Device Mapper mechanism in the Linux system kernel (1) (4)
User space part
Device mapper is relatively simple in user space, mainly including the device mapper library and dmsetup tool. The Device mapper library is an encapsulation of the necessary operations required for ioctl and user space to create and delete device mapper logical devices. dmsetup is a command line tool that provides users with a directly available command line tool for creating and deleting device mapper devices. Because their functions and processes are relatively simple, their details will not be introduced in this article. The user space is mainly responsible for the following work:
1. Discover the target device related to each mapped device;
2. Create based on configuration information Mapping table;
3. Pass the mapping table constructed by user space to the kernel, and let the kernel build the dm_table structure corresponding to the mapped device;
4. Save the current mapping information for future reconstruction.
Below we mainly illustrate the use of dmsetup through examples, and further explain the mapping mechanism of device mapper. The most important work in user space is to build and save the mapping table. Here are some examples of mapping tables:
1) 0 1024 linear /dev/sda 204 1024 512 linear /dev/sdb 766 1536 128 linear /dev/sdc 0 2) 0 2048 striped 2 64 /dev/sda 1024 /dev/sdb 0 3) 0 4711 mirror core 2 64 nosync 2 /dev/sda 2048 /dev/sdb 1024
In Example 1, the three addresses of logical devices are sectors 0~1023, sectors 1024~1535, and 1536~1663. The range is mapped to the area starting from sector No. 204 of the /dev/sda device, sector No. 766 of the /dev/sdb device, and sector No. 0 of the /dev/sdc device in a linear mapping manner.
In Example 2, the 2048-sector segment of the logical device starting from sector 0 is mapped to the 1024th sector of the /dev/sda device and the /dev/sdb device in a striped manner. The area starting from sector 0. At the same time, it tells the kernel that the target driver of this stripe type has two stripe devices mapped to logical devices, and the size of the stripe is 64 sectors, so that the driver can use this value to split IO requests across devices.
In Example 3, the 4711-sector segment of the logical device starting from sector 0 is mapped to the 2048th sector of the /dev/sda device and the 1024th sector of the /dev/sdb device in a mirroring manner. The area where sector number starts.
After the mapping table is determined, the operations of creating and deleting logical devices are relatively simple. The corresponding operations can be completed through the following dmsetup commands.
dmsetup create 设备名 映射表文件 /* 根据指定的映射表创建一个逻辑设备 */ dmsetup reload 设备名 映射表文件 /* 为指定设备从磁盘中读取映射文件,重新构建映射关系 */ dmsetup remove 设备名 /* 删除指定的逻辑设备 */
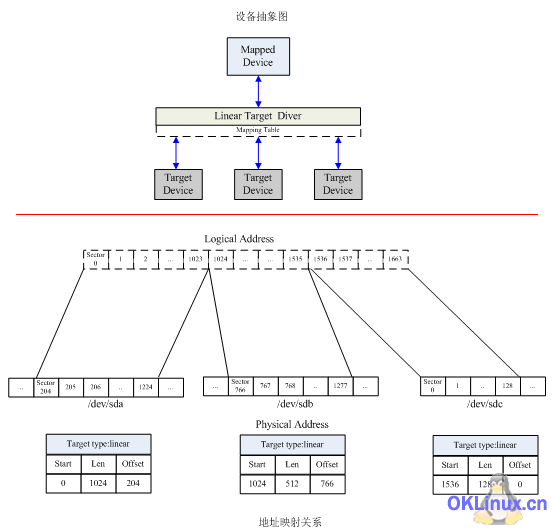
Figure 4 The logical device created in the kernel based on the mapping table in Example 1
When the user space issues a command to create a logical device based on the mapping table, the device mapper in the kernel uses the incoming parameters and mapping relationship Establish a mapping relationship from logical addresses to physical addresses. The device established based on the mapping relationship in mapping table example 1 is shown in Figure 4. The lower part of the figure abstractly depicts the mapping relationship between logical addresses and physical addresses established in the kernel according to the mapping table.
The above is the content of the Device Mapper mechanism (1) (4) in the Linux system kernel. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Using Task Manager in Linux
Aug 15, 2024 am 07:30 AM
Using Task Manager in Linux
Aug 15, 2024 am 07:30 AM
There are many questions that Linux beginners often ask, "Does Linux have a Task Manager?", "How to open the Task Manager on Linux?" Users from Windows know that the Task Manager is very useful. You can open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del in Windows. This task manager shows you all the running processes and the memory they consume, and you can select and kill a process from the task manager program. When you first use Linux, you will also look for something that is equivalent to a task manager in Linux. A Linux expert prefers to use the command line to find processes, memory consumption, etc., but you don't have to
 Solve the problem of garbled display of graphs and charts on Zabbix Chinese monitoring server
Jul 31, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
Solve the problem of garbled display of graphs and charts on Zabbix Chinese monitoring server
Jul 31, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
Zabbix's support for Chinese is not very good, but sometimes we still choose Chinese for management purposes. In the web interface monitored by Zabbix, the Chinese under the graphic icon will display small squares. This is incorrect and requires downloading fonts. For example, "Microsoft Yahei", "Microsoft Yahei.ttf" is named "msyh.ttf", upload the downloaded font to /zabbix/fonts/fonts and modify the two characters in the /zabbix/include/defines.inc.php file at define('ZBX_GRAPH_FONT_NAME','DejaVuSans');define('ZBX_FONT_NAME'
 7 ways to help you check the registration date of Linux users
Aug 24, 2024 am 07:31 AM
7 ways to help you check the registration date of Linux users
Aug 24, 2024 am 07:31 AM
Did you know, how to check the creation date of an account on a Linux system? If you know, what can you do? Did you succeed? If yes, how to do it? Basically Linux systems don't track this information, so what are the alternative ways to get this information? You may ask why am I checking this? Yes, there are situations where you may need to review this information and it will be helpful to you at that time. You can use the following 7 methods to verify. Use /var/log/secure Use aureport tool Use .bash_logout Use chage command Use useradd command Use passwd command Use last command Method 1: Use /var/l
 What should I do if the WPS missing fonts under the Linux system causes the file to be garbled?
Jul 31, 2024 am 12:41 AM
What should I do if the WPS missing fonts under the Linux system causes the file to be garbled?
Jul 31, 2024 am 12:41 AM
1. Find the fonts wingdings, wingdings2, wingdings3, Webdings, and MTExtra from the Internet. 2. Enter the main folder, press Ctrl+h (show hidden files), and check if there is a .fonts folder. If not, create one. 3. Copy the downloaded fonts such as wingdings, wingdings2, wingdings3, Webdings, and MTExtra to the .fonts folder in the main folder. Then start wps to see if there is still a "System missing font..." reminder dialog box. If not, just Success! Notes: wingdings, wingdin
 Teach you how to add fonts to Fedora in 5 minutes
Jul 23, 2024 am 09:45 AM
Teach you how to add fonts to Fedora in 5 minutes
Jul 23, 2024 am 09:45 AM
System-wide installation If you install a font system-wide, it will be available to all users. The best way to do this is to use RPM packages from the official software repositories. Before starting, open the "Software" tool in Fedora Workstation, or other tools using the official repository. Select the "Add-ons" category in the selection bar. Then select "Fonts" within the category. You'll see the available fonts similar to the ones in the screenshot below: When you select a font, some details will appear. Depending on several scenarios, you may be able to preview some sample text for the font. Click the "Install" button to add it to your system. Depending on system speed and network bandwidth, this process may take some time to complete
 Centos 7 installation and configuration NTP network time synchronization server
Aug 05, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
Centos 7 installation and configuration NTP network time synchronization server
Aug 05, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
Experimental environment: OS: LinuxCentos7.4x86_641. View the current server time zone & list the time zone and set the time zone (if it is already the correct time zone, please skip it): #timedatectl#timedatectllist-timezones#timedatectlset-timezoneAsia/Shanghai2. Understanding of time zone concepts: GMT, UTC, CST, DSTUTC: The entire earth is divided into twenty-four time zones. Each time zone has its own local time. In international radio communication situations, for the sake of unification, a unified time is used, called Universal Coordinated Time (UTC). :UniversalTim
 How to connect two Ubuntu hosts to the Internet using one network cable
Aug 07, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
How to connect two Ubuntu hosts to the Internet using one network cable
Aug 07, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
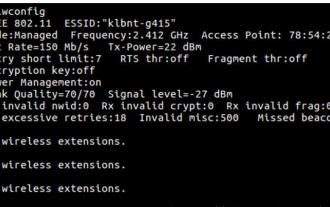
How to use one network cable to connect two ubuntu hosts to the Internet 1. Prepare host A: ubuntu16.04 and host B: ubuntu16.042. Host A has two network cards, one is connected to the external network and the other is connected to host B. Use the iwconfig command to view all network cards on the host. As shown above, the network cards on the author's A host (laptop) are: wlp2s0: This is a wireless network card. enp1s0: Wired network card, the network card connected to host B. The rest has nothing to do with us, no need to care. 3. Configure the static IP of A. Edit the file #vim/etc/network/interfaces to configure a static IP address for interface enp1s0, as shown below (where #==========
 toss! Running DOS on Raspberry Pi
Jul 19, 2024 pm 05:23 PM
toss! Running DOS on Raspberry Pi
Jul 19, 2024 pm 05:23 PM
Different CPU architectures mean that running DOS on the Raspberry Pi is not easy, but it is not much trouble. FreeDOS may be familiar to everyone. It is a complete, free and well-compatible operating system for DOS. It can run some older DOS games or commercial software, and can also develop embedded applications. As long as the program can run on MS-DOS, it can run on FreeDOS. As the initiator and project coordinator of FreeDOS, many users will ask me questions as an insider. The question I get asked most often is: "Can FreeDOS run on a Raspberry Pi?" This question is not surprising. After all, Linux runs very well on the Raspberry Pi




