C#基礎知識整理 基礎知識(16) IList介面-非泛型
了解了ICollection介面、迭代以及泛型集合,下面再詳細了解IList介面。
透過MSDN可以看到IList介面有兩種:
元素為object類型的IList接口,可以放不同類型的物件參考;
IList
其實,IList和IList
可以看到IList和IList
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)] public interface IList : ICollection, IEnumerable public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
現在再返回去看下,IList和IList
public class IListClass
{
void test()
{
TestClass1 c1 = null;
ArrayList arryList = new ArrayList();
arryList.Add(c1);
List<TestClass1> list = new List<TestClass1>();
list.Add(c1);
//取值
TestClass1 getC1Array = arryList[0] as TestClass1;//必须要一次强制转换
TestClass1 getC1List = list[0];//不需要转换,所谓泛型
}
}
public class TestClass1
{
}這下就比較明白了。
一、IList介面概述
ILis介面從ICollection介面繼承,具備下列特性,
Count屬性-取得集合元素數量;
GetEnumerator方法-可迭代;
CopyTo方法-將指定元素複製到另一個陣列中;
Clear方法-清空整個集合。
IList新增特性,
索引器屬性-依據索引存取集合中任意元素;
Add方法-將元素新增至集合末端;
Insert方法-向集合指定位置插入元素;
Remove方法-移除指定元素;(包括RemoveAt)
Contains方法-判斷物件是否在集合中;
IndexOf方法-找出指定物件在集合中的索引位置。
另外,IList介面集合依序存放元素,不改變元素存放順序。
2、演算法
向量集合和陣列一樣,具備隨即存取的特性。即無論存取向量集合的任何一個單元,所需的存取時間是完全相同的。在向量類別中,實際上依然使用普通數組來記錄集合數據,向量類別使用了一些演算法技巧,讓整個類別對外表現不同於普通數組的重要特徵:可以動態改變數組長度。具體演算法如下:
在內部數組足夠長的情況下,直接進行添加和插入操作,在內部數組長度不足的情況下,按照內部數組長度增加2倍作為新的數組的長度,然後進行資料搬移(即把就數組數組移到新數組中)。向量在分配元素儲存空間時,會多分配一些冗餘空間,盡量減少記憶體分配次數。在資料刪除時,並不會改變內部數組長度,只是使用被刪除資料之後的資料覆蓋被刪除的資料。
不過向量每次分配空間時都多分配一些冗餘空間,會造成記憶體的壓力,因此在程式中應該盡量避免集中的次數繁多的記憶體分配。
三、實作類別
IList和IList
ArrayList類別處於System.Collection命名空間下;
List
四、實作程式碼(非泛型)
/// <summary>
/// 实现IList,非泛型
/// </summary>
public class ArrayList : IList
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代
/// </summary>
public struct Enumertor : IEnumerator
{
/// <summary>
/// 迭代索引
/// </summary>
private int index;
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器所属的向量类对象的引用
/// </summary>
private ArrayList arrayList;
/// <summary>
/// 构造函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="arrayList">迭代器所属的集合类</param>
public Enumertor(ArrayList arrayList)
{
this.arrayList = arrayList;
this.index = -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取当前对象,根据index的值返回向量对应的对象引用
/// </summary>
public object Current
{
get
{
return arrayList[index];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 将迭代器指向下一个数据位置,通过改变index的值,加1或减1
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (this.index < arrayList.Count)
{
++this.index;
}
return this.index < arrayList.Count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 迭代器回到起始位置,将index置为-1
/// </summary>
public void Reset()
{
this.index = -1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保存集合的数组
/// </summary>
private object[] array = new object[1];
/// <summary>
/// 当前集合的长度
/// </summary>
private int count;
/// <summary>
/// 默认构造函数
/// </summary>
public ArrayList()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// 参数构造函数,通过参数指定内部数组长度,减少重新分配空间
/// </summary>
/// <param name="capacity"></param>
public ArrayList(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
if (capacity == 0)
{
capacity = 1;
}
this.array = new object[capacity];
this.count = 0;
}
public int Count
{
get
{
return this.count;//该属性只读
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 集合实际使用长度
/// </summary>
public int Capacity
{
get
{
return this.array.Length;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否固定大小
/// </summary>
public bool IsFixedSize
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否只读集合
/// </summary>
public bool IsReadOnly
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 是否同步,即是否支持多线程访问
/// </summary>
public bool IsSynchronized
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 同步对象
/// </summary>
public object SyncRoot
{
get
{
return null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 当array长度不足时,重新分配新的长度足够的数组
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private object[] GetNewArray()
{
return new object[(this.array.Length + 1) * 2];
}
public int Add(object value)
{
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)//长度不足
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
this.array = newArray;//重新引用,指向新数组
}
//增加新元素
this.array[this.count] = value;
this.count = newCount;
//返回新元素的索引位置
return this.count - 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 索引器属性,按索引返回向量中的某一项
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
return this.array[index];
}
set
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
this.array[index] = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除集合中的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="count"></param>
public void RemoveRange(int index, int count)
{
if (index < 0)
{
throw new Exception();
}
int removeIndex = index + count;//计算集合中最后一个被删元素的索引
if (count < 0 || removeIndex > this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//删除其实是将要删除元素之后的所有元素拷贝到要删除元素的位置覆盖掉
Array.Copy(this.array, index + 1, this.array, index + count - 1, this.count - removeIndex);
//重新设置集合长度
this.count -= count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查找对应的数组项,实际是遍历查找
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int IndexOf(object value)
{
int index = 0;
if (value == null)
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index] == null)
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
else
{
while (index < this.count)
{
if (this.array[index].Equals(value))
{
return index;
}
++index;
}
}
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Remove(object value)
{
int index = this.IndexOf(value);
if (index >= 0)
{
this.RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 从集合中删除指定位置的元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void RemoveAt(int index)
{
RemoveRange(index, 1);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取最后一个元素的引用后删除最后一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PopBack()
{
object obj = this.array[this.count - 1];
RemoveAt(this.count - 1);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取第一个元素引用并删除第一个元素
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object PropFront()
{
object obj = this.array[0];
RemoveAt(0);
return obj;
}
/// <summary>
/// 插入元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="index"></param>
/// <param name="value"></param>
public void Insert(int index, object value)
{
if (index >= this.count)
{
throw new Exception();
}
//插入元素当空间不足时也是声明新的2倍长度数组,并拷贝旧数据。
//插入数据原理是,将指定位置后的数据全部后移,再将新数据放在指定位置。
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (this.array.Length < newCount)
{
object[] newArray = GetNewArray();
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, index);
this.array = newArray;
}
Array.Copy(this.array, index, this.array, index + 1, this.count - index);
this.array[index] = value;
this.count = newCount;
}
/// <summary>
/// 查看当前集合是否包含指定对象
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Contains(object value)
{
return this.IndexOf(value) >= 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 将集合的长度改变为实际长度
/// </summary>
public void TrimToSize()
{
//为了消除Add和Insert时增加的冗余,原理是新生成一个和实际长度相同的数组,然后将值全部移过来。
if (this.array.Length > this.count)
{
object[] newArray = null;
if (this.count > 0)
{
newArray = new object[this.count];
Array.Copy(this.array, newArray, this.count);
}
else
{
newArray = new object[1];
}
this.array = newArray;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 清空集合
/// </summary>
public void Clear()
{
this.count = 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取集合的迭代器
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
Enumertor enumerator = new Enumertor(this);
return enumerator;
}
/// <summary>
/// 转移集合元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetArray"></param>
/// <param name="index"></param>
public void CopyTo(Array targetArray, int index)
{
Array.Copy(this.array, 0, targetArray, index, this.count);
}
}
呼叫測試:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//调用测试
ArrayList myArrayList = new ArrayList();
myArrayList.Add(40);
myArrayList.Add(80);
myArrayList.Add("Hello");
//使用for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < myArrayList.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myArrayList[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
//使用迭代循环
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Insert(1, "Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Remove("Insert");
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.RemoveAt(1);
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
myArrayList.Clear();
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
myArrayList.Add(rand.Next(10));
}
foreach (object obj in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.WriteLine("---------------------");
Console.WriteLine("集合是否包含为1的元素 ? " + (myArrayList.Contains(0) ? "包含" : "不包含"));
Console.WriteLine("元素1的位置 " + myArrayList.IndexOf(1));
Console.ReadLine();
}結果: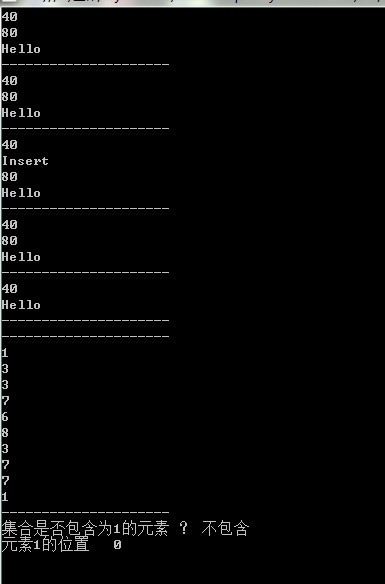
結果:

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 c#.net的持續相關性:查看當前用法
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
c#.net的持續相關性:查看當前用法
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C#.NET依然重要,因為它提供了強大的工具和庫,支持多種應用開發。 1)C#結合.NET框架,使開發高效便捷。 2)C#的類型安全和垃圾回收機制增強了其優勢。 3).NET提供跨平台運行環境和豐富的API,提升了開發靈活性。
 C#作為多功能.NET語言:應用程序和示例
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:26 AM
C#作為多功能.NET語言:應用程序和示例
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:26 AM
C#在企業級應用、遊戲開發、移動應用和Web開發中均有廣泛應用。 1)在企業級應用中,C#常用於ASP.NETCore開發WebAPI。 2)在遊戲開發中,C#與Unity引擎結合,實現角色控制等功能。 3)C#支持多態性和異步編程,提高代碼靈活性和應用性能。
 將C#.NET應用程序部署到Azure/AWS:逐步指南
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:06 AM
將C#.NET應用程序部署到Azure/AWS:逐步指南
Apr 23, 2025 am 12:06 AM
如何將C#.NET應用部署到Azure或AWS?答案是使用AzureAppService和AWSElasticBeanstalk。 1.在Azure上,使用AzureAppService和AzurePipelines自動化部署。 2.在AWS上,使用AmazonElasticBeanstalk和AWSLambda實現部署和無服務器計算。
 C#和.NET運行時:它們如何一起工作
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AM
C#和.NET運行時:它們如何一起工作
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AM
C#和.NET運行時緊密合作,賦予開發者高效、強大且跨平台的開發能力。 1)C#是一種類型安全且面向對象的編程語言,旨在與.NET框架無縫集成。 2).NET運行時管理C#代碼的執行,提供垃圾回收、類型安全等服務,確保高效和跨平台運行。
 C#.NET:使用.NET生態系統構建應用程序
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:12 AM
C#.NET:使用.NET生態系統構建應用程序
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:12 AM
如何利用.NET構建應用?使用.NET構建應用可以通過以下步驟實現:1)了解.NET基礎知識,包括C#語言和跨平台開發支持;2)學習核心概念,如.NET生態系統的組件和工作原理;3)掌握基本和高級用法,從簡單控制台應用到復雜的WebAPI和數據庫操作;4)熟悉常見錯誤與調試技巧,如配置和數據庫連接問題;5)應用性能優化與最佳實踐,如異步編程和緩存。
 .NET框架與C#:解碼術語
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
.NET框架與C#:解碼術語
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
.NETFramework是一個軟件框架,C#是一種編程語言。 1..NETFramework提供庫和服務,支持桌面、Web和移動應用開發。 2.C#設計用於.NETFramework,支持現代編程功能。 3..NETFramework通過CLR管理代碼執行,C#代碼編譯成IL後由CLR運行。 4.使用.NETFramework可快速開發應用,C#提供如LINQ的高級功能。 5.常見錯誤包括類型轉換和異步編程死鎖,調試需用VisualStudio工具。
 C#.NET開發:入門的初學者指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:17 AM
C#.NET開發:入門的初學者指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:17 AM
要開始C#.NET開發,你需要:1.了解C#的基礎知識和.NET框架的核心概念;2.掌握變量、數據類型、控制結構、函數和類的基本概念;3.學習C#的高級特性,如LINQ和異步編程;4.熟悉常見錯誤的調試技巧和性能優化方法。通過這些步驟,你可以逐步深入C#.NET的世界,並編寫高效的應用程序。
 c#和.net:了解兩者之間的關係
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:07 AM
c#和.net:了解兩者之間的關係
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:07 AM
C#和.NET的關係是密不可分的,但它們不是一回事。 C#是一門編程語言,而.NET是一個開發平台。 C#用於編寫代碼,編譯成.NET的中間語言(IL),由.NET運行時(CLR)執行。






