list集合中contains() 用于判断集合中 是否 包含指定的元素。list会将括号内的元素和list中存在的元素进行逐个比对,若有相等的,返回结果为true,若没有则返回结果为false。
用下方代码验证:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List newList = new ArrayList();//创建一个空数组
newList.add("name");
newList.add("age");
newList.add("sex");
newList.add("birth");//往数组中加一些元素
boolean res = false;
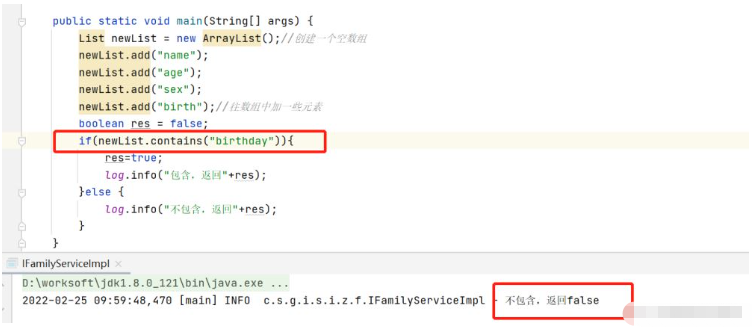
if(newList.contains("birthday")){
res=true;
log.info("包含,返回"+res);
}else {
log.info("不包含,返回"+res);
}
}测试newList数组中是否包含元素“birthday”
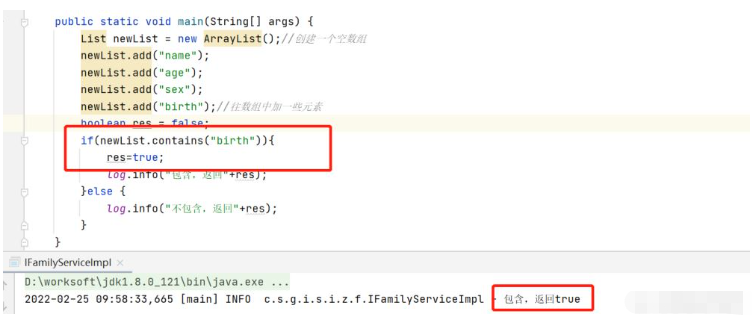
测试newList数组中是否包含元素“birth”
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
String类中的contains()方法:当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列,即判断指定内容中是否包含括号中的内容。
举例说明:
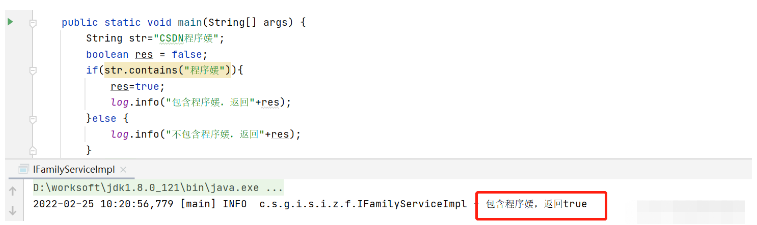
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="CSDN程序媛";
boolean res = false;
if(str.contains("程序媛")){
res=true;
log.info("包含程序媛,返回"+res);
}else {
log.info("不包含程序媛,返回"+res);
}测试String类型“CSDN程序媛”是否包含“程序媛”
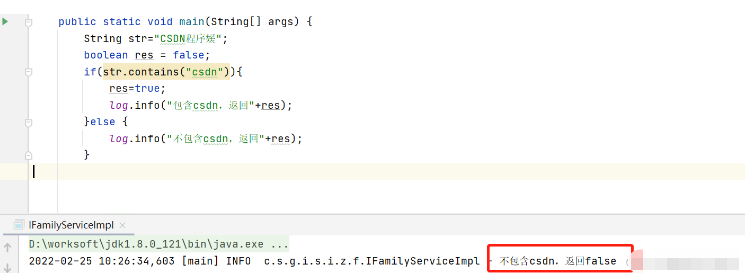
如果String类型的字符串中包含字母时,需要注意区分大小写
测试String类型“CSDN程序媛”是否包含小写“csdn”
使用List.contains(Object object)方法判断ArrayList是否包含一个元素对象(针对于对象的属性值相同,但对象地址不同的情况),如果没有重写List
使用List.contains(Object object)方法判断ArrayList是否包含一个元素对象(针对于对象的属性值相同,但对象地址不同的情况),如果没有重写List
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.equals(o);
}将导致contains方法始终返回false。
查看ArrayList的contains方法的源码如下:
/**
* Searches this {@code ArrayList} for the specified object.
*
* @param object
* the object to search for.
* @return {@code true} if {@code object} is an element of this
* {@code ArrayList}, {@code false} otherwise
*/
@Override public boolean contains(Object object) {
Object[] a = array;
int s = size;
if (object != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (object.equals(a[i])) {
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
if (a[i] == null) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}可以看出,contains方法依据Object的equals方法来判断是否包含某一元素,继续查看Object类中的equals方法,源码如下:
public boolean equals(Object o) {
return this == o;
}所以,使用“==”比较对象的地址,如果是同一对象即地址相同的情况下,才会返回true,而对于对象属性值相同但地址不同的不同对象,始终返回false!
如果需要依据对象属性值是否相同来判断ArrayList是否包含某一对象,则需要重写Object的equals方法,并在equals方法中一一比较对象的每个属性值,如:
package com.feng.lejuan.entity;
public class QuestionInfo {
private String questionId;
private String answerId;
private String subQuestionId;
private String result;
public QuestionInfo() {
super();
}
public QuestionInfo(String questionId, String answerId,
String subQuestionId, String result) {
super();
this.questionId = questionId;
this.answerId = answerId;
this.subQuestionId = subQuestionId;
this.result = result;
}
public String getQuestionId() {
return questionId;
}
public void setQuestionId(String questionId) {
this.questionId = questionId;
}
public String getAnswerId() {
return answerId;
}
public void setAnswerId(String answerId) {
this.answerId = answerId;
}
public String getSubQuestionId() {
return subQuestionId;
}
public void setSubQuestionId(String subQuestionId) {
this.subQuestionId = subQuestionId;
}
public String getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(String result) {
this.result = result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o instanceof QuestionInfo) {
QuestionInfo question = (QuestionInfo) o;
return this.questionId.equals(question.questionId)
&& this.subQuestionId.equals(question.subQuestionId)
&& this.answerId.equals(question.answerId)
&& this.result.equals(question.result);
}
return super.equals(o);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "QuestionInfo [questionId=" + questionId + ", answerId="
+ answerId + ", subQuestionId=" + subQuestionId + ", result="
+ result + "]";
}
}以上就是Java中list.contains()怎么使用的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号