python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6实现的一个计算器方法(附代码)
这篇文章主要介绍了python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6实现的一个计算器方法(附代码),在windows7 32位系统可以完美运行 计算器,有兴趣的可以了解一下。
目前可以实现简单的计算。计算前请重置,设计的时候默认数字是0,学了半天就做出来个这么个结果,bug不少。 python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6 在windows7 32位系统可以完美运行 计算器,简单学了半天就画个图实现的存在bug,部分按钮还未实现,后续优化。
代码结构如图:
jisuan.py
import re
#匹配整数或小数的乘除法,包括了开头存在减号的情况
mul_p=re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(\*|/)(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配整数或小数的加减法,包括了开头存在减号的情况
plus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(-|\+)(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配括号
bracket=re.compile("\([^()]*\)")
#匹配乘法的时候出现乘以负数的情况,包括了开头存在减号的情况
mul_minus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(\*-)(\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#匹配除法的时候出现乘以负数的情况,包括了开头存在减号的情况
p_minus_minus = re.compile("(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?(/-)(\d+)(\.\d+)?")
#定义一个两位数的加减乘除法的运算,匹配左边的右边的数字和左边的数字,然后进行计算
def touble_cale(str_expire):
if str_expire.count("+") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("+")+1):])
left_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("+")])
return str(right_num+left_num)
elif str_expire[1:].count("-") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("-",1)])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("-", 1) + 1):])
return str(right_num - left_num)
elif str_expire.count("*") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("*")])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("*")+1):])
return str(right_num * left_num)
elif str_expire.count("/") == 1:
right_num = float(str_expire[:str_expire.find("/")])
left_num = float(str_expire[(str_expire.find("/") + 1):])
return str(right_num / left_num)
#定义一个方法用于判断是否存在乘以负数和除以负数的情况
def judge_mul_minus(str_expire):
#判断公式中乘以负数的部分
if len(re.findall("(\*-)", str_expire)) != 0:
#调用上面的正则取得*-的公式
temp_mul_minus = mul_minus_minus.search(str_expire).group()
#将匹配的部分的*-换成*并将-放到前面
temp_mul_minus_2 = temp_mul_minus.replace(temp_mul_minus,"-" + temp_mul_minus.replace("*-","*"))
#经更改的的部分与原来的部分进行替换
str_expire=str_expire.replace(temp_mul_minus,temp_mul_minus_2)
return judge_mul_minus(str_expire)
#return str_expire
# 判断公式中除以负数的部分
elif len(re.findall(r"(/-)", str_expire)) != 0:
# 调用上面的正则取得/-的公式
temp_dev_minus = p_minus_minus.search(str_expire).group()
# 将匹配的部分的/-换成/并将-放到前面
temp_dev_minus_2 = temp_dev_minus.replace(temp_dev_minus,"-" + temp_dev_minus.replace("/-","/"))
# 经更改的的部分与原来的部分进行替换
str_expire = str_expire.replace(temp_dev_minus,temp_dev_minus_2)
return judge_mul_minus(str_expire)
#调用change_sign将公式中的++换成= +-换成-
return change_sign(str_expire)
#定义一个方法取将--更改为+ +-改为-
def change_sign(str_expire):
if len(re.findall(r"(\+-)", str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace("+-", "-")
return change_sign(str_expire)
elif len(re.findall(r"(--)", str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace("--", "+")
return change_sign(str_expire)
return str_expire
#定义一个方法用于计算只有加减乘除的公式,优先处理乘法
def cale_mix(str_expire):
#如果公式中出现符号数字的情况即+5 -6 *8 /8的这种情况直接放回数字否则则先计算乘除在处理加减
while len(re.findall("[-+*/]",str_expire[1:])) != 0:
if len(re.findall("(\*|/)",str_expire)) != 0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace(mul_p.search(str_expire).group(),touble_cale(mul_p.search(str_expire).group()))
elif len(re.findall("(\+|-)",str_expire)) !=0:
str_expire = str_expire.replace(plus_minus.search(str_expire).group(),touble_cale(plus_minus.search(str_expire).group()))
return str_expire
#定义一个方法用于去括号,并调用上述的方法进行计算
def remove_bracket(str_expire):
#判断公式中是否有括号
if len(bracket.findall(str_expire)) == 0:
return cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(str_expire))
elif len(bracket.findall(str_expire))!=0:
while len(bracket.findall(str_expire)) !=0:
#print(bracket.search(str_expire).group())
#只有存在括号优先处理括号中的内容并对内容进行替换,直到没有括号位置
str_expire = str_expire.replace(bracket.search(str_expire).group(),cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(bracket.search(str_expire).group()[1:-1])))
str_expire = cale_mix(judge_mul_minus(str_expire))
return str_expire
if name == "main":
while True:
user_input_expire = input("请输入你的公式:(不要带空格,q表示退出):")
print("%s=%s" %(user_input_expire,remove_bracket(user_input_expire)))
continueuntitled.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
from Ui_untitled import Ui_Dialog
from jisuan import remove_bracket
class Dialog(QDialog, Ui_Dialog):
def init(self, parent=None):
super(Dialog, self).init(parent)
self.setupUi(self)
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_6_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('6')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_2_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('2')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_3_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('3')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_pingfang_clicked(self):
me=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
m=int(me) *int(me)
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_add_clicked(self):
h=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h+'+')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_jian_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '-')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_9_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('9')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_chu_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '/')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_cheng_clicked(self):
h = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(h + '*')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_8_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('8')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_4_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('4')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_esc_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_7_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('7')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_1_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('1')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_5_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('5')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_xiaoshu_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('.')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_0_clicked(self):
self.Edit_xianshi.insertPlainText('0')
@pyqtSlot()
def on_Button_dengyu_clicked(self):
pe=self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
m=remove_bracket(pe)
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
def on_Button_fenzhi_clicked(self):
pe = self.Edit_xianshi.toPlainText()
if int(pe) ==0:
QMessageBox.information(self,u'提示',u'零不能作为分母')
Dialog()
else:
m=1/(int(pe))
self.Edit_xianshi.clear()
self.Edit_xianshi.append(str(m))
Dialog()
if name =="main":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
app.processEvents()
ui = Dialog()
ui.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())Ui_untitled.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\pyqt5\untitled.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.5
#
# WARNING! All changes made in this file will be lost!
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_Dialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setObjectName("Dialog")
Dialog.resize(357, 320)
Dialog.setStyleSheet("font: 75 16pt \"Aharoni\";\n"
"background-color: rgb(206, 255, 251);")
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel(Dialog)
self.label.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(201, 210, 301, 21))
self.label.setText("")
self.label.setObjectName("label")
self.Edit_xianshi = QtWidgets.QTextEdit(Dialog)
self.Edit_xianshi.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 351, 41))
self.Edit_xianshi.setStyleSheet("font: 75 16pt \"Aharoni\";")
self.Edit_xianshi.setObjectName("Edit_xianshi")
self.gridLayoutWidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(Dialog)
self.gridLayoutWidget.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 30, 351, 281))
self.gridLayoutWidget.setObjectName("gridLayoutWidget")
self.gridLayout = QtWidgets.QGridLayout(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.gridLayout.setObjectName("gridLayout")
self.Button_6 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_6.setObjectName("Button_6")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_6, 2, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_2.setObjectName("Button_2")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_2, 3, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_3 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_3.setObjectName("Button_3")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_3, 3, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_fenzhi = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_fenzhi.setObjectName("Button_fenzhi")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_fenzhi, 1, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_pingfang = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_pingfang.setObjectName("Button_pingfang")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_pingfang, 0, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_add = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_add.setObjectName("Button_add")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_add, 2, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_jian = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_jian.setObjectName("Button_jian")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_jian, 3, 3, 1, 1)
self.Button_9 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_9.setObjectName("Button_9")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_9, 1, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_chu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_chu.setObjectName("Button_chu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_chu, 0, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_cheng = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_cheng.setObjectName("Button_cheng")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_cheng, 0, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_8 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_8.setObjectName("Button_8")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_8, 1, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_4 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_4.setObjectName("Button_4")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_4, 2, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_esc = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_esc.setObjectName("Button_esc")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_esc, 0, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_7 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_7.setObjectName("Button_7")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_7, 1, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_1.setObjectName("Button_1")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_1, 3, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_5 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_5.setObjectName("Button_5")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_5, 2, 1, 1, 1)
self.pushButton_17 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.pushButton_17.setText("")
self.pushButton_17.setObjectName("pushButton_17")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.pushButton_17, 4, 0, 1, 1)
self.Button_xiaoshu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_xiaoshu.setObjectName("Button_xiaoshu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_xiaoshu, 4, 1, 1, 1)
self.Button_0 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_0.setStyleSheet("")
self.Button_0.setObjectName("Button_0")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_0, 4, 2, 1, 1)
self.Button_dengyu = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.gridLayoutWidget)
self.Button_dengyu.setObjectName("Button_dengyu")
self.gridLayout.addWidget(self.Button_dengyu, 4, 3, 1, 1)
self.retranslateUi(Dialog)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Dialog)
def retranslateUi(self, Dialog):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
Dialog.setWindowTitle(_translate("Dialog", "Dialog"))
self.Edit_xianshi.setHtml(_translate("Dialog", "<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/strict.dtd\">\n"
"<html><head><meta name=\"qrichtext\" content=\"1\" /><style type=\"text/css\">\n"
"p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }\n"
"</style></head><body style=\" font-family:\'Aharoni\'; font-size:16pt; font-weight:72; font-style:normal;\">\n"
"<p style=\" margin-top:0px; margin-bottom:0px; margin-left:0px; margin-right:0px; -qt-block-indent:0; text-indent:0px;\"><span style=\" font-family:\'SimSun\'; font-weight:400;\">0</span></p></body></html>"))
self.Button_6.setText(_translate("Dialog", "6"))
self.Button_2.setText(_translate("Dialog", "2"))
self.Button_3.setText(_translate("Dialog", "3"))
self.Button_fenzhi.setText(_translate("Dialog", "1/^"))
self.Button_pingfang.setText(_translate("Dialog", "^2"))
self.Button_add.setText(_translate("Dialog", "+"))
self.Button_jian.setText(_translate("Dialog", "-"))
self.Button_9.setText(_translate("Dialog", "9"))
self.Button_chu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "/"))
self.Button_cheng.setText(_translate("Dialog", "*"))
self.Button_8.setText(_translate("Dialog", "8"))
self.Button_4.setText(_translate("Dialog", "4"))
self.Button_esc.setText(_translate("Dialog", "esc"))
self.Button_7.setText(_translate("Dialog", "7"))
self.Button_1.setText(_translate("Dialog", "1"))
self.Button_5.setText(_translate("Dialog", "5"))
self.Button_xiaoshu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "."))
self.Button_0.setText(_translate("Dialog", "0"))
self.Button_dengyu.setText(_translate("Dialog", "="))
if name == "main":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
Dialog = QtWidgets.QDialog()
ui = Ui_Dialog()
ui.setupUi(Dialog)
Dialog.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())效果图:
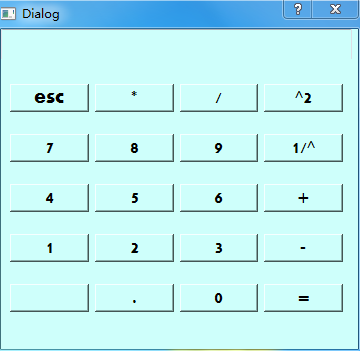
以上是python3.5 + PyQt5 +Eric6实现的一个计算器方法(附代码)的详细内容。更多信息请关注PHP中文网其他相关文章!

热AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智能驱动的应用程序,用于创建逼真的裸体照片

AI Clothes Remover
用于从照片中去除衣服的在线人工智能工具。

Undress AI Tool
免费脱衣服图片

Clothoff.io
AI脱衣机

Video Face Swap
使用我们完全免费的人工智能换脸工具轻松在任何视频中换脸!

热门文章

热工具

记事本++7.3.1
好用且免费的代码编辑器

SublimeText3汉化版
中文版,非常好用

禅工作室 13.0.1
功能强大的PHP集成开发环境

Dreamweaver CS6
视觉化网页开发工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神级代码编辑软件(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解释了不同的范例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解释了不同的范例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是过程式编程,但也支持面向对象编程(OOP);Python支持多种范式,包括OOP、函数式和过程式编程。PHP适合web开发,Python适用于多种应用,如数据分析和机器学习。
 在PHP和Python之间进行选择:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之间进行选择:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP适合网页开发和快速原型开发,Python适用于数据科学和机器学习。1.PHP用于动态网页开发,语法简单,适合快速开发。2.Python语法简洁,适用于多领域,库生态系统强大。
 sublime怎么运行代码python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
sublime怎么运行代码python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
在 Sublime Text 中运行 Python 代码,需先安装 Python 插件,再创建 .py 文件并编写代码,最后按 Ctrl B 运行代码,输出会在控制台中显示。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他们的历史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他们的历史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源于1994年,由RasmusLerdorf开发,最初用于跟踪网站访问者,逐渐演变为服务器端脚本语言,广泛应用于网页开发。Python由GuidovanRossum于1980年代末开发,1991年首次发布,强调代码可读性和简洁性,适用于科学计算、数据分析等领域。
 Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:学习曲线和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更适合初学者,学习曲线平缓,语法简洁;JavaScript适合前端开发,学习曲线较陡,语法灵活。1.Python语法直观,适用于数据科学和后端开发。2.JavaScript灵活,广泛用于前端和服务器端编程。
 Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸缩性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸缩性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang在性能和可扩展性方面优于Python。1)Golang的编译型特性和高效并发模型使其在高并发场景下表现出色。2)Python作为解释型语言,执行速度较慢,但通过工具如Cython可优化性能。
 vscode在哪写代码
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
vscode在哪写代码
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
在 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)中编写代码简单易行,只需安装 VSCode、创建项目、选择语言、创建文件、编写代码、保存并运行即可。VSCode 的优点包括跨平台、免费开源、强大功能、扩展丰富,以及轻量快速。
 notepad 怎么运行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
notepad 怎么运行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
在 Notepad 中运行 Python 代码需要安装 Python 可执行文件和 NppExec 插件。安装 Python 并为其添加 PATH 后,在 NppExec 插件中配置命令为“python”、参数为“{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}”,即可在 Notepad 中通过快捷键“F6”运行 Python 代码。






