同级目录下新建dup_video
import json
import os
import shutil
import cv2
import imagehash
from PIL import Image
from loguru import logger
from PySimpleGUI import popup_get_folder
class VideoDuplicate(object):
'''
返回整个视频的图片指纹列表
从1秒开始,每3秒抽帧,计算一张图像指纹
'''
def __init__(self):
self._over_length_video: list = []
self._no_video: list = []
def _video_hash(self, video_path) -> list:
'''
@param video_path -> 视频绝对路径;
'''
hash_arr = []
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path) ##打开视频文件
logger.info(f'开始抽帧【{video_path}】')
n_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT)) # 视频的帧数
logger.warning(f'视频帧数:{n_frames}')
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) # 视频的帧率
logger.warning(f'视频帧率:{fps}')
dur = n_frames / fps * 1000 # 视频大致总长度
cap_set = 1000
logger.warning(f'视频大约总长:{dur / 1000}')
if dur // 1000 > 11:
logger.error(f'视频时长超出规定范围【6~10】;当前时长:【{dur // 1000}】;跳过该视频;')
self._over_length_video.append(video_path)
return []
while cap_set < dur: # 从3秒开始,每60秒抽帧,计算图像指纹。总长度-3s,是因为有的时候计算出来的长度不准。
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC, cap_set)
logger.debug(f'开始提取:【{cap_set // 1000}】/s的图片;')
# 返回该时间点的,图像(numpy数组),及读取是否成功
success, image_np = cap.read()
if success:
img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image_np, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) # 转成cv图像格式
h = str(imagehash.dhash(img))
logger.success(f'【{cap_set}/s图像指纹:【{h}】')
hash_arr.append(h) # 图像指纹
else:
logger.error(str(cap_set / 1000))
cap_set += 1000 * 2
cap.release() # 释放视频
return hash_arr
def start(self, base_dir):
'''
@param base_dir -> 主文件路径;
'''
data: list = []
for video in os.listdir(base_dir):
logger.debug(f'-' * 80)
name, ext = os.path.splitext(video)
if ext not in ('.mp4', '.MP4'):
logger.error(f'视频文件格式不符;【{video}】;执行跳过;')
continue
abs_video_path = os.path.join(base_dir, video)
video_hash_list = self._video_hash(abs_video_path)
if video_hash_list:
data.append({'video_abs_path': abs_video_path, 'hash': video_hash_list})
self._write_log(data)
return data
@staticmethod
def _write_log(data: list) -> None:
'''视频哈希后的值写入日志文件'''
with open(f'log.txt', 'w+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(data))
def __call__(self, base_dir, *args, **kwargs):
self.start(base_dir)
logger.debug(f'-----------------------------------开始比对关键帧差值感知余弦算法-----------------------------')
with open('log.txt') as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
for i in range(0, len(data) - 1):
for j in range(i + 1, len(data)):
if data[i]['hash'] == data[j]['hash']:
_, filename = os.path.split(data[i]['video_abs_path'])
logger.error(f'移动文件:【{filename}】')
shutil.move(
os.path.join(base_dir, filename),
os.path.join(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'dup_video'), filename)
)
logger.warning('---------------------超长视频----------------------')
for i in self._over_length_video:
_, name = os.path.split(i)
logger.error(name)
def main():
path = popup_get_folder('请选择[视频去重]文件夹')
v = VideoDuplicate()
v(path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()方法补充
python+opencv抽取视频帧并去重
import os
import sys
import cv2
import glob
import json
import numpy as np
import skimage
from skimage import metrics
import hashlib
print(skimage.__version__)
def load_json(json_file):
with open(json_file) as fp:
data = json.load(fp)
return data['outputs']
def ssim_dis(im1, im2):
ssim = metrics.structural_similarity(im1, im2, data_range=255, multichannel=True)
return ssim
# cv2
def isdarkOrBright(grayImg, thre_dark=10, thre_bright=230):
mean = np.mean(grayImg)
if mean < thre_dark or mean > thre_bright:
return True
else:
return False
def get_file_md5(file_name):
"""
caculate md5
: param file_name
: return md5
"""
m = hashlib.md5()
with open(file_name, 'rb') as fobj:
while True:
data = fobj.read(4096)
if not data:
break
m.update(data)
return m.hexdigest()
def extract_frame(video_path, save_dir, prefix, ssim_thre=0.90):
count = 0
md5set = {}
last_frame = None
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
index = 0
tmp_frames = []
while cap.isOpened():
frameState, frame = cap.read()
if not frameState or frame is None:
break
grayImg = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# if isdarkOrBright(grayImg):
# index += 1
# continue
assert cv2.imwrite('tmp.jpg', frame, [cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 100])
md5 = get_file_md5('tmp.jpg')
if md5 in md5set:
md5set[md5] += 1
index += 1
continue
md5set[md5] = 1
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, prefix+'_'+str(index).rjust(4, '0')+'.jpg')
if last_frame is None:
if cv2.imwrite(save_path, frame, [cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 100]):
count += 1
last_frame = frame
tmp_frames.append(frame)
else:
dis = ssim_dis(last_frame, frame)
if dis <= ssim_thre:
save_frame = tmp_frames[len(tmp_frames)//2]
if cv2.imwrite(save_path, save_frame, [cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 100]):
count += 1
last_frame = frame
tmp_frames = [frame]
else:
tmp_frames.append(frame)
index += 1
cap.release()
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
video_path = "videos/***.mp4"
video_name = video_path.split("/")[-1]
prefix = video_name[:-4]
save_imgs_dir = prefix
if not os.path.exists(save_imgs_dir):
os.mkdir(save_imgs_dir)
N = extract_frame(video_path, save_imgs_dir, prefix)
print(video_name, N)对图片,视频,文件进行去重
import os
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import messagebox
import tkinter.filedialog
root=Tk()
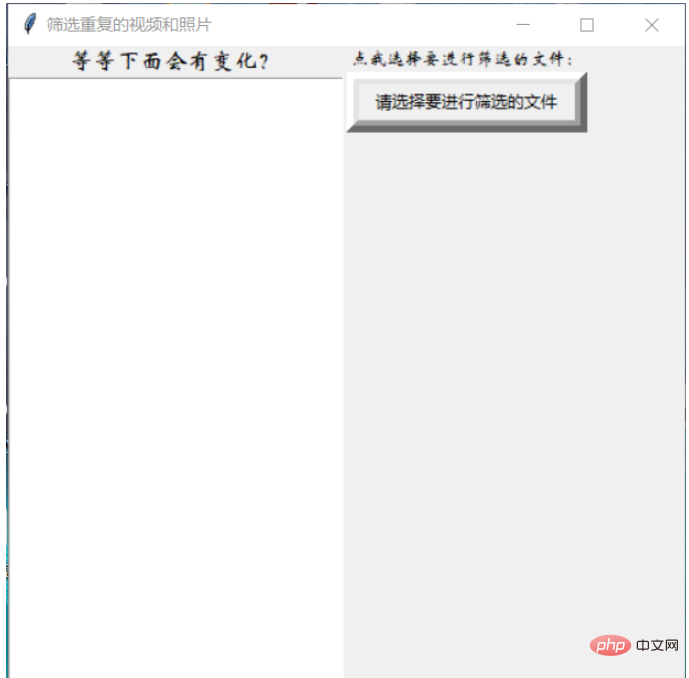
root.title("筛选重复的视频和照片")
root.geometry("500x500+500+200")
def wbb():
a=[]
c={}
filename=tkinter.filedialog.askopenfilenames()
for i in filename:
with open(i,'rb') as f:
a.append(f.read())
for j in range(len(a)):
c[a[j]]=filename[j]
filename1=tkinter.filedialog.askdirectory()
if filename1!="":
p=1
lb1.config(text=filename1+"下的文件为:")
for h in c:
k=c[h].split(".")[-1]
with open(filename1+"/"+str(p)+"."+k,'wb') as f:
f.write(h)
p=p+1
for g in os.listdir(filename1):
txt.insert(END,g+'\n')
else:
messagebox.showinfo("提示",message ='请选择路径')
frame1=Frame(root,relief=RAISED)
frame1.place(relx=0.0)
frame2=Frame(root,relief=GROOVE)
frame2.place(relx=0.5)
lb1=Label(frame1,text="等等下面会有变化?",font=('华文新魏',13))
lb1.pack(fill=X)
txt=Text(frame1,width=30,height=50,font=('华文新魏',10))
txt.pack(fill=X)
lb=Label(frame2,text="点我选择要进行筛选的文件:",font=('华文新魏',10))
lb.pack(fill=X)
btn=Button(frame2,text="请选择要进行筛选的文件",fg='black',relief="raised",bd="9",command=wbb)
btn.pack(fill=X)
root.mainloop()效果图
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
以上就是如何使用Python实现视频去重的小工具的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

python怎么学习?python怎么入门?python在哪学?python怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了python速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号