unicode 是一个国际字符集,包含来自全球多种语言的大量字符、符号和脚本。 java 编程语言独立于平台,内置对 unicode 字符的支持,允许开发人员创建可与多种语言和脚本无缝协作的应用程序。
在Java中,char数据类型用于存储Unicode字符,在源代码中使用字符文字来表示这些字符。字符文字是用单引号 (' ') 括起来的单个 Unicode 字符,可以直接分配给 char 变量。
第 1 步 - 声明一个 char 变量。
声明一个具有合适名称的 char 变量。
示例:char myChar;
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
步骤 2 - T将 Unicode 字符文字分配给变量。
将单引号括起来的 Unicode 字符文字分配给 char 变量
示例:myChar = '\u0041'; (将 Unicode 字符“A”分配给 myChar)
步骤 3 - (可选)执行操作或操纵 Unicode 字符。
根据程序的要求,对存储在 char 变量中的 Unicode 字符执行任何操作。
第 4 步 - 打印存储的 Unicode 字符。
使用 System.out.println() 方法打印存储在 char 变量中的 Unicode 字符。
示例:System.out.println("存储的字符:" + myChar); (将“存储的字符:A”打印到控制台)
在 Java 中使用 Unicode 字符有两种方法:使用 Unicode 转义序列和直接存储 Unicode 字符。
第一种方法涉及使用转义序列表示 Unicode 字符,当无法在 Java 代码中直接键入或显示字符时非常有用。第二种方法是将 Unicode 字符直接存储在变量中,当可以直接键入或显示字符时会更方便。
方法的选择取决于程序的具体要求。但一般来说,当可以直接输入或显示字符时,采用方法二更为简单、方便;而当不能直接输入或显示字符时,则需要采用方法一。
在 Java 中存储 Unicode 字符的一种方法是使用 Unicode 转义序列。转义序列是表示特殊字符的一系列字符。在 Java 中,Unicode 转义序列以字符“\u”开头,后跟代表所需字符的 Unicode 代码点的四个十六进制数字。
public class UnicodeCharacterLiteral {
public static void main (String[]args)
{
//Unicode escape sequence
char unicodeChar = '\u0041';
// point for 'A'
System.out.println("Stored Unicode Character: " + unicodeChar);
}
}
Stored Unicode Character: A
在上面的代码片段中,Unicode 转义序列“\u0041”代表字符“A”。转义序列被分配给 char 变量 unicodeChar,然后将存储的字符打印到控制台。
或者,您可以通过将字符括在单引号中,直接将 Unicode 字符存储在 char 变量中。但是,对于无法直接使用键盘输入或不可见的字符(例如控制字符),此方法可能不可行。
public class UnicodeCharacterLiteral {
public static void main(String[] args) { // Storing Unicode character directly
char unicodeChar = 'A';
// Directly storing the character 'A'
System.out.println("Stored Unicode Character: " + unicodeChar);
}
}
Stored Unicode Character: A
在此示例中,字符“A”直接用单引号括起来并分配给 char 变量 unicodeChar。然后将存储的字符打印到控制台。
public class UnicodeCharacterExamples {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Storing Unicode characters using escape sequences
char letterA = '\u0041';
char letterSigma = '\u03A3';
char copyrightSymbol = '\u00A9';
// Storing Unicode characters directly
char letterZ = 'Z';
char letterOmega = 'Ω';
char registeredSymbol = '®';
// Printing the stored Unicode characters
System.out.println("Stored Unicode Characters using Escape Sequences:");
System.out.println("Letter A: " + letterA);
System.out.println("Greek Capital Letter Sigma: " + letterSigma);
System.out.println("Copyright Symbol: " + copyrightSymbol);
System.out.println("\nStored Unicode Characters Directly:");
System.out.println("Letter Z: " + letterZ);
System.out.println("Greek Capital Letter Omega: " + letterOmega);
System.out.println("Registered Symbol: " + registeredSymbol);
}
}
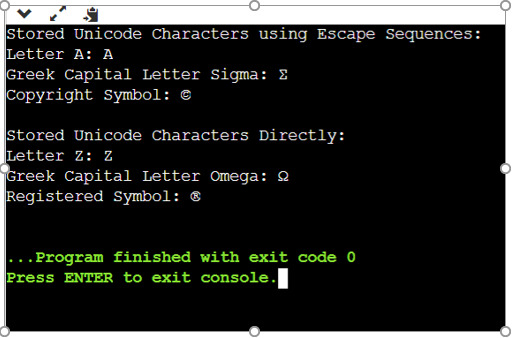
Stored Unicode Characters using Escape Sequences: Letter A: A Greek Capital Letter Sigma: Σ Copyright Symbol: © Stored Unicode Characters Directly: Letter Z: Z Greek Capital Letter Omega: Ω Registered Symbol: ®
此示例演示如何操作存储的 Unicode 字符。它计算大写字母“A”和小写字母“a”之间的差异,并使用该差异来计算大写字母“C”。然后,它通过将大写字母“C”的 Unicode 代码点添加 32 来计算小写字母“c”。所操作的 Unicode 字符将打印到控制台。
public class UnicodeCharacterManipulation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Storing Unicode characters using escape sequences
char letterA = '\u0041';
char letterSmallA = '\u0061';
// Storing Unicode characters directly
char letterB = 'B';
char letterSmallB = 'b';
// Manipulating the stored Unicode characters
int difference = letterA - letterSmallA;
char letterC = (char) (letterB + difference);
char letterSmallC = (char) (letterC + 32);
// Printing the manipulated Unicode characters
System.out.println("Manipulated Unicode Characters:");
System.out.println("Difference between A and a: " + difference);
System.out.println("Calculated Letter C: " + letterC);
System.out.println("Calculated Letter c: " + letterSmallC);
}
}
Manipulated Unicode Characters: Difference between A and a: -32 Calculated Letter C: C Calculated Letter c: c
在 Java 中,您可以通过使用 Unicode 转义序列或直接将字符括在单引号中,使用字符文字存储 Unicode 字符。两种方法都有其优点和局限性。转义序列提供了一种一致的方式来表示源代码中的任何 Unicode 字符,而在处理可以轻松键入或显示的字符时,直接存储字符会更方便。
本文提供了一种在 Java 中存储 Unicode 字符的算法,讨论了存储这些字符的两种不同方法,并演示了每种方法的工作示例。了解这些技术将帮助开发人员创建可与不同语言和脚本无缝协作的应用程序,并利用 Java 编程中 Unicode 的强大功能。
以上就是使用字符字面量存储Unicode字符的Java程序的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

java怎么学习?java怎么入门?java在哪学?java怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了java速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号