浅谈Python单向链表的实现
链表由一系列不必在内存中相连的结构构成,这些对象按线性顺序排序。每个结构含有表元素和指向后继元素的指针。最后一个单元的指针指向NULL。为了方便链表的删除与插入操作,可以为链表添加一个表头。
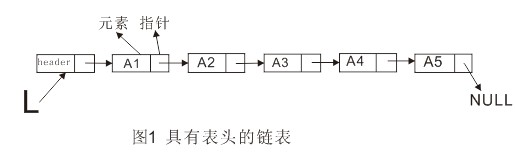
删除操作可以通过修改一个指针来实现。
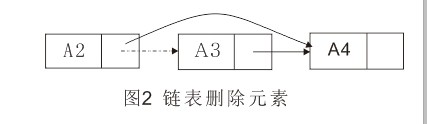
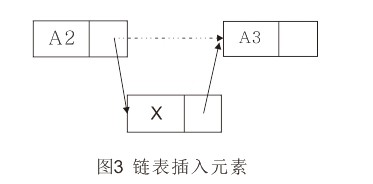
插入操作需要执行两次指针调整。
1. 单向链表的实现
1.1 Node实现
每个Node分为两部分。一部分含有链表的元素,可以称为数据域;另一部分为一指针,指向下一个Node。
class Node():
__slots__=['_item','_next'] #限定Node实例的属性
def __init__(self,item):
self._item=item
self._next=None #Node的指针部分默认指向None
def getItem(self):
return self._item
def getNext(self):
return self._next
def setItem(self,newitem):
self._item=newitem
def setNext(self,newnext):
self._next=newnext
1.2 SinglelinkedList的实现
class SingleLinkedList():
def __init__(self):
self._head=None #初始化链表为空表
self._size=0
1.3 检测链表是否为空
def isEmpty(self): return self._head==None
1.4 add在链表前端添加元素
def add(self,item): temp=Node(item) temp.setNext(self._head) self._head=temp
1.5 append在链表尾部添加元素
def append(self,item):
temp=Node(item)
if self.isEmpty():
self._head=temp #若为空表,将添加的元素设为第一个元素
else:
current=self._head
while current.getNext()!=None:
current=current.getNext() #遍历链表
current.setNext(temp) #此时current为链表最后的元素
1.6 search检索元素是否在链表中
def search(self,item):
current=self._head
founditem=False
while current!=None and not founditem:
if current.getItem()==item:
founditem=True
else:
current=current.getNext()
return founditem
1.7 index索引元素在链表中的位置
def index(self,item):
current=self._head
count=0
found=None
while current!=None and not found:
count+=1
if current.getItem()==item:
found=True
else:
current=current.getNext()
if found:
return count
else:
raise ValueError,'%s is not in linkedlist'%item
1.8 remove删除链表中的某项元素
def remove(self,item):
current=self._head
pre=None
while current!=None:
if current.getItem()==item:
if not pre:
self._head=current.getNext()
else:
pre.setNext(current.getNext())
break
else:
pre=current
current=current.getNext()
1.9 insert链表中插入元素
def insert(self,pos,item):
if pos<=1:
self.add(item)
elif pos>self.size():
self.append(item)
else:
temp=Node(item)
count=1
pre=None
current=self._head
while count<pos:
count+=1
pre=current
current=current.getNext()
pre.setNext(temp)
temp.setNext(current)
全部代码
class Node():
__slots__=['_item','_next']
def __init__(self,item):
self._item=item
self._next=None
def getItem(self):
return self._item
def getNext(self):
return self._next
def setItem(self,newitem):
self._item=newitem
def setNext(self,newnext):
self._next=newnext
class SingleLinkedList():
def __init__(self):
self._head=None #初始化为空链表
def isEmpty(self):
return self._head==None
def size(self):
current=self._head
count=0
while current!=None:
count+=1
current=current.getNext()
return count
def travel(self):
current=self._head
while current!=None:
print current.getItem()
current=current.getNext()
def add(self,item):
temp=Node(item)
temp.setNext(self._head)
self._head=temp
def append(self,item):
temp=Node(item)
if self.isEmpty():
self._head=temp #若为空表,将添加的元素设为第一个元素
else:
current=self._head
while current.getNext()!=None:
current=current.getNext() #遍历链表
current.setNext(temp) #此时current为链表最后的元素
def search(self,item):
current=self._head
founditem=False
while current!=None and not founditem:
if current.getItem()==item:
founditem=True
else:
current=current.getNext()
return founditem
def index(self,item):
current=self._head
count=0
found=None
while current!=None and not found:
count+=1
if current.getItem()==item:
found=True
else:
current=current.getNext()
if found:
return count
else:
raise ValueError,'%s is not in linkedlist'%item
def remove(self,item):
current=self._head
pre=None
while current!=None:
if current.getItem()==item:
if not pre:
self._head=current.getNext()
else:
pre.setNext(current.getNext())
break
else:
pre=current
current=current.getNext()
def insert(self,pos,item):
if pos<=1:
self.add(item)
elif pos>self.size():
self.append(item)
else:
temp=Node(item)
count=1
pre=None
current=self._head
while count<pos:
count+=1
pre=current
current=current.getNext()
pre.setNext(temp)
temp.setNext(current)
if __name__=='__main__':
a=SingleLinkedList()
for i in range(1,10):
a.append(i)
print a.size()
a.travel()
print a.search(6)
print a.index(5)
a.remove(4)
a.travel()
a.insert(4,100)
a.travel()

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".




