What is the difference between router and broadband?
The difference between router and broadband: 1. Functional aspect; 2. Network connection aspect; 3. Transmission rate aspect; 4. Equipment aspect; 5. Scope of application; 6. Protocol aspect; 7. Security aspect ; 8. Price. Detailed introduction: 1. In terms of function, the main function of the router is to convert a network address into a private IP address that can be used by one or more personal computers, thereby enabling multiple computers to access the Internet at the same time; 2. In terms of network connection, the router can It enables multiple computers to access the Internet at the same time, while broadband can only provide a single network connection and so on.

The operating system for this tutorial: Windows 10 system, DELL G3 computer.
A router is a hardware device that connects two or more networks and acts as a gateway between networks. It can read the address in each data packet and then decide how to transmit it, and can transmit each data packet to the designated location according to the best route according to the selected routing algorithm. A router can be understood as a device specifically used to manage network traffic between the Internet and various client devices. It can guide and process traffic between different networks so that various client devices can access the Internet normally. .
Routers usually consist of two parts: one is the control part, that is, the router control unit, which is responsible for processing data packets and deciding how to transmit them; the other part is the data part, that is, the router forwarding unit, which is responsible for routing data packets from One network forwards to another network.
There are obvious differences between routers and broadband in terms of functions, network connections, and transmission rates.
1. Functional aspects: The main function of the router is to convert a network address into a private IP address that can be used by one or more personal computers, thereby enabling multiple computers to operate at the same time. Internet functionality. In addition, the router can also perform functions such as port mapping, virtual private network, domain name resolution, firewall and packet filtering. The main function of broadband is to provide a network connection so that personal computers can access the Internet. Broadband can be divided into many types according to different network protocols and data transmission rates, such as ADSL, VDSL, Cable Modem, etc.
2. Network connection: Routers can enable multiple computers to access the Internet at the same time, while broadband can only provide a single network connection. However, broadband network connections are faster than routers because broadband has a larger bandwidth and can handle more data at the same time.
3. Transmission rate: The transmission rate of broadband is faster than that of router. The transmission rate of broadband can usually reach tens or even hundreds of megabits per second, while the transmission rate of routers is usually only a few to tens of megabits per second.
4. Equipment: Routers need to be connected to computers or other devices to use them, while broadband can be used without connecting to other devices.
5. Scope of application: The router is suitable for small networks, such as homes or small offices, and can enable multiple computers to access the Internet at the same time. Broadband is suitable for large-scale networks, such as campus networks or corporate networks, and can provide faster network connection speeds and greater bandwidth.
6. Protocol: The protocols used by routers and broadband are different. The router uses the TCP/IP protocol, while the broadband uses the PPPoE protocol.
7. Security: The security of the router is higher than that of the broadband. Routers have functions such as firewalls and packet filtering to prevent external attacks and the leakage of personal information. Broadband network security is poor and vulnerable to hacker attacks and personal information leakage.
8. In terms of price: The price of routers is usually higher than that of broadband. However, if there are a large number of computers that need to access the Internet at the same time, it may be more cost-effective to use a router.
In short, there are obvious differences between routers and broadband in terms of functions, network connections, and transmission rates. Appropriate network equipment needs to be selected based on actual needs and usage scenarios.
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between router and broadband?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Can the router be placed upside down?
Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
Can the router be placed upside down?
Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
Can. However, you need to pay attention to some issues: 1. Placing the router upside down may have a certain impact on heat dissipation, causing heat to accumulate at the bottom of the router, affecting the heat dissipation effect. Long-term overheating may reduce the performance of the router and adversely affect its lifespan. ; 2. Placing the router upside down may affect the operation and management of the device, and the indicator lights and interfaces may be blocked or inconvenient to operate; 3. Placing the router upside down may also have a certain impact on network security, and the default user name and password may cause This information is more susceptible to prying eyes.
 What are the benefits of turning on ipv6 on the router 'Advantages of using the latest IPv6'
Feb 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
What are the benefits of turning on ipv6 on the router 'Advantages of using the latest IPv6'
Feb 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
Students who know computers all know that if our computer wants to connect to the network, it must have an IP address. This IP address can be manually configured, such as 172.16.19.20; it can also be automatically obtained by the DHCP server of the computer network card, such as 192.168.1.100 etc. These IP addresses are what we often call IPV4 addresses, and the corresponding IPV6 is also a type of IP address. What is IPV6 IPV6 is a new IP address that emerged in response to the exhaustion of IPV4 address resources. Its full name is "Internet Protocol Version 6", and its Chinese name is the sixth generation of Internet Protocol. The number of IPv6 addresses is theoretically 2^128
 How many lights on the router are normal? 'Recommended detailed explanation of the normal status of the router indicator lights'
Feb 06, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
How many lights on the router are normal? 'Recommended detailed explanation of the normal status of the router indicator lights'
Feb 06, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
The first light is on, indicating that the router is powered on. Which port is plugged in, the light of which port is on, and flashing means data is being transmitted. Wireless routers usually have three indicator lights: SYS, LAN and WAN. When the wireless router is powered on, the SYS light will light up. When the wireless router is connected to the network modem, the WAN light will light up. The LAN light corresponds to each interface of the wireless router. As long as the network cable is inserted into the corresponding interface, the corresponding LAN light will light up. 1. If it keeps flashing, it means it is transmitted by data, and the router settings should be normal. 2. If you have always been able to access the Internet, but you can't get online recently; it is probably a problem with the external line, that is, a problem with the operator (usually there is a problem with the line, causing the data signal to attenuate too much, although the line is good)
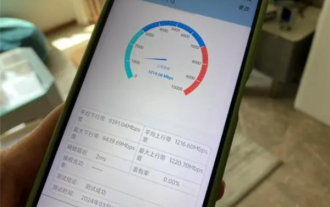 Up/down 10000M! Shanghai Telecom's 10G broadband will achieve city-wide coverage in 2026, and the 299 yuan package will be free
Aug 10, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Up/down 10000M! Shanghai Telecom's 10G broadband will achieve city-wide coverage in 2026, and the 299 yuan package will be free
Aug 10, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
According to news on August 10, according to domestic media reports, in response to the call, Shanghai strives to initially build a global dual 10G city symbolized by 5G-A and 10G optical network by 2026. Shanghai Telecom officially announced that it will officially launch the "Beautiful Home 10G Convergence Package" on August 30. At the same time, it will release the industry-leading "5G-A package" with high speed, launch the "Suiyixuan" Yunyi Smart Selection gift package, and carry out " "Broadband Leap" plan to popularize 10G cloud broadband for all people. According to official statements, Shanghai Telecom will accelerate the construction of 10 Gigabit optical network communities and complete the first batch of 26 benchmark community coverage within the year, and will achieve full coverage in 2026.
 What is the impact of turning off dhcp on the router?
Dec 01, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
What is the impact of turning off dhcp on the router?
Dec 01, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
The impact of turning off dhcp on the router: 1. The client cannot automatically obtain an IP address; 2. The IP address needs to be configured manually; 3. It may cause network connection problems; 4. It affects the communication of network devices; 5. IP address conflicts; 6. Unable to proceed Dynamic address allocation; 7. Network isolation cannot be performed; 8. Traffic control cannot be performed; 9. Access control cannot be performed. It is recommended that before turning off the DHCP service, carefully consider whether it really needs to be turned off, or keep the DHCP service to ensure that the client can automatically obtain the correct IP address.
 Will placing the router upside down have any impact on the network?
Sep 22, 2023 pm 04:45 PM
Will placing the router upside down have any impact on the network?
Sep 22, 2023 pm 04:45 PM
Placing the router upside down may have some effects on the network, including reduced signal coverage, blocked signal transmission, poor temperature and heat dissipation, and reduced network speed. Detailed introduction: 1. The signal coverage is reduced. Routers are usually designed to radiate signals outward in a horizontal direction. Therefore, placing the router upside down may cause the signal coverage to be reduced, which may cause signal in some areas. Weakening, thus affecting the stability and speed of the connection; 2. Signal transmission is blocked. Placing the router upside down may cause signal transmission to be blocked, etc.
 A brief history of broadband Internet technology
Apr 16, 2024 am 09:00 AM
A brief history of broadband Internet technology
Apr 16, 2024 am 09:00 AM
In today's digital age, broadband has become a necessity for each of us and every family. Without it, we would be restless and restless. So, do you know the technical principles behind broadband? From the earliest 56k "cat" dial-up to the current Gigabit cities and Gigabit homes, what kind of changes has our broadband technology experienced? In today’s article, let’s take a closer look at the “Broadband Story”. Have you seen this interface between █xDSL and ISDN? I believe that many friends born in the 70s and 80s must have seen it and are very familiar with it. That's right, this was the interface for "dial-up" when we first came into contact with the Internet. That was more than 20 years ago, when Xiao Zaojun was still in college. In order to surf the Internet, I
 What is the difference between campus network and broadband?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
What is the difference between campus network and broadband?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
The differences between campus network and broadband are in terms of usage scenarios and network range, speed and bandwidth, service providers, usage restrictions and service content. Detailed introduction: 1. Usage scenarios and network scope. Campus network is a local area network service provided within schools, universities or educational institutions. It mainly covers the school’s teaching buildings, dormitory buildings and other areas, and provides network connection services for students, faculty and staff. Usually built and managed by the school itself, it provides specific network resources and services. Broadband is a wide area network service that provides high-speed Internet connections for individual users or families, etc.



