批改状态:合格
老师批语:选择器博大精深

-css 选择器规定了 css 规则会被应用到那些元素上
-1.通配选择器:选择所有元素,不区分类型
-2.类选择器:也可以叫属性选择器,根据元素的class的属性进行匹配
-3.群组选择器:可以同时选择器多个不同类型的元素, 通过用“ , ”的方式连接
-4.id选择器:按照 id 属性选择一个与之匹配的元素。需要注意的是,一个文档中,每个 ID 属性都应当是唯一的
-5.元素选择器:根据元素的标签名进行匹配

-祖先元素:拥有子元素,孙元素等所有层级的后代元素
-父级元素:仅拥有子元素层级的元素
-后代元素:与其它层级元素一起拥有共同祖先元素
-子级元素:与其它同级元素一起拥有共同父级元素
| 序号 | 选择器 | 操作符 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 后代选择器 | 空格 |
选择当前元素的所有后代元素 | div p, body * |
| 2 | 父子选择器 | > |
选择当前元素的所有子元素 | div > h2 |
| 3 | 同级相邻选择器 | + |
选择拥有共同父级且相邻的元素 | li.red + li |
| 4 | 同级所有选择器 | ~ |
选择拥有共同父级的后续所有元素 | li.red ~ li |
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title><style>/* 后代选择器 */div span {display: block;/* color: teal; */border: 1px solid red;}/* 父子选择器 */div > ul {display: block;/* color: tomato; */border: 1px solid red;}/* 同级相邻选择器 */.d + .e {color: yellowgreen;}/* 同级所有选择器 */.d ~ .l {color: red;}</style></head><body><div><span><p>总理莫迪:印度抗击疫情为全球树立榜样</p></span><span>频频变脸,美国为何改口接受中国标准口罩?</span><span>胡锡进:攻击蔡依林,台湾绿营舆论凸显蝇营狗苟</span></div><br /><div><ul class="a"><li class="d">深圳南山最高5500万豪宅半天售罄 "喝茶费"重现江湖</li><li class="e">北方第三城之争:今年或明年郑州有望取代青岛</li><li class="g">两个多月后,湖北这个数字终于是零了</li><li class="h">国务院要求北京上海广州等城市加强病毒检测</li><li class="j">武汉解封倒计时,重启途中的人与城</li><li class="l">两武汉将“解封” !究竟解什么?</li></ul></div></body></html>

-学习之前,先分析上下文选择器的局限性,例如选择同一个父级下的第二个子元素,就没那么简单
-而伪类就正好弥补了上下文选择器的短板, 所以伪类,大多数是基于文档中元素结构的
-伪: 本意是假的,不存在的意思, 这里是特指, 不需要在元素上添加额外的属性来获取元素
-类: 暗指伪类的级别, 仍然是属于”class”级别, 仍然属于属性选择器范畴,级别高于元素选择器
结构伪类
| 序号 | 选择器 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
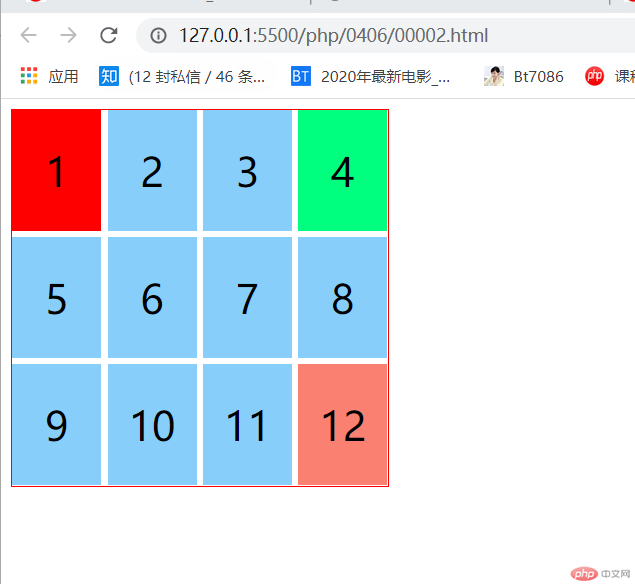
| 1 | :first-child |
匹配第一个子元素 | div :first-child |
| 2 | :last-child |
匹配最后一个子元素 | div :last-child |
| 3 | :only-child |
选择元素的唯一子元素 | div :only-child |
| 4 | :nth-child(n) |
匹配任意位置的子元素 | div :nth-child(n) |
| 5 | :nth-last-child(n) |
匹配倒数任意位置的子元素 | div :nth-last-child(n) |
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title><style>.container {width: 300px;height: 300px;display: grid;border: 1px solid red;grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 1fr);gap: 5px;}.box {font-size: 2rem;background-color: lightskyblue;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;}/* 使用first-child时,为避免设置其他元素,要指定它的父级 *//* 选择第一个元素 */.container > :first-child {background-color: red;}/* 选择最后一个元素 */.container > :last-child {background-color: salmon;}/* 选择器第"n"个 元素 *//* "n"可以是表达式 *//* "n"的索引时从零开始计算 */.container > :nth-child(4) {background-color: springgreen;</style></head><body><div class="container"><div class="box">1</div><div class="box">2</div><div class="box">3</div><div class="box">4</div><div class="box">5</div><div class="box">6</div><div class="box">7</div><div class="box">8</div><div class="box">9</div><div class="box">10</div><div class="box">11</div><div class="box">12</div></div></body></html>
| 序号 | 选择器 | 描述 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | :first-of-type |
匹配按类型分组后的第一个子元素 | div :first-of-type |
| 2 | :last-of-type |
匹配按类型分组后的最后一个子元素 | div :last-of-type |
| 3 | :only-of-type |
匹配按类型分组后的唯一子元素 | div :only-of-type |
| 4 | :nth-of-type() |
匹配按类型分组后的任意位置的子元素 | div :nth-of-type(n) |
| 5 | :nth-last-of-type() |
匹配按类型分组后倒数任意位置的子元素 | div :nth-last-of-type(n) |
-允许使用表达式来匹配一组元素,表达式中的”n”是从”0”开始计数,且必须写到前面
-“-n”表示获取前面一组元素,正数表示从指定位置获取余下元素
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title><style>/* 选择第一个元素 */span:first-of-type {background-color: springgreen;}/* 选择最后一个元素 */li:last-of-type {background-color: wheat;}/* 选择第n个元素 */span:nth-of-child(4) {background-color: springgreen;}</style></head><body><div><span><p>总理莫迪:印度抗击疫情为全球树立榜样</p></span><span>频频变脸,美国为何改口接受中国标准口罩?</span><span>胡锡进:攻击蔡依林,台湾绿营舆论凸显蝇营狗苟</span></div></body></html>

-选择器的作用就是快速的在一个文档中找到你要找的其中一个或者多个元素,
-然后通过css的规则进行添加样式。
-注意表达式的应用

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号