且有强大标准库。选择时应根据项目需求决定。
 PHP的影响:网络开发及以后
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP的影响:网络开发及以后
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP:许多网站的基础
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:许多网站的基础
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP成为许多网站首选技术栈的原因包括其易用性、强大社区支持和广泛应用。1)易于学习和使用,适合初学者。2)拥有庞大的开发者社区,资源丰富。3)广泛应用于WordPress、Drupal等平台。4)与Web服务器紧密集成,简化开发部署。
 PHP与Python:用例和应用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP与Python:用例和应用程序
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP适用于Web开发和内容管理系统,Python适合数据科学、机器学习和自动化脚本。1.PHP在构建快速、可扩展的网站和应用程序方面表现出色,常用于WordPress等CMS。2.Python在数据科学和机器学习领域表现卓越,拥有丰富的库如NumPy和TensorFlow。
 H5:工具,框架和最佳实践
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:11 AM
H5:工具,框架和最佳实践
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:11 AM
H5开发需要掌握的工具和框架包括Vue.js、React和Webpack。1.Vue.js适用于构建用户界面,支持组件化开发。2.React通过虚拟DOM优化页面渲染,适合复杂应用。3.Webpack用于模块打包,优化资源加载。






