本篇文章给大家带来了关于redis的相关知识,其中主要整理了jedis基本使用的相关问题,包括了jedis基本操作、jedis连接池的使用等等内容,下面一起来看一下,希望对大家有帮助。

推荐学习:Redis视频教程
Jedis = Java + Redis
Redis不仅可以使用命令来操作,现在基本上主流的语言都有API支持,比如Java、C#、C++、PHP、Node.js、Go等。在官方网站里列一些Java的客户端,有Jedis、Redisson、Jredis、JDBC-Redis等其中官方推荐使用Jedis和Redisson。
使用Jedis操作redis需要导入jar包如下:
注:每个方法就是redis中的命令名,方法的参数就是命令的参数
方法 |
功能 |
new Jedis(host, port) |
创建Jedis的连接,参数:主机名,端口号6379 |
set(key,value) |
添加一个字符串的键和值 |
get(key) |
得到指定键的值 |
del(key) |
删除指定键和值 |
hset(key,field,value) |
添加一个hash类型的键-字段-值 |
hget(key,field) |
通过hash键-字段得到它的值 |
lpush(key,values) |
从左边添加一个list类型的键和元素 |
lpop(key) |
从左边弹出一个元素 |
rpop(key) |
从右边弹出一个元素 |
close() |
关闭连接 |
操作步骤:
创建Jedis对象,指定服务器地址和端口号
向服务器写入
set字符串类型的数据,person=张三
lpush添加list类型的数据,cities=珠海,深圳,广州
从服务器中读取上面的数据打印输出
get得到字符串的值
lrange得到list所有的列表元素
关闭Jedis对象,释放资源
通过客户端查看数据库中是否有数据
控制台输出:

数据库中

代码:
package com.itheima.jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 使用Jedis向redis中添加string和list,读取它们的值
*/
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Jedis连接对象
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
//添加string类型
jedis.set("person", "张三");
//添加list类型
jedis.lpush("cities", "广州","上海","东莞");
//读取string类型
String person = jedis.get("person");
//读取list类型
List<String> cities = jedis.lrange("cities", 0, -1);
//输出到控制器上
System.out.println("person:" + person);
System.out.println("cities:" + cities);
//关闭连接对象
jedis.close();
}
}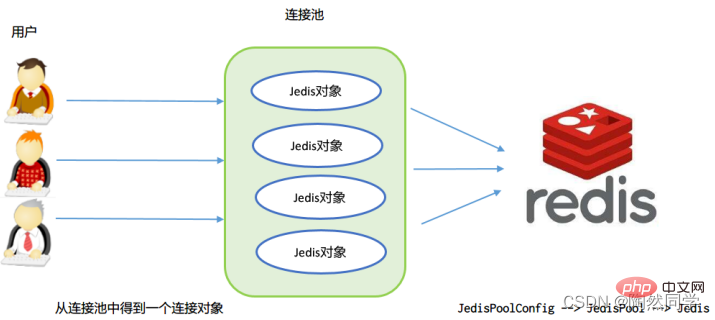
jedis连接资源的创建与销毁是很消耗程序性能,所以jedis为我们提供了jedis的连接池技术,jedis
连接池在创建时初始化一些连接对象存储到连接池中,使用jedis连接资源时不需要自己创建jedis对
象,而是从连接池中获取一个资源进行redis的操作。使用完毕后,不需要销毁该jedis连接资源,
而是将该资源归还给连接池,供其他请求使用。
JedisPoolConfig配置类 |
功能说明 |
JedisPoolConfig() |
创建一个配置对象,使用无参构造方法就可以了 |
void setMaxTotal() |
设置连接池最大的连接数 |
void setMaxWaitMillis() |
设置得到连接对象Jedis最长等待时间 |
JedisPool连接池类 |
说明 |
JedisPool(配置对象,服务器名,端口号) |
创建连接池 参数1:上面的配置对象,参数2:服务器名,参数3:6379 |
Jedis getResource() |
从连接池中得到一个Jedis连接对象 |
void close() |
连接池关闭方法,通常不关闭连接池 |
需求:
使用连接池优化jedis操作
开发步骤
创建连接池配置对象,设置最大连接数10,设置用户最大等待时间2000毫秒
通过配置对象做为参数,创建连接池对象
从连接池里面获取jedis连接对象,执行redis命令。
执行redis命令sadd写入set集合类型的数据:students=白骨精,孙悟空,猪八戒
执行redis命令smembers读取集合中的数据
输出读取的数据
关闭连接对象(通常连接池不关闭)
运行效果

执行代码
package com.itheima.jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 创建Jedis连接池
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1) 创建连接池配置对象,设置最大连接数10,设置用户最大等待时间2000毫秒
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxTotal(10);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(2000);
//2) 通过配置对象做为参数,创建连接池对象
JedisPool pool = new JedisPool(config, "localhost", 6379);
//3) 从连接池里面获取jedis连接对象,执行redis命令。
Jedis jedis = pool.getResource();
//4) 执行redis命令sadd写入set集合类型的数据:students=白骨精,孙悟空,猪八戒
jedis.sadd("students", "白骨精", "孙悟空", "猪八戒");
//5) 执行redis命令smembers读取集合中的数据
Set<String> students = jedis.smembers("students");
//6) 输出读取的数据
System.out.println(students);
//7) 关闭连接对象(通常连接池不关闭)
jedis.close();
pool.close();
}
}java.util.ResourceBundle类是专门用于:读取类路径下Properties配置文件的类
java.util.ResourceBundle类 |
功能 |
static ResourceBundle getBundle("配置基名") |
通过自己的静态方法创建ResourceBundle对象 参数:放在src下.properties文件。参数中不用写扩展名,只要有主名就可以了 |
String getString("键名") |
通过键得到值 |
案例:得到druid.properties中的url属性
package com.itheima.jedis;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 读取属性文件
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//得到资源绑定对象
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("druid");
System.out.println(bundle.getString("url"));
}
}需求:
实现连接池工具类,通过工具类得到Jedis连接对象,配置参数写在属性文件中
调用工具类,对Redis数据库进行操作
执行效果:

实现步骤:
在src目录下创建连接池的工具类: jedis.properties
创建静态成员变量JedisPool对象
在静态代码块中,读取src下的配置文件,得到ResourceBundle对象
得到上面的四个参数,其中host是字符串类型,其它参数要转成整数类型
实例化配置对象,实例化连接池对象
编写静态方法getJedis()返回Jedis对象
创建hash对象:键employee,添加字段名:name,值:NewBoy;字段名: salary,值:3000
使用hgetall读取hash对象输出
关闭jedis对象
jedis.properties配置文件
# 主机名 host=localhost # 端口号 port=6379 # 最大连接数 maxTotal=20 # 最长等待时间 maxWaitMillis=3000
JedisUtils.java
package com.itheima.utils;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 连接池工具类
*/
public class JedisUtils {
//创建一个连接对象
private static JedisPool pool;
static {
//创建连接池的配置对象
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
//设置最大连接数和最长等待时间
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jedis");
//得到配置文件中的属性值
String host = bundle.getString("host");
int port = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("port"));
int maxTotal = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("maxTotal"));
int maxWaitMillis = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("maxWaitMillis"));
//设置配置对象的参数
config.setMaxTotal(maxTotal);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis);
//创建连接池对象
pool = new JedisPool(config, host, port);
}
/**
* 得到redis连接对象
* @return
*/
public static Jedis getJedis() {
return pool.getResource();
}
}使用工具类:
package com.itheima.jedis;
import com.itheima.utils.JedisUtils;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 使用工具类
*/
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//从工具类中得到Jedis对象
Jedis jedis = JedisUtils.getJedis();
//创建hash对象:键employee,添加字段名:name,值:NewBoy;字段名: salary,值:3000
jedis.hset("employee", "name","NewBoy");
jedis.hset("employee", "salary","3000");
//使用hgetall读取hash对象输出
Map<String, String> employee = jedis.hgetAll("employee");
System.out.println(employee);
//关闭jedis对象
jedis.close();
}
}推荐学习:Redis视频教程
以上就是Redis学习之Jedis的基本使用的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号