cocos2dx A*算法
头文件和源文件复制到项目中就能用了! have fun 使用cocos2dx 3.2 原理都一样 淡蓝色的点是地图 深蓝色的点是障碍物 绿色的点是路径 暗绿色的点是搜寻过的点 红色的点是按路径行走的点 dijkstra算法 会发现路径最短,但寻找过的路径比较多(计算速度慢) 最佳优
头文件和源文件复制到项目中就能用了! have fun
使用cocos2dx 3.2 原理都一样
淡蓝色的点是地图
深蓝色的点是障碍物
绿色的点是路径
暗绿色的点是搜寻过的点
红色的点是按路径行走的点
dijkstra算法 会发现路径最短,但寻找过的路径比较多(计算速度慢)

最佳优先搜索算法会发现寻找过的路径少了(计算速度提高了),但走了许多弯路

A星算法 结合了上面2种算法 即寻找到了最短路径, 搜寻过的路径也比较少

#ifndef __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__
#define __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__
#include "cocos2d.h"
#include "vector"
using namespace std;
USING_NS_CC;
class PathSprite : public cocos2d::Sprite//继承Sprite类, 因为要在里面加些其他变量
{
PathSprite():Sprite()
{
m_parent = NULL;
m_child = NULL;
m_costToSource = 0;
m_FValue = 0;
};
public:
static PathSprite* create(const char* ch)
{
PathSprite *pRet = new PathSprite();
if (pRet )
{
pRet->initWithFile(ch);
pRet->autorelease();
return pRet;
}
else
{
delete pRet;
pRet = NULL;
return NULL;
}
}
PathSprite* m_parent;//父节点
PathSprite* m_child;//子节点
float m_costToSource;//到起始点的距离
int m_x;//地图坐标
int m_y;
float m_FValue;
};
class PathSearchInfo//寻路类(主要负责寻路的参数和逻辑)
{
public:
static int m_startX;//开始点
static int m_startY;
static int m_endX;//结束点
static int m_endY;
static vector<pathsprite> m_openList;//开放列表(里面存放相邻节点)
static vector<pathsprite> m_inspectList;//检测列表(里面存放除了障碍物的节点)
static vector<pathsprite> m_pathList;//路径列表
static void barrierTest( vector<pathsprite> &pathList,int x, int y)//模拟障碍物
{
PathSprite* _z = getObjByPointOfMapCoord(pathList, x, y);
if (_z)
{
_z->setColor(ccColor3B::MAGENTA);
removeObjFromList(pathList, _z);
}
}
static float calculateTwoObjDistance(PathSprite* obj1, PathSprite* obj2)//计算两个物体间的距离
{
// float _offsetX = obj1->m_x - obj2->m_x;
// float _offsetY = obj1->m_y - obj2->m_y;
// return sqrt( _offsetX * _offsetX + _offsetY * _offsetY);
float _x = abs(obj2->m_x - obj1->m_x);
float _y = abs(obj2->m_y - obj1->m_y);
return _x + _y;
}
static void inspectTheAdjacentNodes(PathSprite* node, PathSprite* adjacent, PathSprite* endNode)//把相邻的节点放入开放节点中
{
if (adjacent)
{
float _x = abs(endNode->m_x - adjacent->m_x);
float _y = abs(endNode->m_y - adjacent->m_y);
float F , G, H1, H2, H3;
adjacent->m_costToSource = node->m_costToSource + calculateTwoObjDistance(node, adjacent);//获得累计的路程
G = adjacent->m_costToSource;
//三种算法, 感觉H2不错
H1 = _x + _y;
H2 = hypot(_x, _y);
H3 = max(_x, _y);
#if 1 //A*算法 = Dijkstra算法 + 最佳优先搜索
F = G + H2;
#endif
#if 0//Dijkstra算法
F = G;
#endif
#if 0//最佳优先搜索
F = H2;
#endif
adjacent->m_FValue = F;
adjacent->m_parent = node;//设置父节点
adjacent->setColor(Color3B::ORANGE);//搜寻过的节点设为橘色
node->m_child = adjacent;//设置子节点
PathSearchInfo::removeObjFromList(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, adjacent);//把检测过的点从检测列表中删除
PathSearchInfo::m_openList.push_back(adjacent);//加入开放列表
}
}
static PathSprite* getMinPathFormOpenList()//从开放节点中获取路径最小值
{
if (m_openList.size()>0) {
PathSprite* _sp =* m_openList.begin();
for (vector<pathsprite>::iterator iter = m_openList.begin(); iter != m_openList.end(); iter++)
{
if ((*iter)->m_FValue m_FValue)
{
_sp = *iter;
}
}
return _sp;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}
static PathSprite* getObjByPointOfMapCoord( vector<pathsprite> &spriteVector, int x, int y)//根据点获取对象
{
for (int i = 0; i m_x == x && spriteVector[i]->m_y == y)
{
return spriteVector[i];
}
}
return NULL;
}
static bool removeObjFromList(vector<pathsprite> &spriteVector, PathSprite* sprite)//从容器中移除对象
{
for (vector<pathsprite>::iterator iter = spriteVector.begin(); iter != spriteVector.end(); iter++)
{
if (*iter == sprite)
{
spriteVector.erase(iter);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
class HelloWorld : public cocos2d::Layer
{
public:
// there's no 'id' in cpp, so we recommend returning the class instance pointer
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
// Here's a difference. Method 'init' in cocos2d-x returns bool, instead of returning 'id' in cocos2d-iphone
virtual bool init();
// a selector callback
void menuCloseCallback(cocos2d::Ref* pSender);
// implement the "static create()" method manually
CREATE_FUNC(HelloWorld);
bool onTouchBegan(Touch* touch, Event* event);
void onTouchMoved(Touch* touch, Event* event);
void onTouchEnded(Touch* touch, Event* event);
void calculatePath();//计算路径
void drawPath();//绘制路径
vector<pathsprite> m_mapList;//地图
void clearPath();//清理路径
PathSprite* m_player;//人物 用于演示行走
int m_playerMoveStep;//人物当前的行程
void playerMove();//人物走动
};
#endif // __HELLOWORLD_SCENE_H__
</pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite>#include "HelloWorldScene.h"
vector<pathsprite> PathSearchInfo::m_openList;
vector<pathsprite> PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList;
vector<pathsprite> PathSearchInfo::m_pathList;
int PathSearchInfo::m_startX;
int PathSearchInfo::m_startY;
int PathSearchInfo::m_endX;
int PathSearchInfo::m_endY;
Scene* HelloWorld::createScene()
{
// 'scene' is an autorelease object
auto scene = Scene::create();
// 'layer' is an autorelease object
auto layer = HelloWorld::create();
// add layer as a child to scene
scene->addChild(layer);
// return the scene
return scene;
}
// on "init" you need to initialize your instance
bool HelloWorld::init()
{
//////////////////////////////
// 1. super init first
if ( !Layer::init() )
{
return false;
}
Size visibleSize = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleSize();
Vec2 origin = Director::getInstance()->getVisibleOrigin();
Size winSize = Director::getInstance()->getWinSize();
/////////////////////////////
// 2. add a menu item with "X" image, which is clicked to quit the program
// you may modify it.
// add a "close" icon to exit the progress. it's an autorelease object
auto listener = EventListenerTouchOneByOne::create();
listener->setSwallowTouches(true);
listener->onTouchBegan = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchBegan, this);
listener->onTouchMoved = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchMoved, this);
listener->onTouchEnded = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchEnded, this);
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
//模拟一张地图 左上角 为(0,0) 主要是模拟tiledmap 每块的宽度为1
int _width = 25;
int _heigth = 15;
for (int i = 0; i m_x = j;
_sp->m_y = i;
Size _size = _sp->getContentSize();
_sp->setPosition(CCPoint(j * _size.width + 100, - i * _size.height + 600));
m_mapList.push_back(_sp);
this->addChild(_sp);
}
}
//设置障碍物
// for (int i = 0; i removeFromParent();
//设置起始和终点
PathSearchInfo::m_startX =0;
PathSearchInfo::m_startY = 0;
PathSearchInfo::m_endX = 4;
PathSearchInfo::m_endY = 9;
m_player = PathSprite::create("CloseSelected1.png");
m_player->setColor(Color3B::RED);
this->addChild(m_player);
m_player->m_x = PathSearchInfo::m_startX;
m_player->m_y = PathSearchInfo::m_startY;
m_player->setPosition(PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(m_mapList, PathSearchInfo::m_startX, PathSearchInfo::m_startY)->getPosition());
return true;
}
void HelloWorld::calculatePath()
{
//得到开始点的节点
PathSprite* _sp = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, PathSearchInfo::m_startX, PathSearchInfo::m_startY);
//得到开始点的节点
PathSprite* _endNode = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, PathSearchInfo::m_endX, PathSearchInfo::m_endY);
//因为是开始点 把到起始点的距离设为0
_sp->m_costToSource = 0;
_sp->m_FValue = 0;
//把已经检测过的点从检测列表中删除
PathSearchInfo::removeObjFromList(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _sp);
//然后加入开放列表
PathSearchInfo::m_openList.push_back(_sp);
PathSprite* _node = NULL;
while (true)
{
//得到离起始点最近的点
_node = PathSearchInfo::getMinPathFormOpenList();
if (!_node)
{
//找不到路径
break;
}
//把计算过的点从开放列表中删除
PathSearchInfo::removeObjFromList(PathSearchInfo::m_openList, _node);
int _x = _node->m_x;
int _y = _node->m_y;
//
if (_x ==PathSearchInfo::m_endX && _y == PathSearchInfo::m_endY)
{
break;
}
//检测8个方向的相邻节点是否可以放入开放列表中
PathSprite* _adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x + 1, _y + 1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x +1, _y);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x +1, _y-1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x , _y -1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x -1, _y - 1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x -1, _y);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x -1, _y+1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
_adjacent = PathSearchInfo::getObjByPointOfMapCoord(PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList, _x , _y+1);
PathSearchInfo::inspectTheAdjacentNodes(_node, _adjacent, _endNode);
}
while (_node)
{
//PathSprite* _sp = node;
PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.insert(PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.begin(), _node);
_node = _node->m_parent;
}
}
void HelloWorld::drawPath( )
{
for (vector<pathsprite>::iterator iter = PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.begin(); iter != PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.end(); iter++)
{
(*iter)->setColor(ccColor3B::GREEN);
}
}
bool HelloWorld::onTouchBegan(Touch* touch, Event* event)
{
//清除之前的路径
clearPath();
auto nodePosition = convertToNodeSpace( touch->getLocation() );
log("%f, %f", nodePosition.x, nodePosition.y);
for (int i = 0; i getBoundingBox().containsPoint(nodePosition))
{
//获取触摸点, 设置为终点
PathSearchInfo::m_endX = _sp->m_x;
PathSearchInfo::m_endY = _sp->m_y;
//计算路径
calculatePath();
//绘制路径
drawPath( );
playerMove();
}
}
return true;
}
void HelloWorld::onTouchMoved(Touch* touch, Event* event)
{
// If it weren't for the TouchDispatcher, you would need to keep a reference
// to the touch from touchBegan and check that the current touch is the same
// as that one.
// Actually, it would be even more complicated since in the Cocos dispatcher
// you get Sets instead of 1 UITouch, so you'd need to loop through the set
// in each touchXXX method.
}
void HelloWorld::onTouchEnded(Touch* touch, Event* event)
{
}
void HelloWorld::menuCloseCallback(Ref* pSender)
{
#if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WP8) || (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WINRT)
MessageBox("You pressed the close button. Windows Store Apps do not implement a close button.","Alert");
return;
#endif
Director::getInstance()->end();
#if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_IOS)
exit(0);
#endif
}
void HelloWorld::clearPath()
{
for (vector<pathsprite>::iterator iter = m_mapList.begin(); iter != m_mapList.end(); iter++)
{
(*iter)->setColor(ccColor3B::WHITE);
(*iter)->m_costToSource = 0;
(*iter)->m_FValue = 0;
(*iter)->m_parent = NULL;
(*iter)->m_child = NULL;
}
//把移除了障碍物的地图放入检测列表中
PathSearchInfo::m_inspectList = m_mapList;
PathSearchInfo::m_openList.clear();
PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.clear();
PathSearchInfo::m_startX = m_player->m_x;
PathSearchInfo::m_startY = m_player->m_y;
m_player->stopAllActions();
m_playerMoveStep = 0;
}
void HelloWorld::playerMove()
{
m_playerMoveStep++;
if (m_playerMoveStep >= PathSearchInfo::m_pathList.size()) {
return;
}
m_player->m_x = PathSearchInfo::m_pathList[m_playerMoveStep]->m_x;
m_player->m_y = PathSearchInfo::m_pathList[m_playerMoveStep]->m_y;
m_player->runAction(Sequence::create(MoveTo::create(0.2, PathSearchInfo::m_pathList[m_playerMoveStep]->getPosition()), CallFunc::create(this, SEL_CallFunc(&HelloWorld::playerMove)) , NULL));
}
</pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite></pathsprite>
ホットAIツール

Undresser.AI Undress
リアルなヌード写真を作成する AI 搭載アプリ

AI Clothes Remover
写真から衣服を削除するオンライン AI ツール。

Undress AI Tool
脱衣画像を無料で

Clothoff.io
AI衣類リムーバー

Video Face Swap
完全無料の AI 顔交換ツールを使用して、あらゆるビデオの顔を簡単に交換できます。

人気の記事

ホットツール

メモ帳++7.3.1
使いやすく無料のコードエディター

SublimeText3 中国語版
中国語版、とても使いやすい

ゼンドスタジオ 13.0.1
強力な PHP 統合開発環境

ドリームウィーバー CS6
ビジュアル Web 開発ツール

SublimeText3 Mac版
神レベルのコード編集ソフト(SublimeText3)

ホットトピック
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1424
1424
 52
52
 1322
1322
 25
25
 1270
1270
 29
29
 1250
1250
 24
24
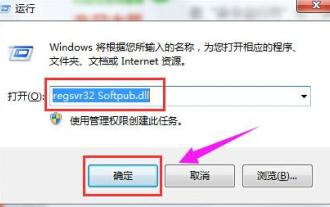 0x80004005 エラー コードが表示された場合の対処方法 エディターは、0x80004005 エラー コードを解決する方法を説明します。
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
0x80004005 エラー コードが表示された場合の対処方法 エディターは、0x80004005 エラー コードを解決する方法を説明します。
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
パソコン上のフォルダーを削除または解凍するときに、「エラー 0x80004005: 不明なエラー」というダイアログ ボックスが表示されることがあります。この状況はどう解決すればよいでしょうか?エラー コード 0x80004005 が表示される理由は実際にはたくさんありますが、そのほとんどはウイルスによって引き起こされます。DLL を再登録して問題を解決できます。以下では、エディターがエラー コード 0x80004005 の処理体験を説明します。 。一部のユーザーは、コンピュータの使用時にエラー コード 0X80004005 を表示されます。0x80004005 エラーは主に、コンピュータが特定のダイナミック リンク ライブラリ ファイルを正しく登録していないこと、またはファイアウォールがコンピュータとインターネット間の HTTPS 接続を許可していないことが原因で発生します。それでどうですか
 QQ Music から歌詞をコピーする方法 歌詞をコピーする方法
Mar 12, 2024 pm 08:22 PM
QQ Music から歌詞をコピーする方法 歌詞をコピーする方法
Mar 12, 2024 pm 08:22 PM
私たちユーザーは、このプラットフォームを使用する際にいくつかの機能の多様性を理解できるはずであり、いくつかの曲の歌詞は非常によく書かれていることがわかります。何度か聞いて、とても深い意味を感じることもあるので、意味を理解したい場合は、そのままコピーしてコピーライティングとして使いたくなりますが、使いたい場合は、まだ必要です 歌詞をコピーする方法を学ぶ必要があります 誰もがこれらの操作に慣れていると思いますが、携帯電話での操作は確かに少し難しいです。 そこで、よりよく理解するために、今日は編集者がは、あなたを助けるためにここにあります。上記の操作エクスペリエンスのいくつかをわかりやすく説明しています。もし気に入ったら、エディターと一緒に見に来てください。お見逃しなく。
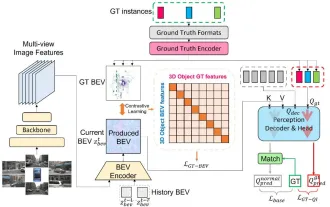 CLIP-BEVFormer: BEVFormer 構造を明示的に監視して、ロングテール検出パフォーマンスを向上させます。
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: BEVFormer 構造を明示的に監視して、ロングテール検出パフォーマンスを向上させます。
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
上記および筆者の個人的な理解: 現在、自動運転システム全体において、認識モジュールが重要な役割を果たしている。道路を走行する自動運転車は、認識モジュールを通じてのみ正確な認識結果を得ることができる。下流の規制および制御モジュール自動運転システムでは、タイムリーかつ正確な判断と行動決定が行われます。現在、自動運転機能を備えた自動車には通常、サラウンドビューカメラセンサー、ライダーセンサー、ミリ波レーダーセンサーなどのさまざまなデータ情報センサーが搭載されており、さまざまなモダリティで情報を収集して正確な認識タスクを実現しています。純粋な視覚に基づく BEV 認識アルゴリズムは、ハードウェア コストが低く導入が容易であるため、業界で好まれており、その出力結果はさまざまな下流タスクに簡単に適用できます。
 Quark Cloud Disk から Baidu Cloud Disk にファイルを転送するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
Quark Cloud Disk から Baidu Cloud Disk にファイルを転送するにはどうすればよいですか?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
Quark Netdisk と Baidu Netdisk は現在、ファイルの保存に最も一般的に使用されている Netdisk ソフトウェアです。Quark Netdisk 内のファイルを Baidu Netdisk に保存したい場合は、どうすればよいですか?今回は、Quark Network Disk コンピュータから Baidu Network Disk にファイルを転送するためのチュートリアル手順を編集者がまとめたので、その操作方法を見てみましょう。 QuarkネットワークディスクファイルをBaiduネットワークディスクに保存するにはどうすればよいですか? Quark Network Disk から Baidu Network Disk にファイルを転送するには、まず Quark Network Disk から必要なファイルをダウンロードし、次に Baidu Network Disk クライアントでターゲット フォルダーを選択して開きます。次に、Quark Cloud Disk からダウンロードしたファイルを Baidu Cloud Disk クライアントによって開かれたフォルダーにドラッグ アンド ドロップするか、アップロード機能を使用してファイルを Baidu Cloud Disk に追加します。アップロードが完了したら、Baidu Cloud Disk にファイルが正常に転送されたかどうかを必ず確認してください。それでおしまい
 C++ での機械学習アルゴリズムの実装: 一般的な課題と解決策
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
C++ での機械学習アルゴリズムの実装: 一般的な課題と解決策
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
C++ の機械学習アルゴリズムが直面する一般的な課題には、メモリ管理、マルチスレッド、パフォーマンスの最適化、保守性などがあります。解決策には、スマート ポインター、最新のスレッド ライブラリ、SIMD 命令、サードパーティ ライブラリの使用、コーディング スタイル ガイドラインの遵守、自動化ツールの使用が含まれます。実践的な事例では、Eigen ライブラリを使用して線形回帰アルゴリズムを実装し、メモリを効果的に管理し、高性能の行列演算を使用する方法を示します。
 C++sort 関数の基礎となる原則とアルゴリズムの選択を調べる
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
C++sort 関数の基礎となる原則とアルゴリズムの選択を調べる
Apr 02, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
C++sort 関数の最下層はマージ ソートを使用し、その複雑さは O(nlogn) で、クイック ソート、ヒープ ソート、安定したソートなど、さまざまなソート アルゴリズムの選択肢を提供します。
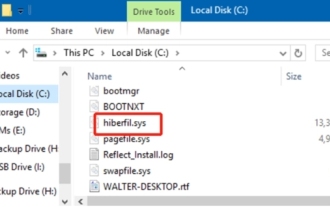 hiberfil.sys ファイルとは何ですか? hiberfil.sysは削除できますか?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
hiberfil.sys ファイルとは何ですか? hiberfil.sysは削除できますか?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
最近、多くのネチズンが編集者に「hiberfil.sys ファイルとは何ですか?」と尋ねました。 hiberfil.sys は C ドライブのスペースを多く消費し、削除される可能性がありますか?エディターは、hiberfil.sys ファイルを削除できることを通知します。以下で詳細を見てみましょう。 hiberfil.sys は Windows システムの隠しファイルであり、システム休止状態ファイルでもあります。通常、C ドライブのルート ディレクトリに保存され、そのサイズはシステムに搭載されているメモリのサイズと同等です。このファイルはコンピュータが休止状態になっているときに使用され、リカバリ中に以前の状態にすばやく復元できるように、現在のシステムのメモリ データが含まれています。そのサイズはメモリ容量と等しいため、より多くのハードドライブスペースを占有する可能性があります。冬休み
 人工知能は犯罪を予測できるのか? CrimeGPT の機能を調べる
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
人工知能は犯罪を予測できるのか? CrimeGPT の機能を調べる
Mar 22, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
人工知能 (AI) と法執行機関の融合により、犯罪の予防と検出の新たな可能性が開かれます。人工知能の予測機能は、犯罪行為を予測するためにCrimeGPT (犯罪予測技術) などのシステムで広く使用されています。この記事では、犯罪予測における人工知能の可能性、その現在の応用、人工知能が直面する課題、およびこの技術の倫理的影響について考察します。人工知能と犯罪予測: 基本 CrimeGPT は、機械学習アルゴリズムを使用して大規模なデータセットを分析し、犯罪がいつどこで発生する可能性があるかを予測できるパターンを特定します。これらのデータセットには、過去の犯罪統計、人口統計情報、経済指標、気象パターンなどが含まれます。人間のアナリストが見逃す可能性のある傾向を特定することで、人工知能は法執行機関に力を与えることができます




