Two-way binding and common instructions of Vue.js data
Two-way binding of data (ES6 writing method)
Effect:
When the value in the input box is not changed:

When clearing the value in the input box:

# Re-enter the input box. After Doudou, the value bound to {{testData.name}} in the span on the page follows the input. Changes when the box value changes.

In Vue.js, you can use the v-model directive to create two-way data binding on form elements. And the v-model directive can only be used for three tags: ,
<template>
<div>
<div class="form-inline mg-top">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label">姓名:</label>
<input type="text" v-model='testData.name' class="form-control">
<span class="control-span">姓名变为:{{testData.name}}</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
ready: function(){
},
methods: {
},
data() {
return {
testData:{
id:'1',
name:'张三',
age:'18'
}
}
}
}
</script>Vue.js components can be understood as ViewModel classes with predefined behaviors. A component can predefine many options, but the core ones are the following:
Template (template): The template declares the mapping relationship between the data and the DOM that is ultimately displayed to the user.
Register components (components): After registration, you can call a child component in the form of a custom element in the parent component template.
Initial data (data): The initial data state of a component. For reusable components, this is usually private state.
Accepted external parameters (props): Data is transferred and shared between components through parameters. Parameters are bound one-way (top to bottom) by default, but can also be explicitly declared two-way.
Methods: Modifications to data are generally performed within the component’s methods. User input events and component methods can be bound through the v-on directive.
Lifecycle hooks: A component will trigger multiple lifecycle hook functions, such as created, attached, destroyed, etc. In these hook functions, we can encapsulate some custom logic. Compared with traditional MVC, it can be understood that the logic of the Controller is dispersed into these hook functions.
Private resources (assets): User-defined instructions, filters, components, etc. are collectively called resources in Vue.js. Since globally registered resources can easily lead to naming conflicts, a component can declare its own private resources. Private resources can only be called by the component and its subcomponents.
Commonly used instructions:
The so-called instructions are actually special tags that appear in the template. Based on these tags, the framework knows what operations need to be performed on the DOM elements here.
Commonly used instructions:
v-if instruction
v-show instruction
v-else instruction
v-for instruction
v-bind directive
v-on directive
v-if directive:
v-if renders elements based on the true or false condition of the value of an expression . The element and its data bindings/components are destroyed and recreated on switch. If the element is , its contents will be raised as a conditional block.
labelShowFlag is an expression that returns a bool value. The expression can be a bool attribute or an operation expression that returns bool.
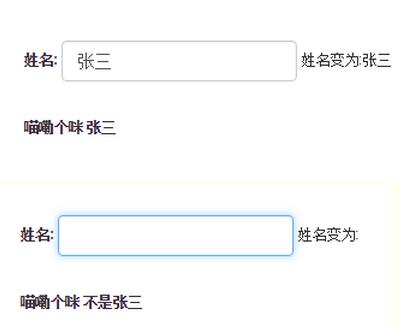
html:
<label class="control-label" v-if='labelShowFlag'>喵嘞个咪</label> <label class="control-label" v-if="testData.name=='张三'" >张三</label>
js:
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
ready: function(){
},
methods: {
},
data() {
return {
labelShowFlag:true,
testData:{
id:'1',
name:'张三',
age:'18'
}
}
}
}
</script>v-show command:
v-show is also conditional rendering The difference between the v-if directive and the v-if directive is that elements using the v-show directive will always be rendered to HTML. v-show simply switches the CSS attribute display of the element.
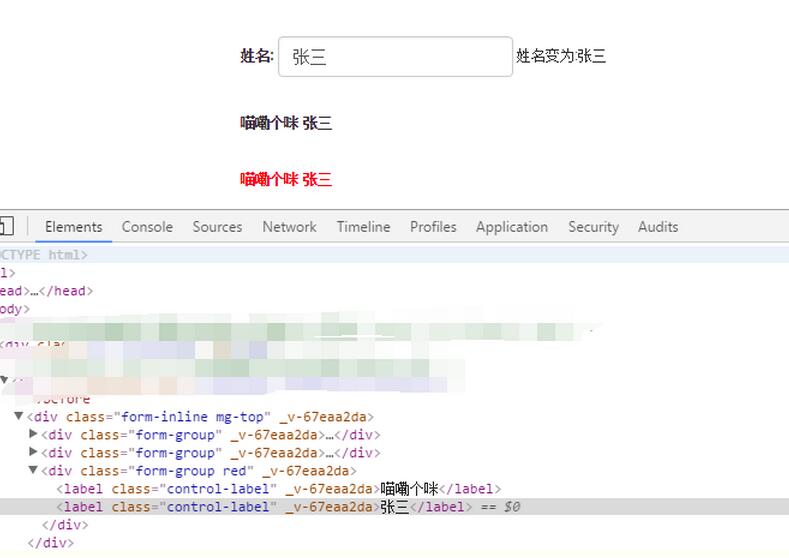
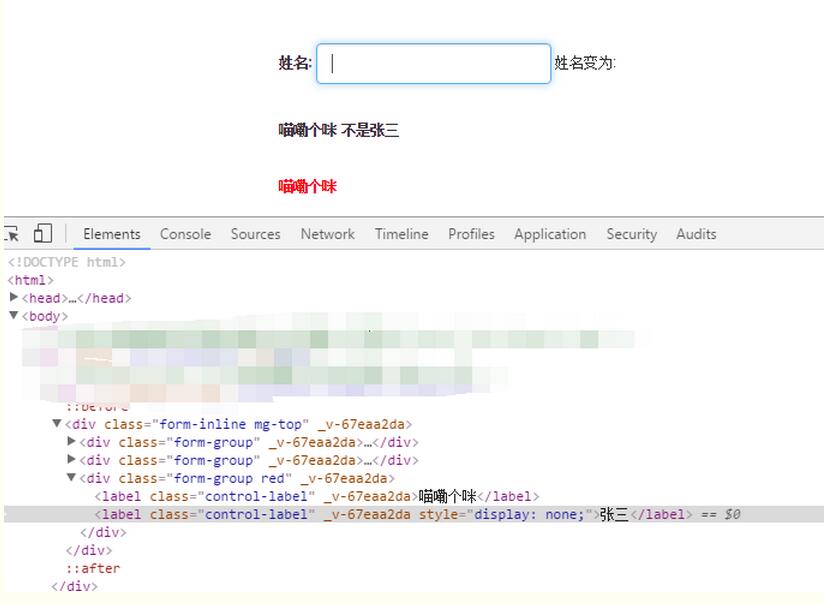
<label class="control-label" v-show='labelShowFlag'>喵嘞个咪</label> <label class="control-label" v-show="testData.name=='张三'" >张三</label>
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
ready: function(){
},
methods: {
},
data() {
return {
labelShowFlag:true,
testData:{
id:'1',
name:'张三',
age:'18'
}
}
}
}
</script>
<label class="control-label" v-if='labelShowFlag'>喵嘞个咪</label> <label class="control-label" v-if="testData.name=='张三'" >张三</label>
 ##html:
##html:
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>js:
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
ready: function(){
},
methods: {
},
data() {
return {
labelShowFlag:true,
testData:{
id:'1',
name:'张三',
age:'18'
},
items: [{
message: '豆豆'
}, {
message: '毛毛'
}],
}
}
}
</script>v-bind directive:
v-bind directive is used to update HTML properties responsively. The form is as follows: v-bind:class
html:
<label class="control-label" v-bind:class="{'pink-label': labelShowFlag}" >我是粉色的</label>
<label class="control-label">默认</label>v-on指令:
v-on 指令用于监听DOM事件 形式如:v-on:click 缩写为 @click;
html:
<input type="button" class="form-control btn btn-primary" value="提交" @click='saveFun'>
js:
<script>
export default {
components: {
},
ready: function(){
},
methods: {
saveFun:function(){
alert('提交');
}
},
data() {
return {
labelShowFlag:true,
testData:{
id:'1',
name:'张三',
age:'18'
},
items: [{
message: '豆豆'
}, {
message: '毛毛'
}],
}
}
}
</script>
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持PHPz中文网。
更多Two-way binding and common instructions of Vue.js data相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
JavaScript and the Web: Core Functionality and Use Cases
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of JavaScript in web development include client interaction, form verification and asynchronous communication. 1) Dynamic content update and user interaction through DOM operations; 2) Client verification is carried out before the user submits data to improve the user experience; 3) Refreshless communication with the server is achieved through AJAX technology.
 JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript in Action: Real-World Examples and Projects
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:13 AM
JavaScript's application in the real world includes front-end and back-end development. 1) Display front-end applications by building a TODO list application, involving DOM operations and event processing. 2) Build RESTfulAPI through Node.js and Express to demonstrate back-end applications.
 Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding the JavaScript Engine: Implementation Details
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Understanding how JavaScript engine works internally is important to developers because it helps write more efficient code and understand performance bottlenecks and optimization strategies. 1) The engine's workflow includes three stages: parsing, compiling and execution; 2) During the execution process, the engine will perform dynamic optimization, such as inline cache and hidden classes; 3) Best practices include avoiding global variables, optimizing loops, using const and lets, and avoiding excessive use of closures.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Role of C/C in JavaScript Interpreters and Compilers
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:01 AM
C and C play a vital role in the JavaScript engine, mainly used to implement interpreters and JIT compilers. 1) C is used to parse JavaScript source code and generate an abstract syntax tree. 2) C is responsible for generating and executing bytecode. 3) C implements the JIT compiler, optimizes and compiles hot-spot code at runtime, and significantly improves the execution efficiency of JavaScript.




