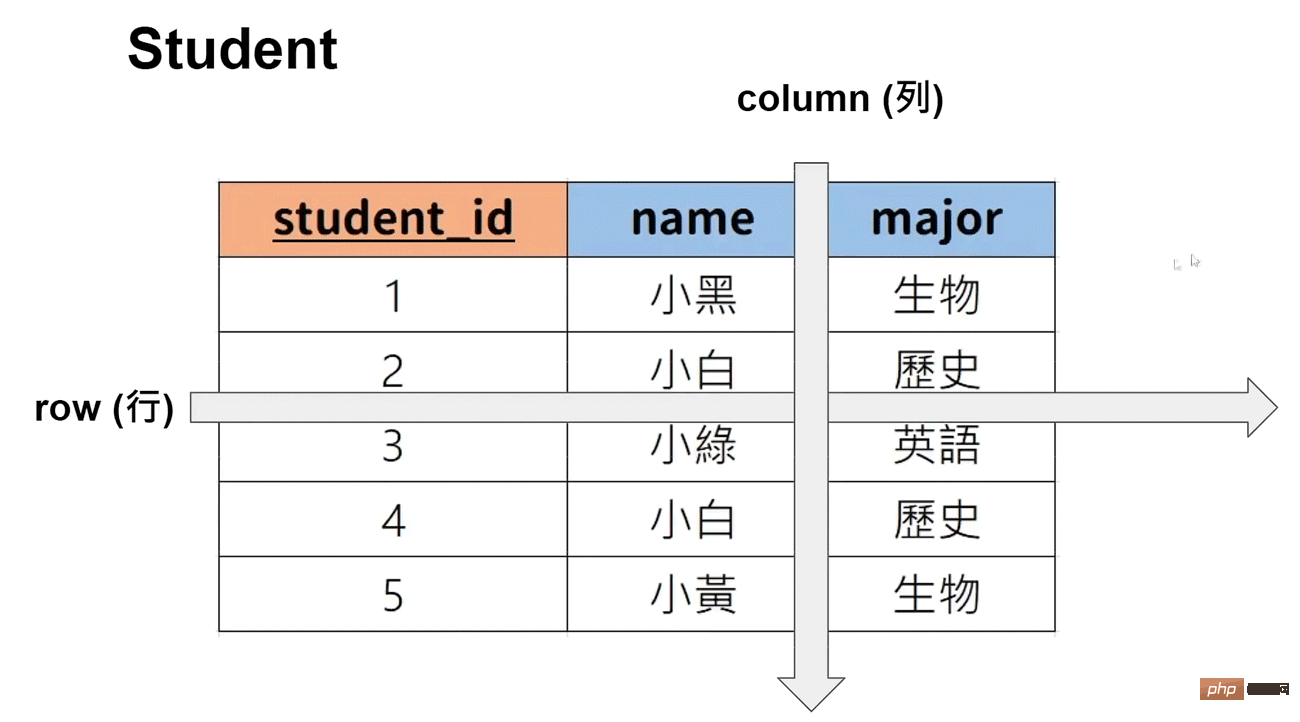
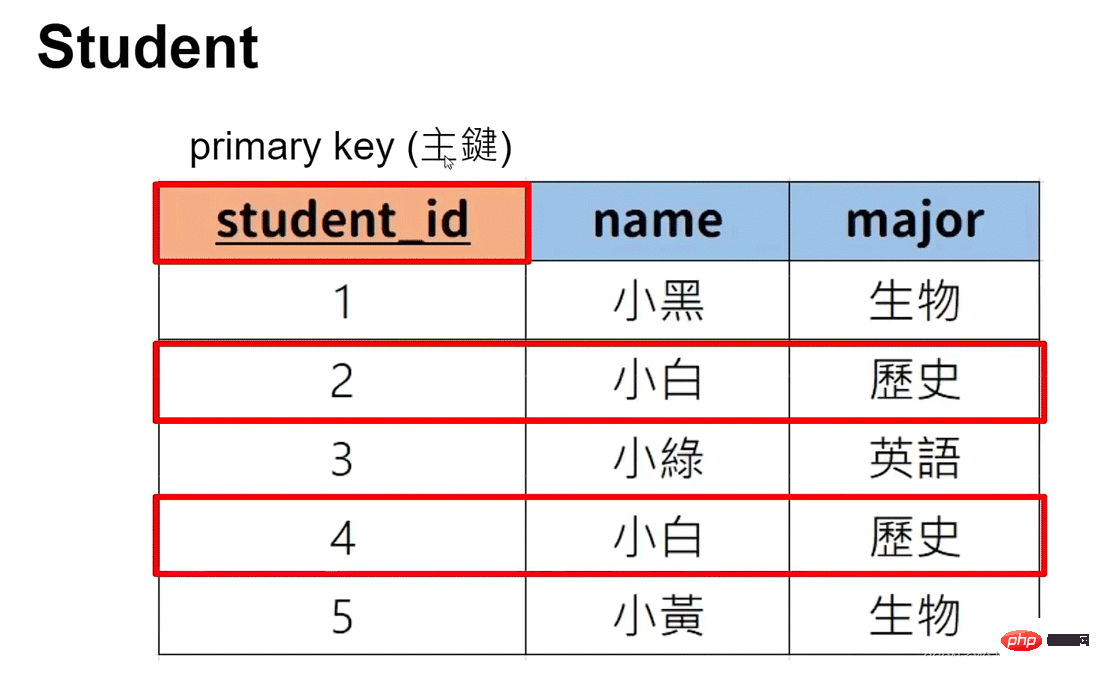
主键:可唯一表示该资料(可以设置多个列表为主键)
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
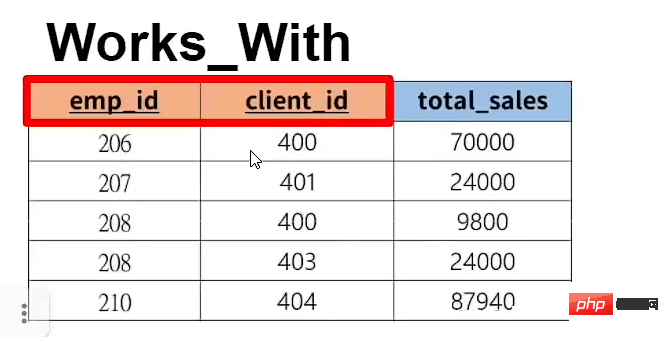
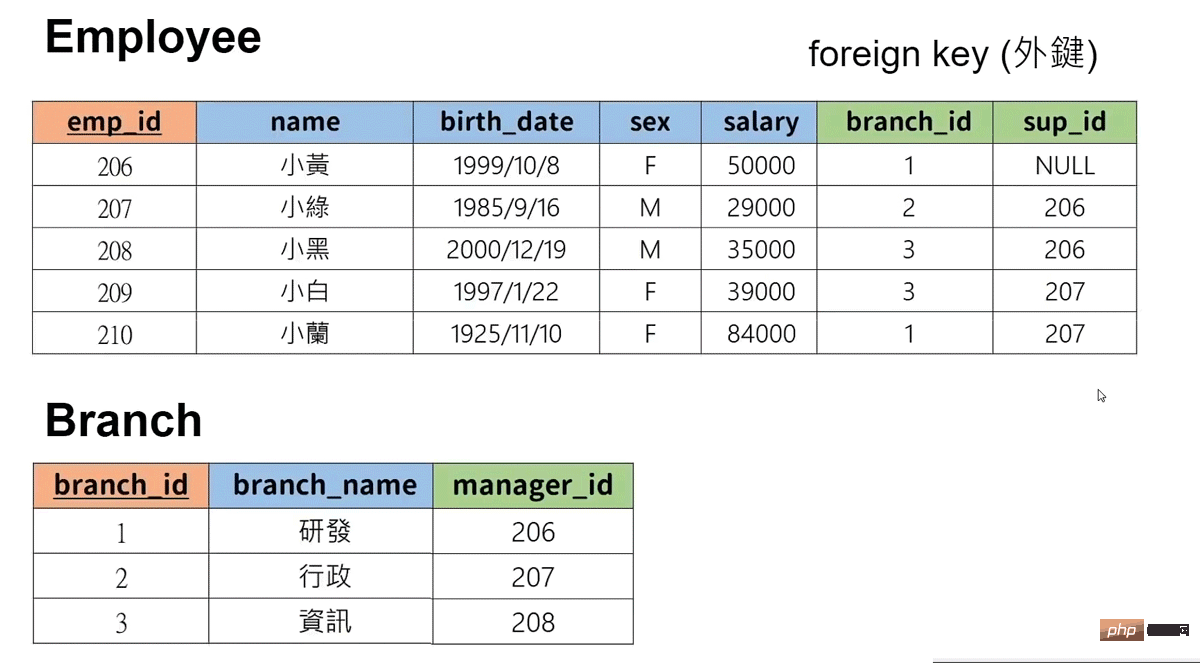
设置外键进行表与表的相连,且外键必须是其他表的主键(外键也可以设置自己表格的主键)
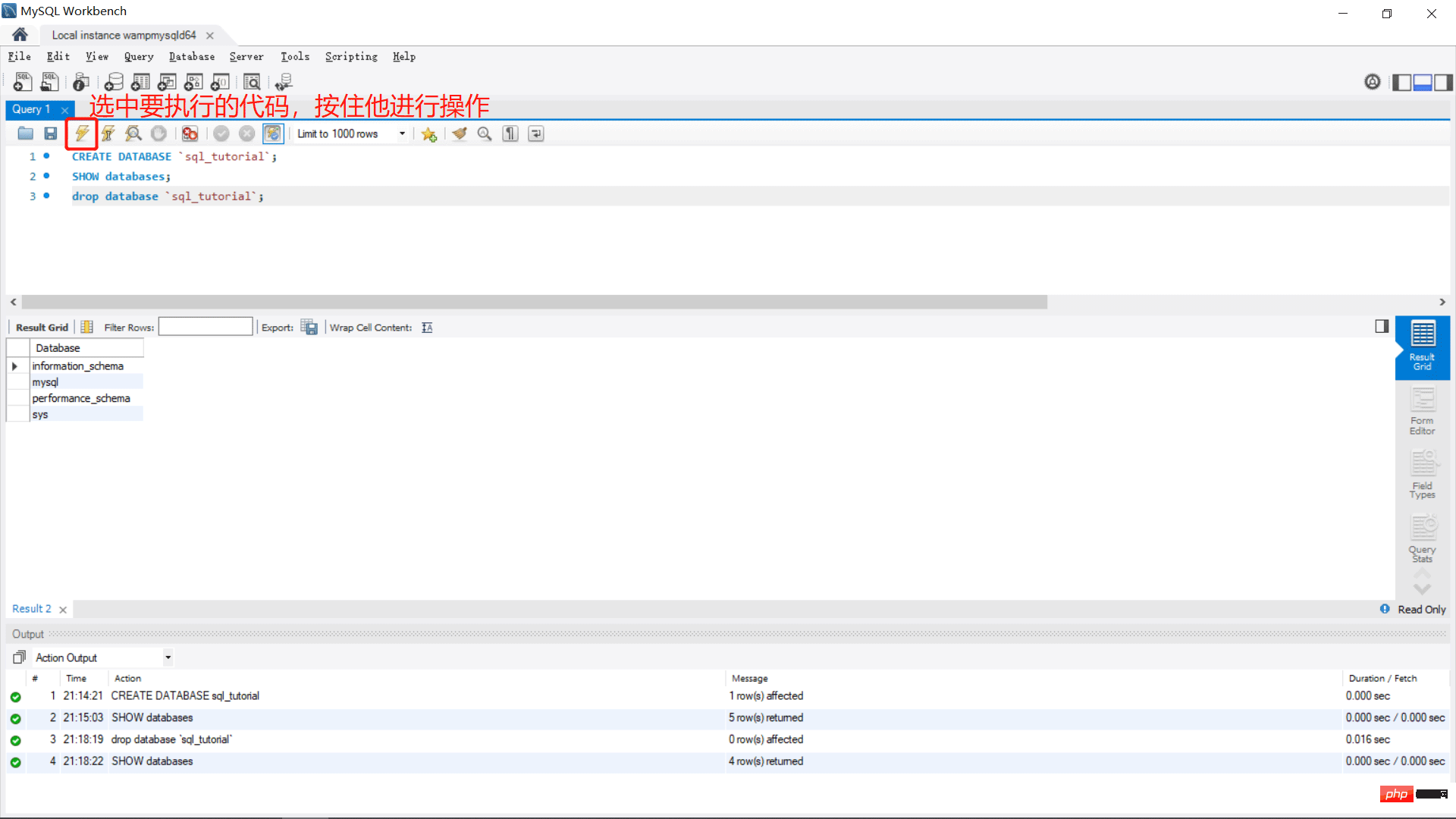
CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; --创建资料库 SHOW databases; --展示资料库 drop database `sql_tutorial`; --删除资料库
–为注释
;为结束命令的格式
MySQL的资料形态:
INT --整形
DECIMAL(m,n) --有小数点的数 (3,2)则是2.33,总共有m位数,小数点站n位
VARCHAR(n) --字串
BLOB --图片 影片 档案…(二进制的资料)
DATE --日期(yyyy-mm-dd)
TIMESTAMP --记录时间(yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss)
CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; -- 创建资料库
SHOW databases; -- 展示资料库
use `sql_tutorial`; -- 选择使用的资料库
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`major` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
describe `student`; -- 展示表格
drop table `student`; -- 删除表格
alter table `student` add gpa decimal(3,2); -- 增加资料属性
alter table `student` drop column gpa ; -- 删除资料属性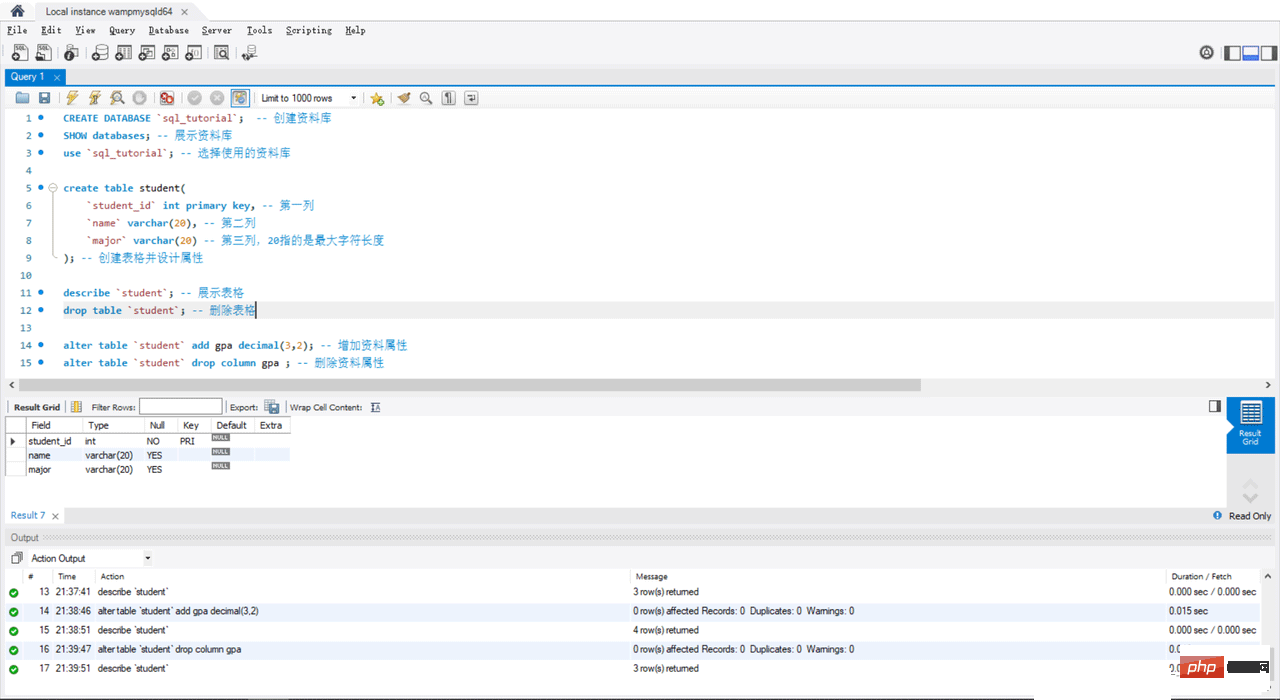
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`major` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student` values(1,'小白','历史'); -- 写入表格数据
insert into `student` values(2,'小黑','生物'); -- 写入表格数据
insert into `student` values(3,'小绿',null); -- 写入表格数据,null为空
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`,`student_id`) values('小蓝','英语','4'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`major`,`student_id`) values('英语','5'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据,没有的数据则为空白null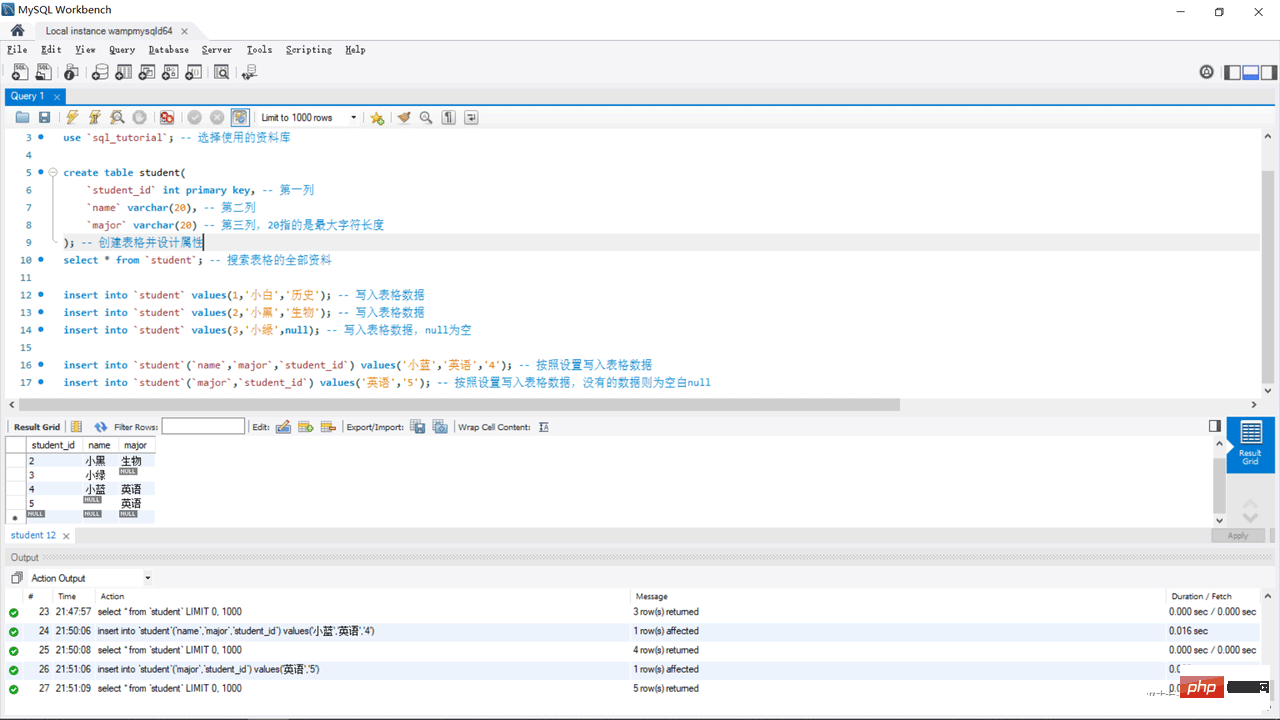
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20) not null, -- 第二列,not null指这个属性不可以为空
`major` varchar(20) unique -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度,unique指每个值不可以重复
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key auto_increment, -- 第一列,auto_increment自动会加一
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列,not null指这个属性不可以为空
`major` varchar(20) default '历史' -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度,default指预设值,如果没有写该属性,则为预设值
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
drop table `student`;
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小蓝','英语'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`) values('小黑'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据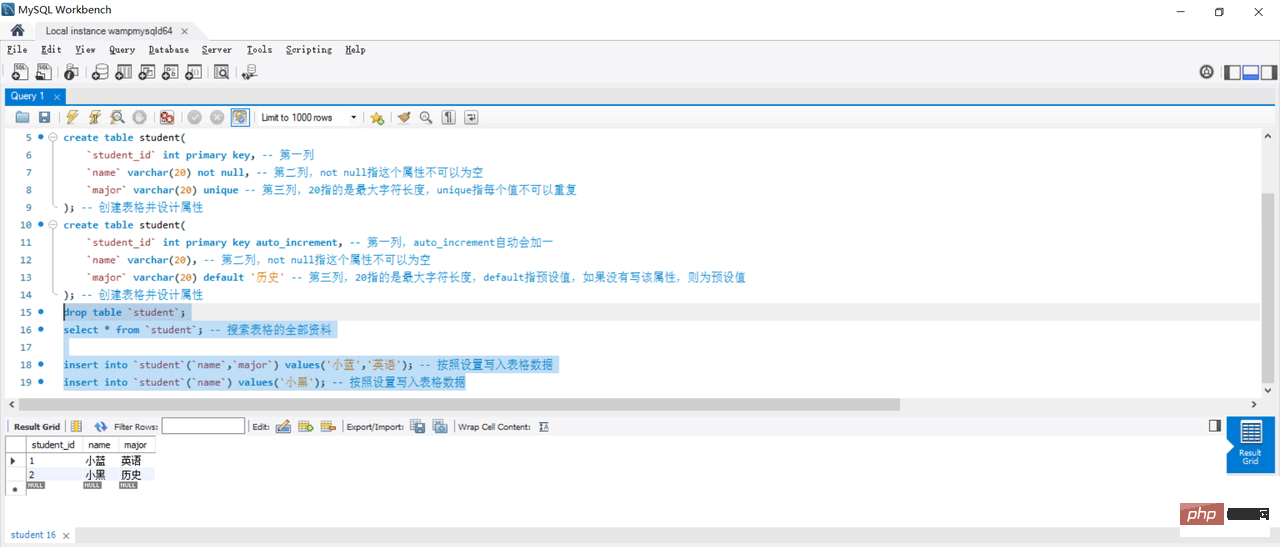
条件:>,=,
set sql_safe_updates = 0; -- 把预设更新模式关闭,这样更新操作才可以成功
create table student(
`student_id` int primary key auto_increment, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`major` varchar(20), -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
`score` int
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
drop table `student`;
select * from `student`; -- 搜索表格的全部资料
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小蓝','英语'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小白','化学'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
insert into `student`(`name`,`major`) values('小黑','生物'); -- 按照设置写入表格数据
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '英语文学' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `major` = '英语'; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
-- 还可以进行多个更新
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '生化' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `major` = '生物' or `major` = '化学' ; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `name` = '小辉',`major` = '生化' -- 将什么更新成什么
where `student_id`=1 ; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新
-- 不加条件则都改
update `student` -- 更新哪个表格
set `major` = '物理'; -- 将其中谁的什么进行更新,都改成了生化
delete from `student`
where `student_id` = 3; -- 删除表格中的数据
-- 条件也可以设置多个
delete from `student`
where `name` = '小白' and `major`='物理'; -- 删除表格中的数据
delete from `student`; -- 删除所有的资料-- 取得资料
select * from `student`; -- 取得表格的全部资料
select `name` from `student`; -- 只取得表格的对应数据
select `name`, `major` from `student`; -- 取得表格的对应多个数据
select * from `student` ORDER BY `score`; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(默认正序)
select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` DESC; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(由高到低,asc是由低到高)
select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` ,`student_id`; -- 取得表格的全部资料,并排序(先有score做排序,score中相同的再由student_id做排序)
select * from `student` LIMIT 3 ; -- 限制资料范围
select * from `student` ORDER BY `score` LIMIT 3 ; -- 排序并限制资料范围
select * from `student` where `major`= '英语'; -- 查找对应资料
select * from `student` where `major`= '英语' and `student_id` = 1; -- 查找对应资料(多条件)
select * from `student` where `major` in('历史','英语','生物'); -- 查找对应资料(多条件)1CREATE DATABASE `sql_tutorial`; -- 创建资料库
SHOW databases; -- 展示资料库
use `sql_tutorial`; -- 选择使用的资料库
create table `employee`(
`emp_id` int primary key, -- 第一列
`name` varchar(20), -- 第二列,20指的是最大字符长度
`bath_date` date, -- 第三列
`sex` varchar(1),
`salary` int,
`branch_id` int,
`sup_id` int
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table `branch`(
`branch_id` int primary key , -- 第一列
`branch_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`manager_id` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
foreign key (`manager_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete set null -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
-- 补充外键(外表格对应)
alter table `employee` -- 在什么表格上进行更新
add foreign key(`branch_id`) -- 在他的什么属性上
references `branch`(`branch_id`) -- 从哪的什么属性对应
on delete set null;
-- 补充外键(内表格对应)
alter table `employee` -- 在什么表格上进行更新
add foreign key(`sup_id`) -- 在他的什么属性上
references `employee`(`emp_id`) -- 从哪的什么属性对应
on delete set null;
create table `client`(
`client_id` int primary key , -- 第一列
`client_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`phone` varchar(20) -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table `works_with`(
`emp_id` int, -- 第一列
`client_id` int, -- 第二列
`total_sales` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
primary key(`emp_id`,`client_id`),
foreign key (`emp_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete cascade, -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
foreign key (`client_id`) references `client`(`client_id`) on delete cascade -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
-- 当增加资料冲突的时候可以先将其设置为null然后再更新
insert into `branch` values(1,'研发',null);
insert into `employee` values(206,'xiaohuang','1998-10-08','F',50000,1,null);
update `branch`
set `manager_id` = 206
where `branch_id` = 1;-- 取得对应表格所有资料 select * from `employee`; -- 取得对应表格所有资料并排序(默认低到高) select * from `employee` order by `salary`; -- 低为加desc -- 增加限制取出条件 select * from `employee` order by `salary` desc limit 3 ; -- 取出前三高 -- 取出对应属性 select `name` from `employee` ; -- 取出对应属性的内容(且不重复) select distinct `name` from `employee` ;
-- 取得人数 select count(*) from `employee`; -- 统计几笔资料 select count(`sup_id`) from `employee`; -- 统计对应属性资料个数(null不计入) -- 增加条件取数 select count(*) from `employee` where `bath_date` > '1970-01-01' and `sex` = 'F'; -- 统计几笔资料 -- 计算对应的属性的平均 select avg(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 计算对应的属性的总和 select sum(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 取得最高的 select max(`salary`) from `employee`; -- 取得最低的 select min(`salary`) from `employee`;
-- %表示多个子元,_表示一个子元 -- 取得尾数335的数据 select * from `client` where `phone` like '%335'; -- 取得姓艾的 select * from `client` where `client_name` like '艾%'; -- 取得生日是10月的 select * from `employee` where `bath_date` like '_____10%';
-- 员工与客户合并为一列(类型必须相同) select `name` from `employee` union select `client_name` from `client`; -- 多个数据合并为多列(类型必须相同) select `emp_id`, `name` from `employee` union select `client_id`, `client_name` from `client`; -- 多个数据合并为多列(类型必须相同)顺便改个名 select `emp_id` as `total_id`, `name` as `total_name` from `employee` union select `client_id`, `client_name` from `client`;
-- 连接 -- 取得所有部门经理名字,这就需要先确定部门再确定经理(二表相连) select * from `employee` join `branch` on `emp_id` = `manager_id`; -- 还可以写成 select * from `employee` join `branch` on `employee`.`emp_id` = `branch`.`manager_id`; -- 附加条件 select * from `employee` left join `branch` on `employee`.`emp_id` = `branch`.`manager_id`; -- 左边的表格(join的左边)返回全部数据,右边的必须满足才可
-- 查询套查询
select `name` from `employee`
where `emp_id` = (
select `manager_id`
from `branch`
where `branch_name` = '研发'
); -- 查找研发部门的经理名字
select `emp_id` from `employee`
where `emp_id` in (
select `emp_id`
from `works_with`
where `total_sales` > 50000
); -- 销售资金超50000的人有哪些On delete set null 的作用是若该数据删除了(或者说对应不到了)则会设置为null
On delete decade 若对应数据删除了(或者说对应不到了)则该表格的这条数据跟着删掉
注:当为主键时则不能设置为on delete set nullcreate table `branch`(
`branch_id` int primary key , -- 第一列
`branch_name` varchar(20), -- 第二列
`manager_id` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
foreign key (`manager_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete set null -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性
create table `works_with`(
`emp_id` int, -- 第一列
`client_id` int, -- 第二列
`total_sales` int, -- 第三列,20指的是最大字符长度
primary key(`emp_id`,`client_id`),
foreign key (`emp_id`) references `employee`(`emp_id`) on delete cascade, -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
foreign key (`client_id`) references `client`(`client_id`) on delete cascade -- 设置好外键(选择什么是并对应什么表格的什么属性)
); -- 创建表格并设计属性# 导入功能包(mysql-connector-python)
import mysql.connector
# 创入连线
connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', # mysql的位置
port='3306', # 连接通道
user='root', # 使用者名称
password='123456') # 使用者密码
'''connection = mysql.connector.connect(host='localhost', # mysql的位置
port='3306', # 连接通道
user='root', # 使用者名称
password='123456', # 使用者密码
database='sql_tutorial') # 直接打开目标资料库'''
# 告知开始使用操作
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 在对mysql操作时即用该格式:cursor.execute("你要执行的mysql语句命令")
# 创建资料库
# cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE `qq`;")
# 取得所有资料库名称
cursor.execute("show databases;")
records = cursor.fetchall() # 取出回传资料库
for r in records:
print(r) # 因为回传列表,为便于观察,进行循环打印
# 选择资料库
cursor.execute("use `sql_tutorial`;")
# 创建表格
# 告知关闭操作
cursor.close()
# 若要懂资料进行修改需要结尾加一个指令,这样才能提交指令生效
connection.commit()
# 关闭连线
connection.close()以上就是MySQL怎么使用Python进行连接的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

python怎么学习?python怎么入门?python在哪学?python怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了python速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号