利用存储过程进行表数据分离的案例分享
某客户有个需求,有2张业务表,数据量比较大,有2000W行,现在的需求是把这2张表中的一部分记录,根据一定的where条件分离出去,创建到另外的归档表中,即做表记录的迁移操作。最后得到的结果是:未满足筛选条件的记录留在原表中,满足筛选条件的表要插入到归
某客户有个需求,有2张业务表,数据量比较大,有2000W行,现在的需求是把这2张表中的一部分记录,根据一定的where条件分离出去,创建到另外的归档表中,即做表记录的迁移操作。最后得到的结果是:未满足筛选条件的记录留在原表中,满足筛选条件的表要插入到归档表中,并且要在原表中删除这些插入到归档表中的全部记录,最后满足:新表记录+归档记录=原表记录数下面我来模拟一下这个过程: 由于没有拿到具体的建表语句,这里把表的内容最简化,只留2个列,作为最基本的演示
--连接到测试用户,创建测试表 SQL> conn zlm/zlm Connected. SQL> select * from cat;
no rows selected SQL> create table tabhdr(tabhdrid number(10),status number(10));
Table created.
SQL> create table tabdet(tabhdrid number(10));
Table created.
SQL> create table arch_tabdet as select * from tabdet;
Table created.
SQL> create table arch_tabhdr as select * from tabhdr;
Table created.
--创建操作日志表 SQL> create table arch_log( 2 archbegintime char(19), 3 archmiddletime char(19), 4 archendtime char(19), 5 archinscount1 number, 6 archdelcount1 number, 7 archinscount2 number, 8 archdelcount2 number, 9 archstatus varchar2(20), 10 archerrorcode varchar2(20), 11 archerrormsg varchar2(1000));
Table created.
操作日志表字段说明: archbegintime->archimiddletime //第一次迁移操作(insert+delete)的时间 archimiddletime->archendtime //第二次迁移操作(insert+delete)的时间 archcount1 //第一次迁移操作(insert+delete)的数据量 archcount2 //第二次迁移操作(insert+delete)的数据量 archstatus //操作状态(success/failure) archerrorcode //报错代码 archerrormsg //报错信息
--插入测试数据(每个表插入10W条记录,仅测试功能没必要用很大的数据) SQL> begin 2 for i in 1..100000 3 loop 4 insert into tabhdr values(i,9); 5 insert into tabdet values(i); 6 end loop; 7 commit; 8 end; 9 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
--创建存储过程detach_pro SQL> create or replace procedure detach_pro 2 is 3 maxrows number default 10000; 4 rowid_table dbms_sql.Urowid_Table; 5 i number; 6 cursor cur_1 is SELECT a.rowid FROM tabdet a WHERE tabhdrid IN(SELECT tabhdrid FROM tabhdr WHERE STATUS=9) order by a.rowid; 7 cursor cur_2 is SELECT a.rowid FROM tabhdr a WHERE status=9 order by a.rowid; 8 9 v_begintime char(19):=to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss'); 10 v_middletime char(19); 11 v_inscount1 number:=0; 12 v_delcount1 number:=0; 13 v_inscount2 number:=0; 14 v_delcount2 number:=0; 15 v_errcode varchar2(100); 16 v_errerrm varchar2(1000); 17 18 begin 19 open cur_1; 20 loop 21 exit when cur_1%notfound; 22 fetch cur_1 bulk collect into rowid_table limit maxrows; 23 24 forall i in 1 .. rowid_table.count 25 insert into arch_tabdet select * from tabdet where rowid = rowid_table(i); 26 commit; 27 v_inscount1:=v_inscount1+rowid_table.count; 28 forall i in 1 .. rowid_table.count 29 delete from tabdet where rowid = rowid_table(i); 30 commit; 31 v_delcount1:= v_delcount1+rowid_table.count; 32 end loop; 33 close cur_1; 34 v_middletime:=to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss'); 35 open cur_2; 36 loop 37 exit when cur_2%notfound; 38 fetch cur_2 bulk collect into rowid_table limit maxrows; 39 40 forall i in 1 .. rowid_table.count 41 insert into arch_tabhdr select * from tabhdr where rowid = rowid_table(i); 42 commit; 43 v_inscount2:=v_inscount2+rowid_table.count; 44 forall i in 1 .. rowid_table.count 45 delete from tabhdr where rowid = rowid_table(i); 46 commit; 47 v_delcount2:= v_delcount2+rowid_table.count; 48 end loop; 49 close cur_2; 50 insert into arch_log values (v_begintime,v_middletime,to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss'), v_inscount1,v_delcount1,v_inscount2,v_delcount2,'success',null,null); 51 commit; 52 exception 53 when others then 54 v_errcode :=sqlcode; 55 v_errerrm :=sqlerrm; insert into arch_log values (v_begintime,v_middletime,to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss'), v_inscount1,v_delcount1,v_inscount2,v_delcount2,'failure',v_errcode,v_errerrm); 57 commit; 58 end; 59 /
Procedure created.
--开始第1次测试 SQL> select count(*) from tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select count(*) from tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 0
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 0
SQL> exec detach_pro;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> select count(*) from tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 0
SQL> select count(*) from tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 0
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select * from arch_log;
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2014-12-30 10:30:45 2014-12-30 10:30:53 2014-12-30 10:31:02 100000 100000 100000 100000 success
可以看到,执行了存储过程detach_pro以后,原来的两张表中都没有数据了,全部分离到归档表arch_tabdet和arch_tabhdr中去了,当然这是一种极端情况,之前插入的数据都是符合插入到归档表的筛选条件的,即字段"status=9"。操作日志表中记录了各表的插入和删除操作,以及执行的时间。
如果有新的记录插入原表,但是并不符合插入归档表中的筛选条件,比如status=8,来看一下测试结果:
--第2次测试(插入100【本文来自鸿网互联 (http://www.68idc.cn)】00条status=8的记录) SQL> begin
2 for i in 1..10000 3 loop 4 insert into tabhdr values(i,8); 5 insert into tabdet values(i); 6 end loop; 7 commit; 8 end; 9 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> exec detach_pro;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> exec detach_pro;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> select count(*) from tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 10000
SQL> select count(*) from tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 10000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 100000
SQL> select * from arch_log;
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2014-12-30 10:30:45 2014-12-30 10:30:53 2014-12-30 10:31:02 100000 100000 100000 100000 success
2014-12-30 10:43:38 2014-12-30 10:43:38 2014-12-30 10:43:38 0 0 0 0 success
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2014-12-30 10:44:28 2014-12-30 10:44:28 2014-12-30 10:44:28 0 0 0 0 success
SQL>
发现执行detach_pro的速度很快,而且原表和归档表的记录都没有发生变化,因为status=8不符合筛选条件,执行存储过程并不会进行迁移操作,即使没有操作成功。由于刚才执行了2次存储过程,就会在记录表中生成2行操作结果的记录
--第3次测试(再次插入1000条符合筛选条件的记录,status=9) SQL> begin
2 for i in 1..1000 3 loop 4 insert into tabhdr values(i,9); 5 insert into tabdet values(i); 6 end loop; 7 commit; 8 end; 9 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> exec detach_pro;
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> select count(*) from tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 9000
SQL> select count(*) from tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 10000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabdet;
COUNT(*) ---------- 102000
SQL> select count(*) from arch_tabhdr;
COUNT(*) ---------- 101000
SQL> select * from arch_log;
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2014-12-30 10:30:45 2014-12-30 10:30:53 2014-12-30 10:31:02 100000 100000 100000 100000 success
2014-12-30 10:43:38 2014-12-30 10:43:38 2014-12-30 10:43:38 0 0 0 0 success
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2014-12-30 10:44:28 2014-12-30 10:44:28 2014-12-30 10:44:28 0 0 0 0 success
2014-12-30 10:53:15 2014-12-30 10:53:15 2014-12-30 10:53:15 2000 2000 1000 1000 success
ARCHBEGINTIME ARCHMIDDLETIME ARCHENDTIME ARCHINSCOUNT1 ARCHDELCOUNT1 ARCHINSCOUNT2 ARCHDELCOUNT2 ------------------- ------------------- ------------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ------------- ARCHSTATUS ARCHERRORCODE -------------------- -------------------- ARCHERRORMSG ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
第一次迁移操作: tabdet表中的2000行记录被插入到arch_tabdet表中,然后删除tabdet表中的2000行相应记录; 因此结果是tabdet表剩下9000条记录,arch_tabdet表增加到12000条记录。
第二次迁移操作:
tabhdr表中的1000行记录被插入到arch_tabhdr表中,然后删除tabhdr表中的1000行相应记录; 因此结果是tabhdr表剩下10000条记录,arch_tabhdr表增加到11000条记录。
在实际生产中,具体是哪些符合迁移条件的表是根据存储过程中具体的where条件来定的,这里的测试并不一定很准确。
最后,可以通过创建job来定期自动运行存储过程,如: declare
v_jobnum number; begin
dbms_job.submit(v_jobnum,'detach_pro',sysdate,'sysdate+1/24');
end; commit; 或:
declare v_jobnum number;
begin
dbms_job.submit
( job => v_jobnum
,what => 'detach_pro'
,next_date => sysdate
,interval => 'SYSDATE+1/24'
,no_parse => TRUE
);
end;
/
commit;
--把存储过程防止到job中,每小时自动运行
SQL> declare v_jobnum number;
2 begin
3 dbms_job.submit
4 ( job => v_jobnum
5 ,what => 'detach_pro'
6 ,next_date => sysdate
7 ,interval => 'SYSDATE+1/24'
8 ,no_parse => TRUE
9 );
10 end;
11 /
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
SQL> desc user_jobs;
Name Null? Type
----------------------------------------------------------------------- -------- ------------------------------------------------
JOB NOT NULL NUMBER
LOG_USER NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30)
PRIV_USER NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30)
SCHEMA_USER NOT NULL VARCHAR2(30)
LAST_DATE DATE
LAST_SEC VARCHAR2(8)
THIS_DATE DATE
THIS_SEC VARCHAR2(8)
NEXT_DATE NOT NULL DATE
NEXT_SEC VARCHAR2(8)
TOTAL_TIME NUMBER
BROKEN VARCHAR2(1)
INTERVAL NOT NULL VARCHAR2(200)
FAILURES NUMBER
WHAT VARCHAR2(4000)
NLS_ENV VARCHAR2(4000)
MISC_ENV RAW(32)
INSTANCE NUMBER
SQL> col interval for a15
SQL> col what for a15
SQL> select job,next_date,interval,what from user_jobs;
JOB NEXT_DATE INTERVAL WHAT
---------- --------- --------------- ---------------
5 30-DEC-14 SYSDATE+1/24 detach_pro
4 01-JAN-00 SYSDATE+1/24/60 xxx_pro;
SQL>
--删除其他无关的job SQL> exec dbms_job.remove(4);
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
SQL> select job,next_date,interval,what from user_jobs;
JOB NEXT_DATE INTERVAL WHAT ---------- --------- --------------- --------------- 5 30-DEC-14 SYSDATE+1/24 detach_pro

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1670
1670
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1274
1274
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
Quark Netdisk and Baidu Netdisk are very convenient storage tools. Many users are asking whether these two softwares are interoperable? How to share Quark Netdisk to Baidu Netdisk? Let this site introduce to users in detail how to save Quark network disk files to Baidu network disk. How to save files from Quark Network Disk to Baidu Network Disk Method 1. If you want to know how to transfer files from Quark Network Disk to Baidu Network Disk, first download the files that need to be saved on Quark Network Disk, and then open the Baidu Network Disk client. , select the folder where the compressed file is to be saved, and double-click to open the folder. 2. After opening the folder, click "Upload" in the upper left corner of the window. 3. Find the compressed file that needs to be uploaded on your computer and click to select it.
 Use ddrescue to recover data on Linux
Mar 20, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Use ddrescue to recover data on Linux
Mar 20, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
DDREASE is a tool for recovering data from file or block devices such as hard drives, SSDs, RAM disks, CDs, DVDs and USB storage devices. It copies data from one block device to another, leaving corrupted data blocks behind and moving only good data blocks. ddreasue is a powerful recovery tool that is fully automated as it does not require any interference during recovery operations. Additionally, thanks to the ddasue map file, it can be stopped and resumed at any time. Other key features of DDREASE are as follows: It does not overwrite recovered data but fills the gaps in case of iterative recovery. However, it can be truncated if the tool is instructed to do so explicitly. Recover data from multiple files or blocks to a single
 Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
0.What does this article do? We propose DepthFM: a versatile and fast state-of-the-art generative monocular depth estimation model. In addition to traditional depth estimation tasks, DepthFM also demonstrates state-of-the-art capabilities in downstream tasks such as depth inpainting. DepthFM is efficient and can synthesize depth maps within a few inference steps. Let’s read about this work together ~ 1. Paper information title: DepthFM: FastMonocularDepthEstimationwithFlowMatching Author: MingGui, JohannesS.Fischer, UlrichPrestel, PingchuanMa, Dmytr
 Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
The performance of JAX, promoted by Google, has surpassed that of Pytorch and TensorFlow in recent benchmark tests, ranking first in 7 indicators. And the test was not done on the TPU with the best JAX performance. Although among developers, Pytorch is still more popular than Tensorflow. But in the future, perhaps more large models will be trained and run based on the JAX platform. Models Recently, the Keras team benchmarked three backends (TensorFlow, JAX, PyTorch) with the native PyTorch implementation and Keras2 with TensorFlow. First, they select a set of mainstream
 Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Facing lag, slow mobile data connection on iPhone? Typically, the strength of cellular internet on your phone depends on several factors such as region, cellular network type, roaming type, etc. There are some things you can do to get a faster, more reliable cellular Internet connection. Fix 1 – Force Restart iPhone Sometimes, force restarting your device just resets a lot of things, including the cellular connection. Step 1 – Just press the volume up key once and release. Next, press the Volume Down key and release it again. Step 2 – The next part of the process is to hold the button on the right side. Let the iPhone finish restarting. Enable cellular data and check network speed. Check again Fix 2 – Change data mode While 5G offers better network speeds, it works better when the signal is weaker
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 How to share NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments_Tutorial on sharing NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:41 AM
How to share NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments_Tutorial on sharing NetEase Cloud Music to WeChat Moments
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:41 AM
1. First, we enter NetEase Cloud Music, and then click on the software homepage interface to enter the song playback interface. 2. Then in the song playback interface, find the sharing function button in the upper right corner, as shown in the red box in the figure below, click to select the sharing channel; in the sharing channel, click the "Share to" option at the bottom, and then select the first "WeChat Moments" allows you to share content to WeChat Moments.
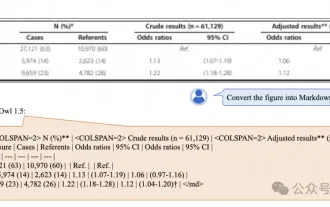 Alibaba 7B multi-modal document understanding large model wins new SOTA
Apr 02, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Alibaba 7B multi-modal document understanding large model wins new SOTA
Apr 02, 2024 am 11:31 AM
New SOTA for multimodal document understanding capabilities! Alibaba's mPLUG team released the latest open source work mPLUG-DocOwl1.5, which proposed a series of solutions to address the four major challenges of high-resolution image text recognition, general document structure understanding, instruction following, and introduction of external knowledge. Without further ado, let’s look at the effects first. One-click recognition and conversion of charts with complex structures into Markdown format: Charts of different styles are available: More detailed text recognition and positioning can also be easily handled: Detailed explanations of document understanding can also be given: You know, "Document Understanding" is currently An important scenario for the implementation of large language models. There are many products on the market to assist document reading. Some of them mainly use OCR systems for text recognition and cooperate with LLM for text processing.




