How to install mysql5.6 from centos source code
How to install mysql5.6 from centos source code: 1. Download the source code package; 2. Pass "[root@localhost ~]# tar zxvf mysql-5.6.41.tar.gz [root@localhost... "Wait for the command to compile and install mysql.

centos source code installation method for mysql5.6
Mysql version introductionWhen preparing to install MySQL, please decide which version and release format to use ( binary or source). First, decide whether to install a development version or a General Availability (GA) version. Development versions have the latest features but are not recommended for production use. Ga release, also called production or stable release, means for production use. We recommend using the latest GA version.
The naming scheme in MySQL 5.6 uses a release name consisting of three numbers and an optional suffix; for example, mysql-5.6.1-m1. The numbers in the release name are explained as follows:
- The first number (5) is the major version number.
- The second number (6) is the minor version number. Taken together, the major and minor numbers make up the issue series number. Serial numbers describe a stable set of characteristics.
- The third number (1) is the version number in the release series. For every new bug fix release, this value will be increased. In most cases, the latest version in a series is the best choice.
- mN (for example, M1, M2, M3) represents a milestone number. MySQL development uses a milestone model, where each milestone introduces a small set of thoroughly tested features. After a milestone is released, development continues with another small set of releases focusing on the next set of features. From one milestone to the next, functional interfaces may change, or even be removed, based on feedback provided by community members who experimented with these early versions. Features in milestone releases may be considered pre-production quality features.
- rc indicates a Release Candidate (RC). Release candidates are considered stable and have passed all MySQL's internal testing. New features may still be introduced in the RC version, but the focus shifts to fixing bugs to stabilize features introduced earlier in this series.
- No suffix indicates General Availability (GA) or production releases. GA releases are stable, successfully passed the early release phase, and are considered reliable, free of serious bugs, and suitable for use in production systems.
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/
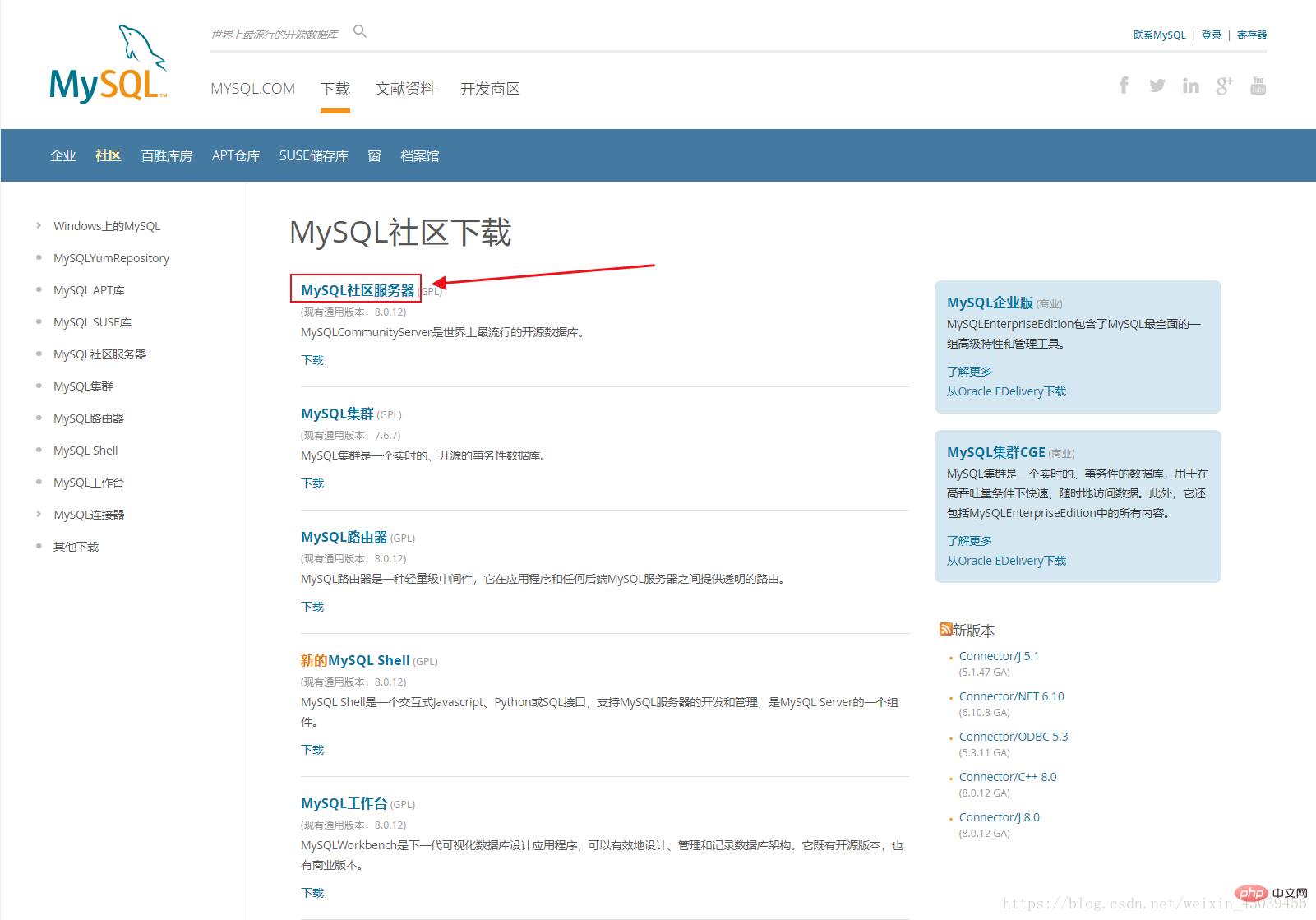
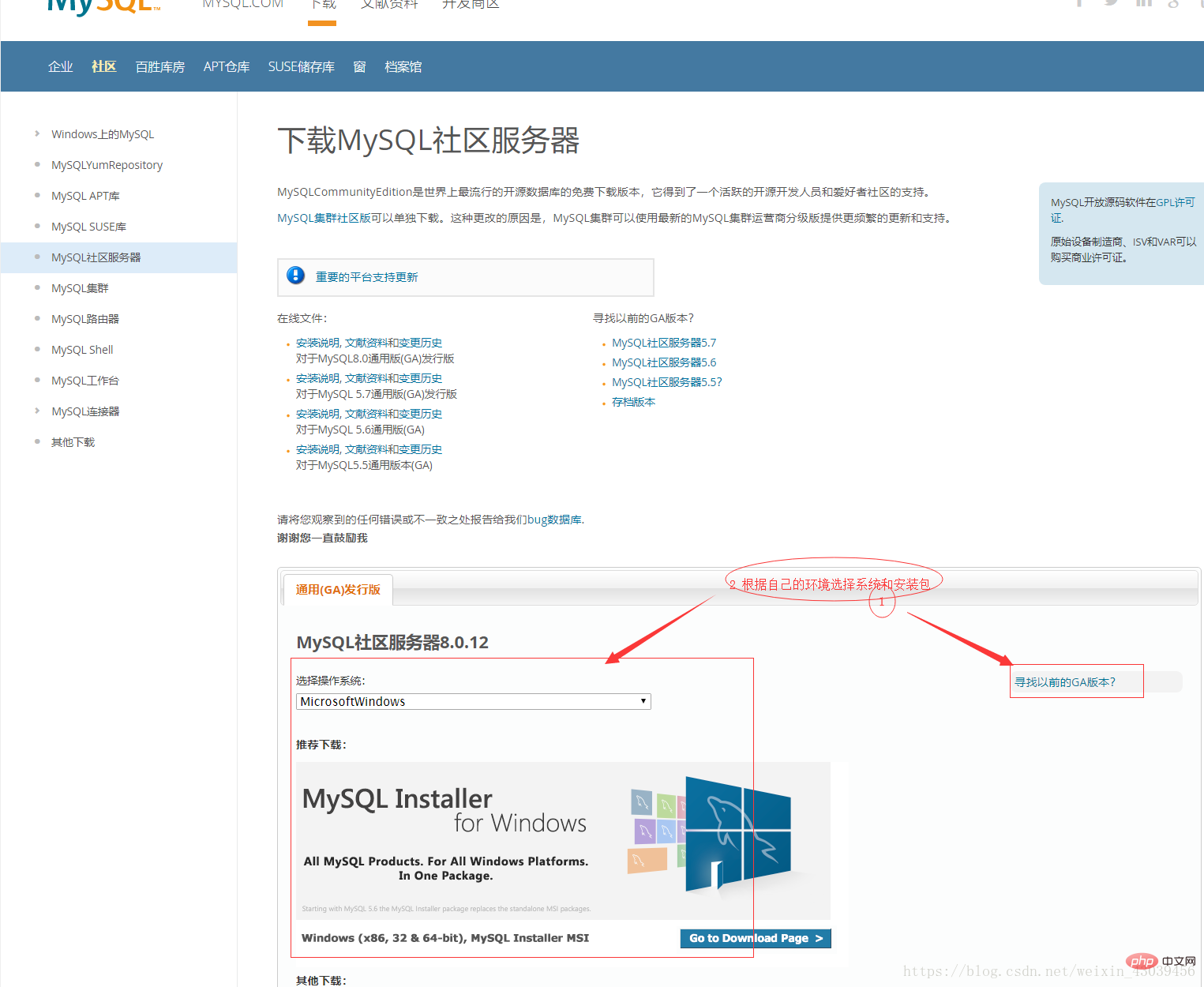
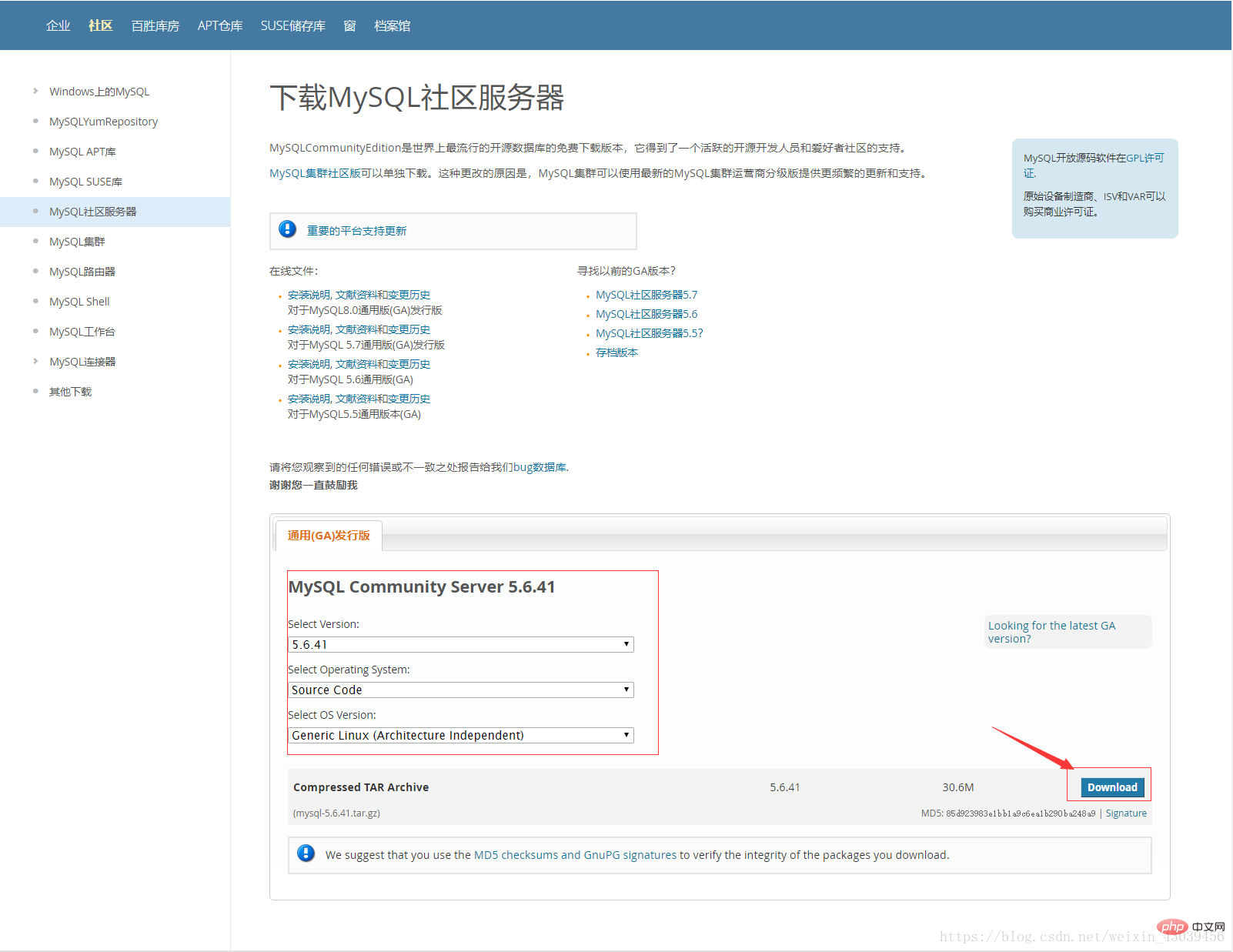
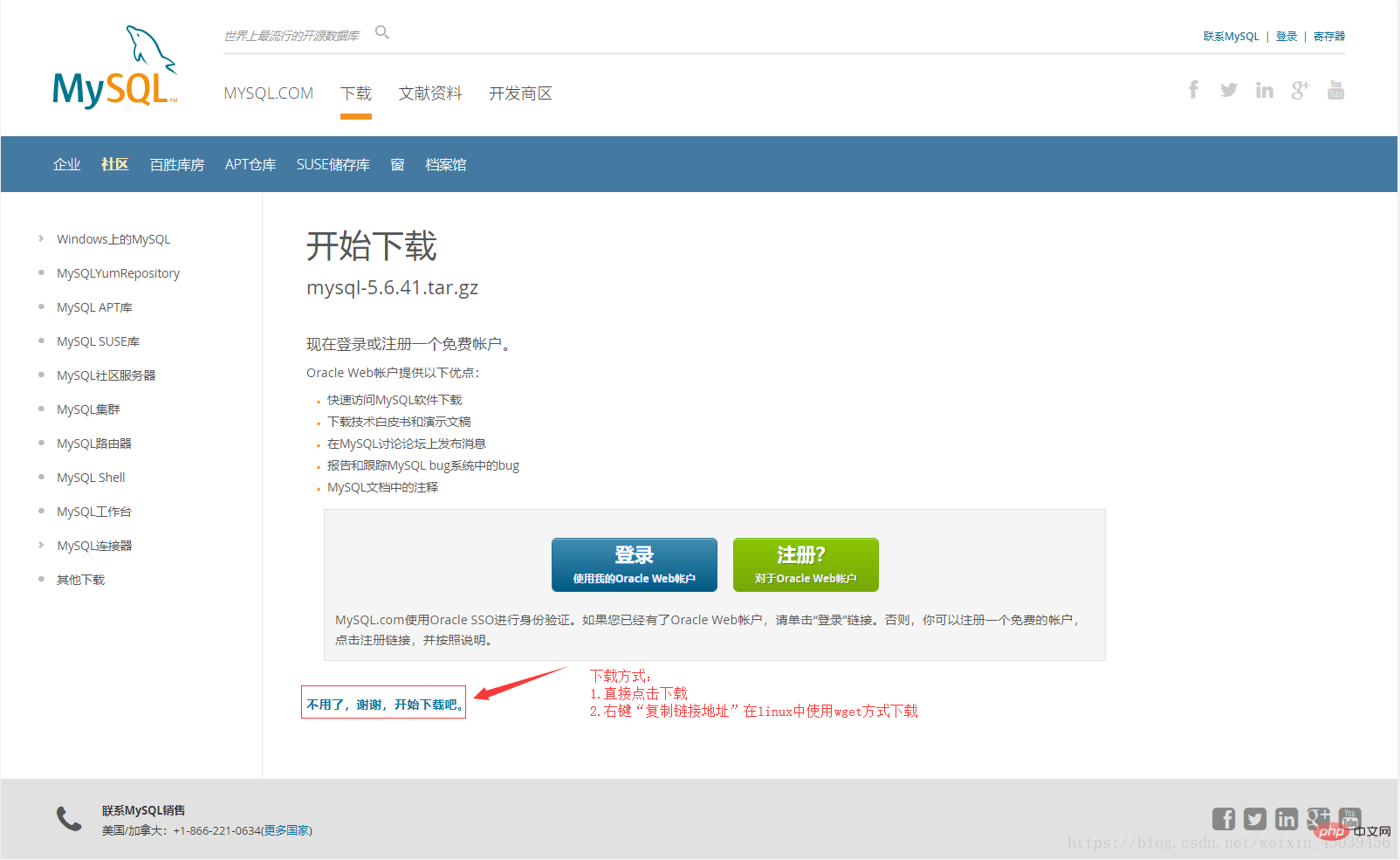 ## Recommended study: "
## Recommended study: "
1. Close selinux and iptables
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/iptables stopiptables:将链设置为政策 ACCEPT:filter [确定] iptables:清除防火墙规则: [确定] iptables:正在卸载模块: [确定] [root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0setenforce: SELinux is disabled
2. Uninstall mysql-server and mysql in rpm
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep mysqlmysql-libs-5.1.73-8.el6_8.x86_64 如果安装了mysql-server使用rpm -e命令将其卸载
3. Install mysql dependency package
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y cmake gcc gcc-c++ ncurses-devel bison zlib openssl
4. Create mysql user and related folders
[root@localhost ~]# groupadd msyql[root@localhost ~]# useradd -g mysql -s /sbin/nologin mysql[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /public/mysql/data
Compile and install mysql
[root@localhost ~]# tar zxvf mysql-5.6.41.tar.gz [root@localhost mysql-5.6.41]# cd mysql-5.6.41 [root@localhost mysql-5.6.41]# cmake \ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/public/mysql \ -DINSTALL_DATADIR=/public/mysql/data \ -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 \ -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci \ -DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all \ -DWITH_EMBEDDED_SERVER=1 \ -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 \ -DWITH_MYISAM_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DWITH_ARCHIVE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DWITH_BLACKHOLE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DWITH_FEDERATED_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DWITH_PARTITION_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ -DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/tmp/mysql.sock \ -DMYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306 \ -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 \ -DSYSCONFDIR=/public/mysql [root@localhost mysql-5.6.41]# make && make install
Instructions
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql \ #安装路径 -DMYSQL_DATADIR=/usr/local/mysql/data \ #数据文件存放位置 -DSYSCONFDIR=/etc \ #my.cnf路径 -DWITH_MYISAM_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ #支持MyIASM引擎 -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ #支持InnoDB引擎 -DWITH_MEMORY_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ #支持Memory引擎 -DWITH_READLINE=1 \ #快捷键功能(我没用过) -DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/tmp/mysqld.sock \ #连接数据库socket路径 -DMYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306 \ #端口 -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 \ #允许从本地导入数据 -DWITH_PARTITION_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 \ #安装支持数据库分区 -DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all \ #安装所有的字符集 -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 \ #默认字符 -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci
Post-installation optimization operations
[root@localhost mysql-5.6.41]# chown -R mysql:mysql /public/mysql \ #修改msyql安装目录的属主与属组 [root@localhost mysql-5.6.41]# cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld [root@localhost ~]# echo "PATH=$PATH:/public/mysql/bin" > /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh [root@localhost ~]# source /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh [root@localhost ~]# chkconfig mysqld on \ #开机自启 [root@localhost ~]# vim /public/mysql/my.cnf [mysqld] basedir = /public/mysql datadir = /public/mysql/data port = 3306 server_id = 11 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
my.cnf temporarily With this configuration, you can start the database and have time to organize an article on my.cnf
#my.cnf文件优先顺序[root@localhost ~]# mysql --help | grep my.cnf
order of preference, my.cnf, $MYSQL_TCP_PORT,
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf /public/mysql/my.cnf ~/.my.cnfInitialize the database and set the password
[root@localhost ~]# /public/mysql/scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --basedir=/public/mysql --datadir=/public/mysql/data \ #初始化数据库 [root@localhost ~]# mysqladmin -u root password 'Aa123456' \ #设置root密码(需先启动mysql)
Mysql operation
#启动、停止、重启、状态 [root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/mysqld start [root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/mysqld stop [root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/mysqld restart [root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/mysqld status [root@localhost ~]# netstat -utpln | grep mysqld #登录mysql [root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -pAa123456 \ #-p后面的密码不要有空格
utpln | grep mysqld#Log in to mysql[root@localhost ~]# mysql -u root -pAa123456 \ #-The password after #-p should not have spaces
The above is the detailed content of How to install mysql5.6 from centos source code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Explain the role of InnoDB redo logs and undo logs.
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Explain the role of InnoDB redo logs and undo logs.
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
InnoDB uses redologs and undologs to ensure data consistency and reliability. 1.redologs record data page modification to ensure crash recovery and transaction persistence. 2.undologs records the original data value and supports transaction rollback and MVCC.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 How does MySQL index cardinality affect query performance?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:18 AM
How does MySQL index cardinality affect query performance?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL index cardinality has a significant impact on query performance: 1. High cardinality index can more effectively narrow the data range and improve query efficiency; 2. Low cardinality index may lead to full table scanning and reduce query performance; 3. In joint index, high cardinality sequences should be placed in front to optimize query.
 MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The basic operations of MySQL include creating databases, tables, and using SQL to perform CRUD operations on data. 1. Create a database: CREATEDATABASEmy_first_db; 2. Create a table: CREATETABLEbooks(idINTAUTO_INCREMENTPRIMARYKEY, titleVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, authorVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, published_yearINT); 3. Insert data: INSERTINTObooks(title, author, published_year)VA
 MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL is suitable for web applications and content management systems and is popular for its open source, high performance and ease of use. 1) Compared with PostgreSQL, MySQL performs better in simple queries and high concurrent read operations. 2) Compared with Oracle, MySQL is more popular among small and medium-sized enterprises because of its open source and low cost. 3) Compared with Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL is more suitable for cross-platform applications. 4) Unlike MongoDB, MySQL is more suitable for structured data and transaction processing.
 Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Explain the InnoDB Buffer Pool and its importance for performance.
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:24 AM
InnoDBBufferPool reduces disk I/O by caching data and indexing pages, improving database performance. Its working principle includes: 1. Data reading: Read data from BufferPool; 2. Data writing: After modifying the data, write to BufferPool and refresh it to disk regularly; 3. Cache management: Use the LRU algorithm to manage cache pages; 4. Reading mechanism: Load adjacent data pages in advance. By sizing the BufferPool and using multiple instances, database performance can be optimized.
 MySQL: Structured Data and Relational Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL: Structured Data and Relational Databases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL efficiently manages structured data through table structure and SQL query, and implements inter-table relationships through foreign keys. 1. Define the data format and type when creating a table. 2. Use foreign keys to establish relationships between tables. 3. Improve performance through indexing and query optimization. 4. Regularly backup and monitor databases to ensure data security and performance optimization.




